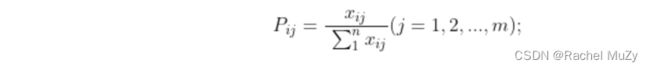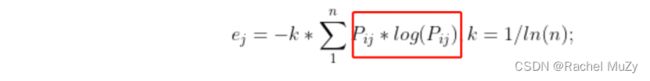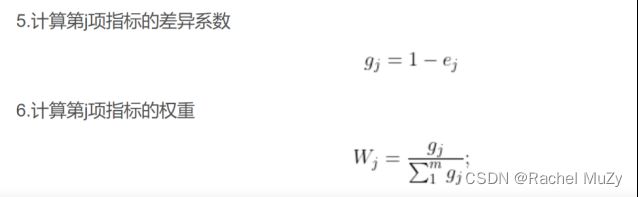【人因工程】熵值法求权重正反向化的分析
目录
一、问题提出
二、问题分析
1. 第一步:
2. 第二步
3. 第三步
三、进一步分析
总结
一、问题提出
所需数据集见链接:
人因工程熵值法求权重正反向化的分析配套数据-数据集文档类资源-CSDN文库![]() https://download.csdn.net/download/mzy20010420/86774031该文件免费下载,请放心食用!
https://download.csdn.net/download/mzy20010420/86774031该文件免费下载,请放心食用!
前面介绍了求权重的方法,本文主要分析熵值法。代码见往期文章:
【人因工程】熵值法与CRITIC法求权重_Rachel MuZy的博客-CSDN博客【人因工程】熵值法与CRITIC法求权重https://blog.csdn.net/mzy20010420/article/details/127327787我对于输入数据,第一个影响因素越大越好、第二个影响因素越小越好。改进代码如下:
import numpy as np
#标准
# feature_name = np.load('D:/site-packages/l2rpn_baselines/DQfD_simple_V2_v0110/feature_name_simple.npy')
#读入数据
x1 = np.load('x1.npy')
x_simulate_set1 = np.load('x_simulate_set1.npy')
action_set1 = np.load('action_set1.npy')
x2 = np.load('x2.npy')
x_simulate_set2 = np.load('x_simulate_set2.npy')
action_set2 = np.load('action_set2.npy')
#action_set1_number
#动作元素的个数
action_set1_num = np.array([4, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 3])
#todo:action_Set2_num我是乱填的,需要重新弄
action_set2_num = np.array([4, 6, 6, 7, 17, 17, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 4, 7, 17, 7, 7, 7, 3])
x = x2
x_simulate_set = x_simulate_set2
action_set_num = action_set2_num
action_set = action_set2
x_load_rate_list = []
for i in range (x_simulate_set.shape[0]):
x_load_rate = []
for j in range(x_simulate_set.shape[1]):
if x_simulate_set[i,j,1] >= 0.8:
x_load = 0.2 * x_simulate_set[i,j,1]
x_load_rate.append(x_load)
if (0 < x_simulate_set[i,j,1] < 0.8):
x_load = 0.8 * x_simulate_set[i,j,1]
x_load_rate.append(x_load)
x_load_rate = (np.sum(np.array(x_load_rate)))/np.array(x_load_rate).size
x_load_rate_list.append(x_load_rate)
#input data
#线路负载率的情况和元素动作的个数
data = np.array([x_load_rate_list, action_set_num])
#weight
#求二者权重
#todo;两个数据的权重,第一个是越高越好,第二个是越低越好,需要修改
def cal_weight(x):
'''熵值法计算变量的权重'''
# 正向化指标
x_1 = x[0, :]
x_1 = (x_1 - np.min(x_1)) / (np.max(x_1) - np.min(x_1))
# 反向化指标
x_2 = x[1, :]
x_2 = (np.max(x_2) - x_2) / (np.max(x_2) - np.min(x_2))
x = [x_1, x_2]
x = np.array(x)
#计算第i个研究对象某项指标的比重
Pij = x / np.sum(x, axis=1).reshape((2, 1))
ajs = []
#某项指标的熵值e
for i in Pij:
for j in i:
if j != 0:
a = j * np.log(j)
ajs.append(a)
else:
a = 0
ajs.append(a)
ajs = np.array(ajs).reshape((2, x.shape[1]))
e = -(1 / np.log(x.shape[1])) * np.sum(ajs, axis=1)
#计算差异系数
g = 1 - e
#给指标赋权,定义权重
w = g / np.sum(g, axis=0)
return w
#带数据
w = cal_weight(data)
#选前五
w = np.array(w).reshape((2, 1))
data_weight = w * data
data_wei_sum = np.sum(data_weight, axis=0)
