数据结构之链表
文章目录
- 1.1链表的概念及结构
-
- 1.2逻辑结构和物理结构
-
- 1.3单链表的优势
-
- 1.4单链表的实现
-
- 1.5完整代码
1.1链表的概念及结构
概念:
- 链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的
- 实际中要实现的链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
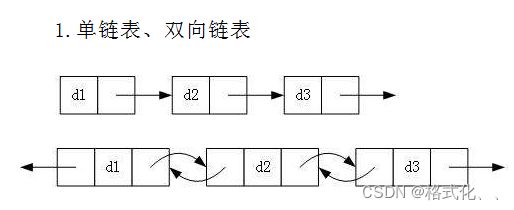
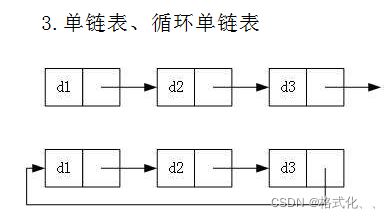
1、单向、双向
2、带头、不带头
3、循环、非循环
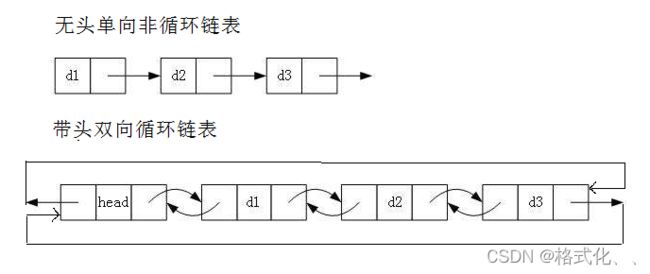
- 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多(单链表最多缺陷)。
- 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了,后面我们代码实现了就知道了。
1.2逻辑结构和物理结构
1.3单链表的优势
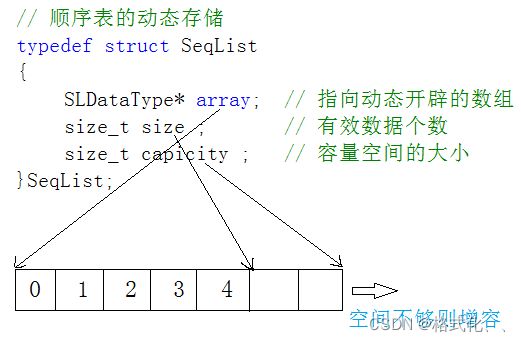
- 首先来说说动态顺序表的优劣势
优势:连续的物理空间,方便下标随机访问
缺陷:1.插入数据,空间不够时,需要扩容
2.头部或中间插入和删除时,需要挪动数据,时间复杂度为O(n)
3.可能存在一点的空间浪费,当扩容越来越大时
4.不能按需申请和释放空间
- 基于顺序表的劣势,所以设计出了链表,它们是相辅相成的
因为顺序表尾插尾删的时间复杂度都是O(1),而头插头删时间复杂度是O(n)。但是单链表的头插和头删时间复杂度是O(1),尾插尾删是O(n)。所以说它们是相辅相成的。- 单链表的优势:不需要扩容,插入新数据时直接重新开辟节点,解决了内存浪费和不能按需申请的问题,头插头删时间复杂度为O(1)
单链表的缺陷:不能随机访问,只能往前走,尾插尾删时需要找尾节点,高速缓冲命中率低
1.4单链表的实现
单链表的实现
#Slist.h
#ifndef SLIST_H_
#define SLIST_H_
#include 实现函数接口:SListPrint()
void SListPrint(SListNode *phead)
{
//链表一开始为空,无需判断
SListNode *cur = phead;
//遍历链表
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
//每次保存下一个节点的地址
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
实现独立函数接口:BuySListNode() 这个函数是创建新节点
SListNode *BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
//动态开辟新节点
SListNode *newNode = (SListNode *)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
//判断堆区是否已满,已满则malloc()返回NULL
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail!!!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else
{
//不为空则把数据给到新节点
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
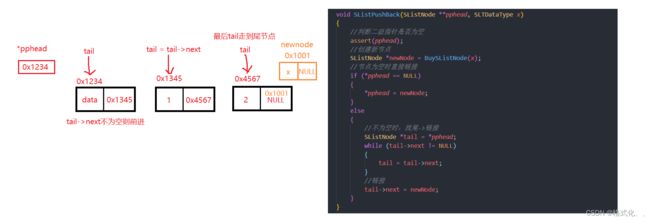
实现函数接口:SListPushBack()
void SListPushBack(SListNode **pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
//判断二级指针是否为空
assert(pphead);
//创建新节点
SListNode *newNode = BuySListNode(x);
//节点为空时直接链接
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newNode;
}
else
{
//不为空时:找尾->链接
SListNode *tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
//链接
tail->next = newNode;
}
}
实现函数接口:SListPushFront()
void SListPushFront(SListNode **pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
//判断二指针是否为空
assert(pphead);
SListNode *newNode = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
}
}
实现函数接口:SListPopBack()
oid SListPopBack(SListNode **pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
//如果节点为空,那么不需要删除
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
//结束函数
return;
}
//只有一个节点时,直接释放节点,然后置为NULL
else if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
//多个节点
SListNode *tail = *pphead;
SListNode *prev = NULL;
//找尾前一个节点
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
函数接口:SListPopFront()
void SListPopFront(SListNode **pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
//保存头节点的next节点,否则free后会找不到
SListNode *next = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
}
}
函数接口:SListFind()
SListNode *SListFind(SListNode *phead, SLTDataType x)
{
SListNode *cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
//逐个节点判断是否有相等的data
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
函数接口:SListInsert()
void SListInsert(SListNode **pphead, SListNode *pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
SListNode *newNode = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else if ((*pphead)->next == pos)
{
//复用头插函数接口
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
SListNode *prev = *pphead;
//找pos前面的节点
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
//链接新节点
newNode->next = pos;
prev->next = newNode;
}
}
函数接口:SListErase()
void SListErase(SListNode **pphead, SListNode *pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
//节点为空即不用删除
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode *prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
}
函数接口:SListInsertAfter()
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode **pphead, SListNode *pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode *newNode = BuySListNode(x);
newNode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newNode;
}
}
函数接口:SListEraseAfter()
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode **pphead, SListNode *pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if (pos->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode *next = pos->next;
if (next)
{
pos->next = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
}
}
}
最后一个接口:SListDestory()
void SListDestory(SListNode **pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
SListNode *cur = *pphead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
//保存上一个节点地址
SListNode *next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}
1.5完整代码
#Slist.h
#ifndef SLIST_H_
#define SLIST_H_
#include 单链表相关知识已经干完了,如有错误请大家指出,感谢!!!