一、前言
前段时间碰到了一个 Keybinding 相关的问题,于是探究了一番,首先大家可能会有两个问题:Monaco Editor 是啥?Keybinding 又是啥?
- Monaco Editor: 微软开源的一个代码编辑器,为 VS Code 的编辑器提供支持,Monaco Editor 核心代码与 VS Code 是共用的(都在 VS Code github 仓库中)。
- Keybinding: Monaco Editor 中实现快捷键功能的机制(其实准确来说,应该是部分机制),可以使得通过快捷键来执行操作,例如打开命令面板、切换主题以及编辑器中的一些快捷操作等。
本文主要是针对 Monaco Editor 的 Keybinding 机制进行介绍,由于源码完整的逻辑比较庞杂,所以本文中的展示的源码以及流程会有一定的简化。
文中使用的代码版本:
Monaco Editor:0.30.1
VS Code:1.62.1
二、举个
这里使用 monaco-editor 创建了一个简单的例子,后文会基于这个例子来进行介绍。
import React, { useRef, useEffect, useState } from "react";
import * as monaco from "monaco-editor";
import { codeText } from "./help";
const Editor = () => {
const domRef = useRef(null);
const [actionDispose, setActionDispose] = useState();
useEffect(() => {
const editorIns = monaco.editor.create(domRef.current!, {
value: codeText,
language: "typescript",
theme: "vs-dark",
});
const action = {
id: 'test',
label: 'test',
precondition: 'isChrome == true',
keybindings: [monaco.KeyMod.CtrlCmd | monaco.KeyCode.KeyL],
run: () => {
window.alert('chrome: cmd + k');
},
};
setActionDispose(editorIns.addAction(action));
editorIns.focus();
return () => {
editorIns.dispose();
};
}, []);
const onClick = () => {
actionDispose?.dispose();
window.alert('已卸载');
};
return (
);
};
export default Editor;
三、原理机制
1. 概览
根据上面的例子,Keybinding 机制的总体流程可以简单的分为以下几步:
- 初始化:主要是初始化服务以及给 dom 添加监听事件
- 注册:注册 keybinding 和 command
- 执行:通过按快捷键触发执行对应的 keybinding 和 command
- 卸载:清除注册的 keybinding 和 command
2. 初始化
回到上面例子中创建 editor 的代码:
const editorIns = monaco.editor.create(domRef.current!, {
value: codeText,
language: "typescript",
theme: "vs-dark",
});
初始化过程如下:
创建 editor 之前会先初始化 services,通过实例化 DynamicStandaloneServices 类创建服务:
let services = new DynamicStandaloneServices(domElement, override);
在 constructor 函数中会执行以下代码注册 keybindingService:
let keybindingService = ensure(IKeybindingService, () =>
this._register(
new StandaloneKeybindingService(
contextKeyService,
commandService,
telemetryService,
notificationService,
logService,
domElement
)
)
);
其中 this._register 方法和 ensure 方法会分别将 StandaloneKeybindingServices 实例保存到 disposable 对象(用于卸载)和 this._serviceCollection 中(用于执行过程查找keybinding)。
实例化 StandaloneKeybindingService,在 constructor 函数中添加 DOM 监听事件:
this._register(
dom.addDisposableListener(
domNode,
dom.EventType.KEY_DOWN,
(e: KeyboardEvent) => {
const keyEvent = new StandardKeyboardEvent(e);
const shouldPreventDefault = this._dispatch(
keyEvent,
keyEvent.target
);
if (shouldPreventDefault) {
keyEvent.preventDefault();
keyEvent.stopPropagation();
}
}
)
);
