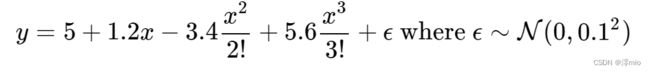深度学习入门(十) 模型选择、过拟合和欠拟合
深度学习入门(十) 模型选择、过拟合和欠拟合
- 前言
- 模型选择
-
- 例子:预测谁会偿还贷款?
- 训练误差和泛化误差
- 验证数据集和测试数据集
- K-则交叉验证
- 总结
- 过拟合和欠拟合
-
- 模型容量
-
- 模型容量的影响
- 估计模型容量
- VC维
-
- 线性分类器的VC维
- VC维的用处
- 数据复杂度
- 总结
- 代码展示
- QA:
前言
核心内容来自博客链接1博客连接2希望大家多多支持作者
本文记录用,防止遗忘
模型选择
例子:预测谁会偿还贷款?
银行雇你来调查谁会偿还贷款
- 你得到了100个申请人的信息
- 其中五个人在3年内违约了
发现:
你发现所有的5个人在面试的时候都穿了蓝色衬衫
你的模型也发现了这个强信号
这会有什么问题?
训练误差和泛化误差
训练误差:模型在训练数据上的误差
泛化误差:模型在新数据上的误差
例子:根据摸考成绩来预测未来考试分数
- 在过去的考试中表现很好(训练误差)不代表未来考试—定会好(泛化误差)
- 学生A通过背书在摸考中拿到很好成绩
- 学生B知道答案后面的原因
验证数据集和测试数据集
验证数据集:一个用来评估模型好坏的数据集
- 例如拿出50%的训练数据
- 不要跟训练数据混在一起(常犯错误)
- 未来的考试
- 我出价的房子的实际成交价
- 用在Kaggle私有排行榜中的数据集
K-则交叉验证
在没有足够多数据时使用(这是常态)
算法:
- 将训练数据分割成K块
- For i = 1,...,K
- 使用第i块作为验证数据集,其余的作为训练数据集·报告K个验证集误差的平均
- 常用:K=5或10
总结
- 训练数据集:训练模型参数
- 验证数据集:选择模型超参数
- 非大数据集上通常使用k-则交叉验证
过拟合和欠拟合
模型容量
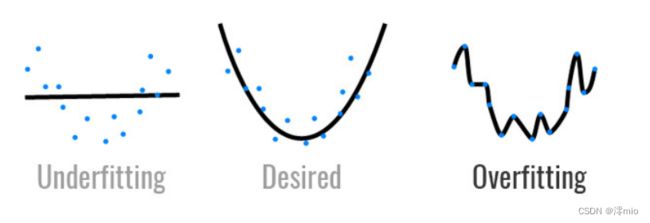
拟合各种函数的能力:
- 低容量的模型难以拟合训练数据
- 高容量的模型可以记住所有的训练数据
模型容量的影响
估计模型容量
难以在不同的种类算法之间比较
- 例如数模型和神经网络
给定一个模型种类,将有两个主要因素
- 参数的个数
- 参数值的选择范围
VC维
- 统计学习理论的一个核心思想
- 对于一个分类模型,VC等于一个最大的数据集的大小,不管如何给定标号,都存在一个模型来对它进行完美分类
线性分类器的VC维
2维输入的感知机,VC维=3
能够分类任何三个点,但不是4个(xor)
 支持N维输入的感知机的VC维是N+1
支持N维输入的感知机的VC维是N+1
一些多层感知机的VC维 O ( N l o g 2 N ) O(Nlog_2N) O(Nlog2N)
VC维的用处
提供为什么一个模型好的理论依据
- 它可以衡量训练误差和泛化误差之间的间隔
- 衡量不是很准确
- 计算深度学习模型的VC维很困难
数据复杂度
多个重要因素
- 样本个数
- 每个样本的元素个数
- 时间、空间结构
- 多样性
总结
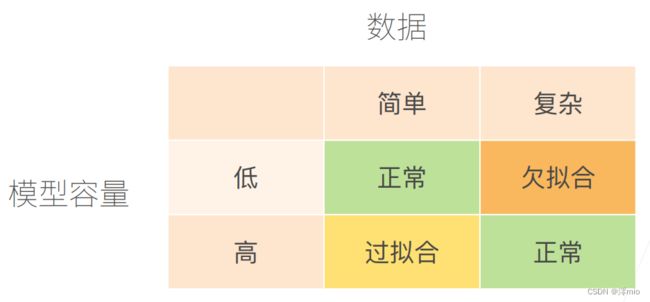
- 模型容量需要匹配数据复杂度,否则可能导致欠拟合和过拟合
- 统计机器学习提供数学工具来衡量模型复杂度
- 实际中一般靠观察训练误差和验证误差
代码展示
通过多项式拟合来交互地探索这些概念
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
使用以下三阶多项式来生成训练和测试数据的标签:
max_degree = 20
n_train, n_test = 100, 100
true_w = np.zeros(max_degree)
true_w[0:4] = np.array([5, 1.2, -3.4, 5.6])
features = np.random.normal(size=(n_train + n_test, 1))
np.random.shuffle(features)
poly_features = np.power(features, np.arange(max_degree).reshape(1, -1))
for i in range(max_degree):
poly_features[:, i] /= math.gamma(i + 1)
labels = np.dot(poly_features, true_w)
labels += np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=labels.shape)
看一下前2个样本
true_w, features, poly_features, labels = [
torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.float32)
for x in [true_w, features, poly_features, labels]]
features[:2], poly_features[:2, :], labels[:2]
输出:
(tensor([[-1.9729],
[-0.1230]]),
tensor([[ 1.0000e+00, -1.9729e+00, 1.9462e+00, -1.2799e+00, 6.3127e-01,
-2.4909e-01, 8.1905e-02, -2.3084e-02, 5.6929e-03, -1.2480e-03,
