刘二大人PyTorch-卷积神经网络(CNN)—基础篇
B站刘二大人的《PyTorch深度学习实践》视频链接
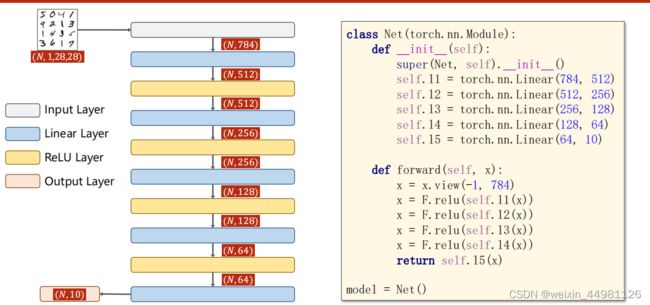
一. 全连接神经网络
注释:网络完全由线性层串行组成的网络
1. 对于常规的卷积操作,通常将单通道的图像先经过一个卷积层,提高通道数量,使得增加可提取的信息,然后经过下采样过程,通道不变,降低图像的宽高,降低运算量.
对于卷积以及下采样的过程称之为特征提取层,而后经过如softmax的操作,来达到分类的目的
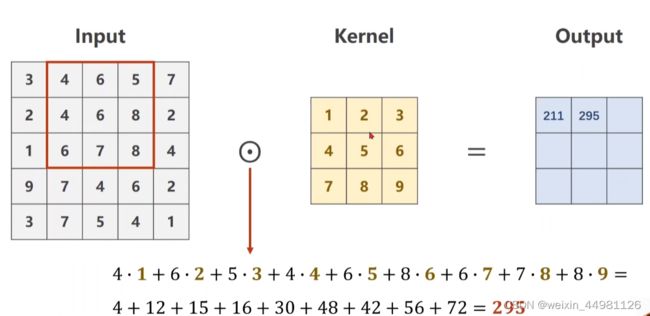
2. 卷积基本操作流程
卷积核按对应大小由左上角向又对相对应图像的栅格对应位置进行数乘求和,将信息存到对应大小的结果通道
对于多通道卷积运算,则每个通道都有其对应的卷积核与他们进行卷积运算,最终将值进行求和,此时得到的是一个单通道的结果。而如果想进行通道增加,则需要准备多个不同的卷积核,分别进行卷积运算,然后将得到的栅格组合,则获取多通道的值
 此时可以看到,卷积核通道数量等于初始图像的通道数量,而最终输出图像的通道,则等于卷积核的数量,这也是所谓的共享权重的概念。
此时可以看到,卷积核通道数量等于初始图像的通道数量,而最终输出图像的通道,则等于卷积核的数量,这也是所谓的共享权重的概念。
3. 代码示例
import torch
in_channels. out_channels = 5, 10 #
width, height = 100, 100 # 图像大小
kernel_size = 3
batch_size = 1
input = torch.randn(batch_size, # Batch
in_channels, # n
width, # W
height) # H
# 卷积层
conv_layer = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size = kernel_size)
#此时卷积核尺寸为 3 * 3,如果使用元组输入一个长方形的卷积尺寸也是可以的,但是一般都采用正方形卷积
output = conv_layer(input)
print(input.shape) # torch.Size([1, 5, 100, 100]) 5通道 100 * 100
print(output.shape) # torch.Size([1, 10, 98, 98)] 10通道 98 * 98
print(conv_layer.weight.shape) # torch.Size([10, 5, 3, 3]) 5输入通道 10 输出通道 3 * 3
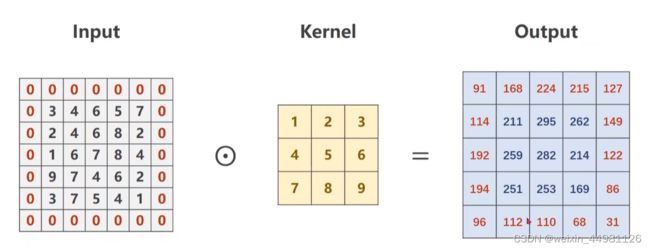
4.如果想得到更大尺寸的输出结果,则需要进行填充0的padding操作
import torch
input = [3,4,6,5,7,
2,4,6,8,2,
1,6,7,8,4,
9,7,4,6,2,
3,7,5,4,1]
#将一个列表转换成一个batch5,通道1,长宽5的张量
input = torch.Tensor(input).view(1, 1, 5, 5)
#卷积层padding=1也就是在外面加一圈
conv_layer = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
#定义一个卷积核
kernel = torch.Tensor([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]).view(1, 1, 3, 3)
#我们将自己设置的卷积核权重设置给卷积层的权重
conv_layer.weight.data = kernel.data
output = conv_layer(input)
print(output.data)
5.如果想得到更小尺寸的输出结果,则需要进行更改步长的stride操作
import torch
input = [3,4,6,5,7,
2,4,6,8,2,
1,6,7,8,4,
9,7,4,6,2,
3,7,5,4,1]
input = torch.Tensor(input).view(1, 1, 5, 5)
#stride=2步长调整为2
conv_layer = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)
kernel = torch.Tensor([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]).view(1, 1, 3, 3)
conv_layer.weight.data = kernel.data
output = conv_layer(input)
print(output.data)
6. 下采样详解
一般使用MaxPooling 最大池化层进行,每次只在相同通道进行最大值采样的操作,通道不变
import torch
input = [3,4,6,5,
2,4,6,8,
1,6,7,8,
9,7,4,6,
]
input = torch.Tensor(input).view(1, 1, 4, 4)
maxpooling_layer = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size = 2)
output = maxpooling_layer(input)
print(output)