以上代码中的 dom.addDisposableListener 方法,会通过 addEventListener 的方式,在 domNode 上添加一个 keydown 事件的监听函数,并且返回一个 DomListener 的实例,该实例包含一个用于移除事件监听的 dispose 方法。然后通过 this._register 方法将 DomListener 的实例保存起来。
3. 注册 keybindings
回到例子中的代码:
const action = {
id: 'test',
label: 'test',
precondition: 'isChrome == true',
keybindings: [monaco.KeyMod.CtrlCmd | monaco.KeyCode.KeyL],
run: () => {
window.alert('chrome: cmd + k');
},
};
setActionDispose(editorIns.addAction(action));
注册过程如下:
当通过 editorIns.addAction 来注册 keybinding 时,会调用 StandaloneKeybindingServices 实例的 addDynamicKeybinding 方法来注册 keybinding。
public addDynamicKeybinding(
commandId: string,
_keybinding: number,
handler: ICommandHandler,
when: ContextKeyExpression | undefined
): IDisposable {
const keybinding = createKeybinding(_keybinding, OS);
const toDispose = new DisposableStore();
if (keybinding) {
this._dynamicKeybindings.push({
keybinding: keybinding.parts,
command: commandId,
when: when,
weight1: 1000,
weight2: 0,
extensionId: null,
isBuiltinExtension: false,
});
toDispose.add(
toDisposable(() => {
for (let i = 0; i < this._dynamicKeybindings.length; i++) {
let kb = this._dynamicKeybindings[i];
if (kb.command === commandId) {
this._dynamicKeybindings.splice(i, 1);
this.updateResolver({
source: KeybindingSource.Default,
});
return;
}
}
})
);
}
toDispose.add(CommandsRegistry.registerCommand(commandId, handler));
this.updateResolver({ source: KeybindingSource.Default });
return toDispose;
}
会先根据传入的 _keybinding 创建 keybinding 实例,然后连同 command、when 等其他信息存入_dynamicKeybindings 数组中,同时会注册对应的 command,当后面触发 keybinding 时便执行对应的 command。返回的 toDispose 实例则用于取消对应的 keybinding 和 command。
回到上面代码中创建 keybinding 实例的地方,createKeybinding 方法会根据传入的 _keybinding 数字和 OS 类型得到实例,大致结构如下(已省略部分属性):
{
parts: [
{
ctrlKey: boolean,
shiftKey: boolean,
altKey: boolean,
metaKey: boolean,
keyCode: KeyCode,
}
],
}
那么,是怎么通过一个 number 得到所有按键信息的呢?往下看↓↓↓
4. key的转换
先看看一开始传入的 keybinding 是什么:
const action = {
id: 'test',
label: 'test',
precondition: 'isChrome == true',
keybindings: [monaco.KeyMod.CtrlCmd | monaco.KeyCode.KeyL],
run: () => {
window.alert('chrome: cmd + k');
},
};
传入的 keybinding 就是上面代码中的 keybindings 数组中的元素,monaco.KeyMod.CtrlCmd = 2048,monaco.KeyCode.KeyL = 42,对应的数字是 monaco-editor 中定义的枚举值,与真实的 keyCode 存在对应关系。所以注册时传入的 keybinding 参数为: 2048 | 42 = 2090
先简单了解下 JS 中的位运算(操作的是32位带符号的二进制整数,下面例子中只用8位简单表示):
按位与(AND)&
对应的位都为1则返回1,否则返回0
例如:
00001010 // 10
00000110 // 6
------
00000010 // 2
按位或(OR)|
对应的位,只要有一个为1则返回1,否则返回0
00001010 // 10
00000110 // 6
-------
00001110 // 14
左移(Left shift)<<
将二进制数每一位向左移动指定位数,左侧移出的位舍弃,右侧补0