2.4621e-04, -4.4159e-05, 7.2602e-06, -1.1018e-06, 1.5527e-07,
-2.0422e-08, 2.5182e-09, -2.9225e-10, 3.2032e-11, -3.3262e-12],
[ 1.0000e+00, -1.2304e-01, 7.5698e-03, -3.1047e-04, 9.5502e-06,
-2.3502e-07, 4.8195e-09, -8.4715e-11, 1.3030e-12, -1.7813e-14,
2.1918e-16, -2.4517e-18, 2.5138e-20, -2.3793e-22, 2.0911e-24,
-1.7153e-26, 1.3191e-28, -9.5474e-31, 6.5263e-33, -4.2264e-35]]),
tensor([-11.1878, 4.9593]))
实现一个函数来评估模型在给定数据集上的损失
def evaluate_loss(net, data_iter, loss):
"""评估给定数据集上模型的损失。"""
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2)
for X, y in data_iter:
out = net(X)
y = y.reshape(out.shape)
l = loss(out, y)
metric.add(l.sum(), l.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]
定义训练函数
def train(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels,
num_epochs=400):
loss = nn.MSELoss()
input_shape = train_features.shape[-1]
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_shape, 1, bias=False))
batch_size = min(10, train_labels.shape[0])
train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features, train_labels.reshape(-1, 1)),
batch_size)
test_iter = d2l.load_array((test_features, test_labels.reshape(-1, 1)),
batch_size, is_train=False)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[1e-3, 1e2],
legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
d2l.train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, trainer)
if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (evaluate_loss(
net, train_iter, loss), evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
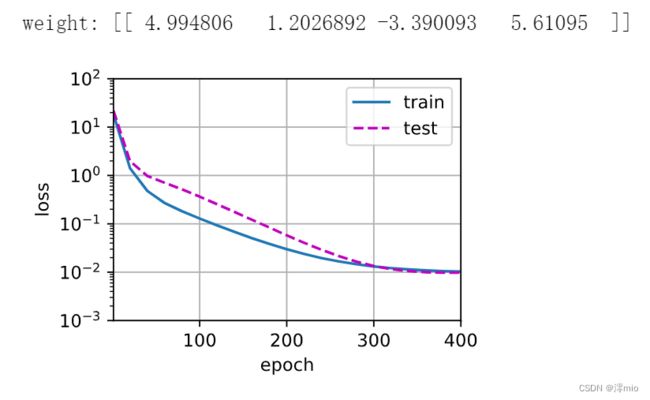
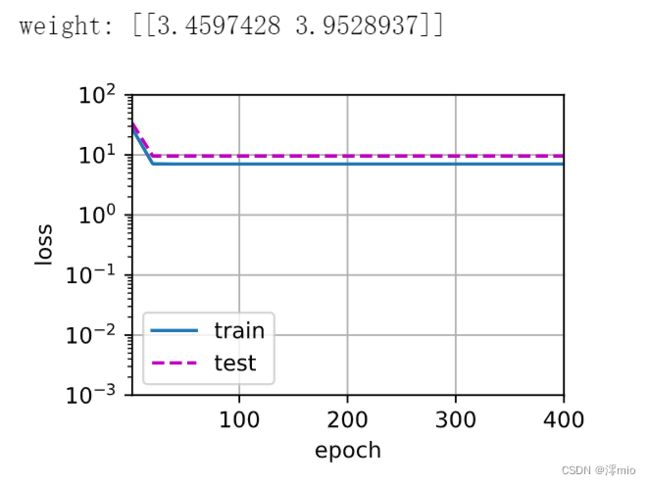
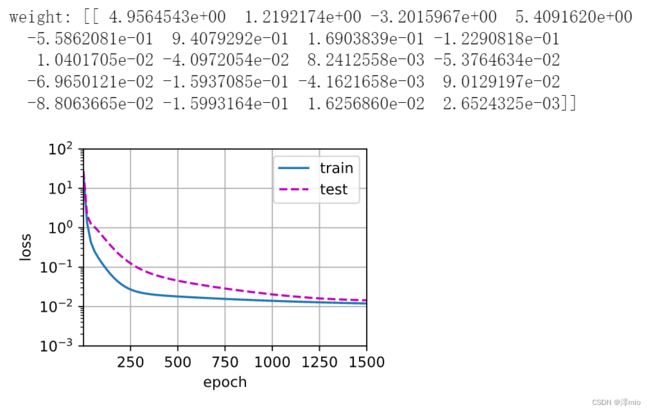
print('weight:', net[0].weight.data.numpy())
三阶多项式函数拟合(正态)
train(poly_features[:n_train, :4], poly_features[n_train:, :4],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])
train(poly_features[:n_train, :2], poly_features[n_train:, :2],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])
train(poly_features[:n_train, :], poly_features[n_train:, :],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:], num_epochs=1500)
QA:
1、SVM应用于分类想比神经网络的缺点?
SVM对于数据样本大的情况不好。SVM可以调的东西不多,比较平滑。
神经网络优点在于它是一个“语言”,神经网络很灵活,可编程线强。虽然SVM数学解释好,但是可解决的问题少。
2、K则交叉验证在大数据集的深度学习中应用不多,因为训练成本高。一般都是在数据量不够的情况下才用。
3、k则交叉验证中,k的确定主要取决的能够承受的计算成本。
4、模型参数≠超参数
模型参数:W,b
超参数:可选的模型参数之外的参数
5、
方案1:k则交叉验证确定超参数,再在整个数据集上训练一次
方案2:用k则交叉验证中的最好的参数
方案3:用k则交叉验证中的k个数据值在结果的均值。