#取前五个索引
k = 5 #前k个
lab = data_wei_sum.argsort()[-k:][::-1] #获取前5个索引
actions =[]
for m in range(lab.size):
action = action_set[lab[m]]
actions.append(action)
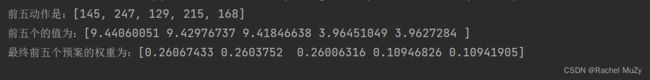
print(f'前五动作是:{actions}')
#取前五个对应的值
new_datas = []
for l in lab:
new_data = data_wei_sum[l]
new_datas.append(new_data)
new_datas = np.array(new_datas)
print(f'前五个的值为:{new_datas}')
#求前五个的权重
final_wei = new_datas / np.sum(new_datas)
print(f'最终前五个预案的权重为:{final_wei}')
具体而言
第一行进行正向化、第二行进行反向化。
结果为:
两个因素的权重为
最终结果为:
以上是理想的情况。如果不考虑这么多,直接给数据整个来一个反向化:
import numpy as np
#标准
feature_name = np.load('D:/site-packages/l2rpn_baselines/DQfD_simple_V2_v0110/feature_name_simple.npy')
#读入数据
x1 = np.load('E:/新加卷/大三暑假/人因工程项目/代码/x2.npy')
x_simulate_set1 = np.load('E:/新加卷/大三暑假/人因工程项目/代码/x_simulate_set2.npy')
action_set1 = np.load('E:/新加卷/大三暑假/人因工程项目/代码/action_set2.npy')
#action_set1_number
action_set1_num = np.array([4, 6, 6, 7, 17, 17, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 4, 7, 17, 7, 7, 7, 3])
#load
load1 = []
for i in x_simulate_set1:
x1_load = i[:-1, 1]
x1_load_operations = []
for j in range(176):
if x1_load[j] >= 0.8:
x1_load_operation = 0.2 * x1_load[j]
x1_load_operations.append(x1_load_operation)
if (x1_load[j] < 0.8) and (x1_load[j] > 0):
x1_load_operation = 0.8 * x1_load[j]
x1_load_operations.append(x1_load_operation)
load1.append(x1_load_operations)
load1 = np.array(load1)
print(load1.shape)
#input data
data = np.array([load1_data, action_set1_num])
#weight
#求二者权重
def cal_weight(x):
'''熵值法计算变量的权重'''
x = (np.max(x, axis=1).reshape((2, 1)) - x) / (np.max(x, axis=1).reshape((2, 1)) - np.min(x, axis=1).reshape((2, 1)))
#计算第i个研究对象某项指标的比重
Pij = x / np.sum(x, axis=1).reshape((2, 1))
ajs = []
#某项指标的熵值e
for i in Pij:
for j in i:
if j != 0:
a = j * np.log(j)
ajs.append(a)
else:
a = 0
ajs.append(a)
ajs = np.array(ajs).reshape((2, 19))
e = -(1 / np.log(19)) * np.sum(ajs, axis=1)
#计算差异系数
g = 1 - e
#给指标赋权,定义权重
w = g / np.sum(g, axis=0)
return w
#带数据
w1 = cal_weight(data)
#选前五
w1 = np.array(w1).reshape((2, 1))
data_weight = w1 * data
data_wei_sum = np.sum(data_weight, axis=0)
#取前五个索引
k = 5 #前k个
lab = data_wei_sum.argsort()[-k:][::-1] #获取前5个索引
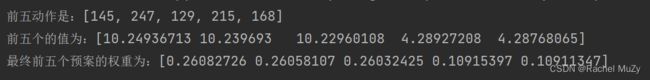
print(f'前五的的索引是:{lab}')
#取前五个对应的值
new_datas = []
for l in lab:
new_data = data_wei_sum[l]
new_datas.append(new_data)
new_datas = np.array(new_datas)
print(f'前五个的值为:{new_datas}')
#求前五个的权重
final_wei = new_datas / np.sum(new_datas)
print(f'最终前五个预案的权重为:{final_wei}')
结果:
两个因素的权重为:
最终结果为:
前面发现全进行反向化和一部分进行正向化,一部分进行反向化两种操作输出的权重差异不大。为此特进行分析。此文件为文章每套数据,可免费下载。放心食用!
二、问题分析
1. 第一步:
正向化与不正向化处理前后数据差异不大
| 正向反向 |
正反向化后的data1 |
0.35513 |
0.14366 |
0.39859 |
0.36779 |
0 |
1 |
0.59063 |
0.35513 |
0.77749 |
0.54686 |
0.52067 |
0.85801 |
0.35513 |
0.53885 |
0.51057 |
0.21699 |
0.31824 |
0.45479 |
0.35513 |
| · |
0.92857 |
0.78571 |
0.78571 |
0.71429 |
0 |
0 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.92857 |
0.71429 |
0 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
1 |
|
| 反向 |
反向化后的data2 |
0.64487 |
0.85634 |
0.60141 |
0.63221 |
1 |
0 |
0.40937 |
0.64487 |
0.22251 |
0.45314 |
0.47933 |
0.14199 |
0.64487 |
0.46115 |
0.48943 |
0.78301 |
0.68176 |
0.54521 |
0.64487 |
| 0.92857 |
0.78571 |
0.78571 |
0.71429 |
0 |
0 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.92857 |
0.71429 |
0 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
0.71429 |
1 |
||
| 数据分析 |
Data3 |
-0.63542 |
-1.56296 |
-0.4448 |
-0.57989 |
-2.19307 |
2.193069 |
0.397516 |
-0.63542 |
1.217109 |
0.205534 |
0.090661 |
1.570281 |
-0.63542 |
0.170401 |
0.046361 |
-1.24132 |
-0.79722 |
-0.1983 |
-0.63542 |
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
即是否正向化前后数据变化并不大
2. 第二步
后续在求所占比重时,会把数据变得更小
下一步是求熵值:
这一步虽然会使数据差异变大(分析见下图)
但由于一方面数据本身在1附近,另一方面还有乘系数k(k<1),使得数据差异放大得非常有限。
因此是否正向化后ej(熵值)的结果如下表所示:
进行正向化:
| 熵值 |
负载率 |
0.94978 |
| 动作数量 |
0.93929 |
不进行正向化:
| 熵值 |
负载率 |
0.9588 |
| 动作数量 |
0.93929 |
差异很小。
3. 第三步
最终的差异系数和权重计算如图所示:
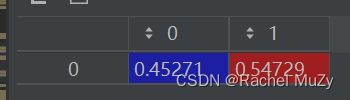
进行正向化:
| 差异系数 |
负载率 |
0.05022 |
| 动作数量 |
0.06071 |
|
| 权重 |
负载率 |
0.45271 |
| 动作数量 |
0.54729 |
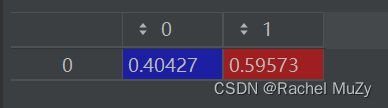
不进行正向化:
| 差异系数 |
负载率 |
0.0412 |
| 动作数量 |
0.06071 |
|
| 权重 |
负载率 |
0.40427 |
| 动作数量 |
0.59573 |
求得的权重很接近。
三、进一步分析
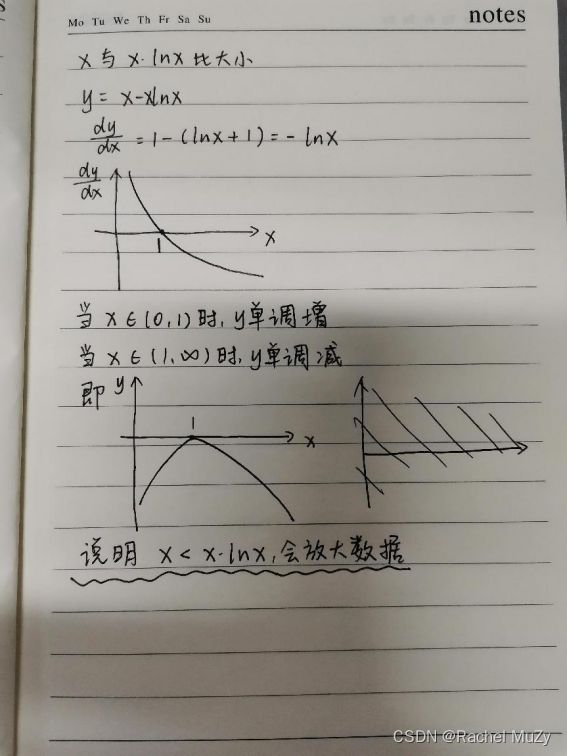
从熵值法的定义来看:
熵值法是计算指标权重的经典算法之一,它是指用来判断某个指标的离散程度的数学方法。离散程度越大,即信息量越大,不确定性就越小,熵也就越小,权重越大;信息量越小,不确定性越大,熵也越大,权重越小。
如果所给的数据最大、最小值和平均值差异很接近,那么是否进行正向化对结果的影响就不大。
比如说这两组数据:
x1: 1 2 2 2 2 10
x2:5 5 5 5 4 6
是否正向化对第一组的影响会很大,但是对第二组就完全没有影响。
总结
此问题的出现与输入数据有很大关系,因此无需慌张,尊重事实即可。