00001010 // 10
------- // 10 << 2
00101000 // 40
右移 >>
将二进制数每位向右移动指定位数,右侧移出的位舍弃,左侧用原来最左边的数补齐
00001010 // 10
------- // 10 >> 2
00000010 // 2
无符号右移 >>>
将二进制数每位向右移动指定位数,右侧移出的位舍弃,左侧补0
00001010 // 10
------- // 10 >> 2
00000010 // 2
接下来看下是怎么根据一个数字,创建出对应的 keybinding 实例:
export function createKeybinding(keybinding: number, OS: OperatingSystem): Keybinding | null {
if (keybinding === 0) {
return null;
}
const firstPart = (keybinding & 0x0000FFFF) >>> 0;
// 处理分两步的keybinding,例如:shift shift,若无第二部分,则chordPart = 0
const chordPart = (keybinding & 0xFFFF0000) >>> 16;
if (chordPart !== 0) {
return new ChordKeybinding([
createSimpleKeybinding(firstPart, OS),
createSimpleKeybinding(chordPart, OS)
]);
}
return new ChordKeybinding([createSimpleKeybinding(firstPart, OS)]);
}
看下 createSimpleKeybinding 方法做了什么
const enum BinaryKeybindingsMask {
CtrlCmd = (1 << 11) >>> 0, // 2048
Shift = (1 << 10) >>> 0, // 1024
Alt = (1 << 9) >>> 0, // 512
WinCtrl = (1 << 8) >>> 0, // 256
KeyCode = 0x000000FF // 255
}
export function createSimpleKeybinding(keybinding: number, OS: OperatingSystem): SimpleKeybinding {
const ctrlCmd = (keybinding & BinaryKeybindingsMask.CtrlCmd ? true : false);
const winCtrl = (keybinding & BinaryKeybindingsMask.WinCtrl ? true : false);
const ctrlKey = (OS === OperatingSystem.Macintosh ? winCtrl : ctrlCmd);
const shiftKey = (keybinding & BinaryKeybindingsMask.Shift ? true : false);
const altKey = (keybinding & BinaryKeybindingsMask.Alt ? true : false);
const metaKey = (OS === OperatingSystem.Macintosh ? ctrlCmd : winCtrl);
const keyCode = (keybinding & BinaryKeybindingsMask.KeyCode);
return new SimpleKeybinding(ctrlKey, shiftKey, altKey, metaKey, keyCode);
}
拿上面的例子:
keybinding = monaco.KeyMod.CtrlCmd | monaco.KeyCode.KeyL,即 keybinding = 2048 | 42 = 2090
然后看上面代码中的:
const ctrlCmd = (keybinding & BinaryKeybindingsMask.CtrlCmd ? true : false);
运算如下:
100000101010 // 2090 -> keybinding
100000000000 // 2048 -> CtrlCmd
----------- // &
100000000000 // 2048 -> CtrlCmd
再看keyCode的运算:
const keyCode = (keybinding & BinaryKeybindingsMask.KeyCode)
100000101010 // 2090 -> keybinding
000011111111 // 255 -> KeyCode
----------- // &
000000101010 // 42 -> KeyL
于是便得到了 ctrlKey,shiftKey,altKey,metaKey,keyCode 这些值,接下来便由这些值生成SimpleKeybinding实例,该实例包含了上面的这些按键信息以及一些操作方法。
至此,已经完成了 keybinding 的注册,将 keybinding 实例及相关信息存入了 StandaloneKeybindingService 实例的 _dynamicKeybindings 数组中,对应的 command 也注册到了 CommandsRegistry 中。
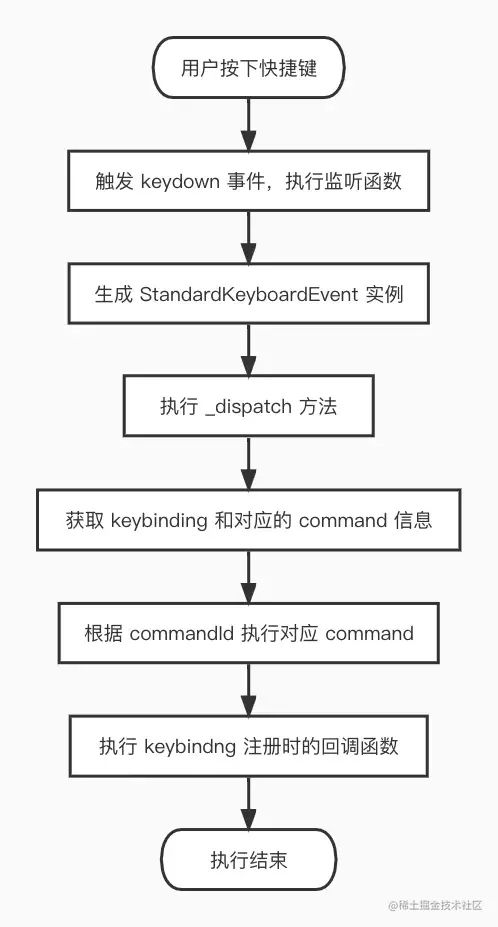
5.执行
当用户在键盘上按下快捷键时,便会触发 keybinding 对应 command 的执行,执行过程如下:
回到 StandaloneKeybindingServices 初始化的时候,在 domNode 上绑定了 keydown 事件监听函数:
(e: KeyboardEvent) => {
const keyEvent = new StandardKeyboardEvent(e);
const shouldPreventDefault = this._dispatch(keyEvent, keyEvent.target);
if (shouldPreventDefault) {
keyEvent.preventDefault();
keyEvent.stopPropagation();
}
};
当 keydown 事件触发后,便会执行这个监听函数,首先会实例化一个 StandardKeyboardEvent 实例,该实例包含了一些按键信息和方法,大致结构如下(已省略部分属性):
{
target: HTMLElement,
ctrlKey: boolean,
shiftKey: boolean,
altKey: boolean,
metaKey: boolean,
keyCode: KeyCode,
}
其中 keyCode 是经过处理后得到的,由原始键盘事件的 keyCode 转换为 monoco-editor 中的 keyCode,转换过程主要就是兼容一些不同的浏览器,并根据映射关系得到最终的 keyCode。准换方法如下:
function extractKeyCode(e: KeyboardEvent): KeyCode {
if (e.charCode) {
// "keypress" events mostly
let char = String.fromCharCode(e.charCode).toUpperCase();
return KeyCodeUtils.fromString(char);
}
const keyCode = e.keyCode;
// browser quirks
if (keyCode === 3) {
return KeyCode.PauseBreak;
} else if (browser.isFirefox) {
if (keyCode === 59) {
return KeyCode.Semicolon;
} else if (keyCode === 107) {
return KeyCode.Equal;
} else if (keyCode === 109) {
return KeyCode.Minus;
} else if (platform.isMacintosh && keyCode === 224) {
return KeyCode.Meta;
}
} else if (browser.isWebKit) {
if (keyCode === 91) {
return KeyCode.Meta;
} else if (platform.isMacintosh && keyCode === 93) {
// the two meta keys in the Mac have different key codes (91 and 93)
return KeyCode.Meta;
} else if (!platform.isMacintosh && keyCode === 92) {
return KeyCode.Meta;
}
}
// cross browser keycodes:
return EVENT_KEY_CODE_MAP[keyCode] || KeyCode.Unknown;
}
得到了 keyEvent 实例对象后,便通过 this._dispatch(keyEvent, keyEvent.target) 执行。
protected _dispatch(
e: IKeyboardEvent,
target: IContextKeyServiceTarget
): boolean {
return this._doDispatch(
this.resolveKeyboardEvent(e),
target,
/*isSingleModiferChord*/ false
);
}
直接调用了 this._doDispatch 方法,通过 this.resolveKeyboardEvent(e) 方法处理传入的 keyEvent,得到一个包含了许多 keybinding 操作方法的实例。
接下来主要看下 _doDispatch 方法主要干了啥(以下仅展示了部分代码):
private _doDispatch(
keybinding: ResolvedKeybinding,
target: IContextKeyServiceTarget,
isSingleModiferChord = false
): boolean {
const resolveResult = this._getResolver().resolve(
contextValue,
currentChord,
firstPart
);
if (resolveResult && resolveResult.commandId) {
if (typeof resolveResult.commandArgs === 'undefined') {
this._commandService
.executeCommand(resolveResult.commandId)
.then(undefined, (err) =>
this._notificationService.warn(err)
);
} else {
this._commandService
.executeCommand(
resolveResult.commandId,
resolveResult.commandArgs
)
.then(undefined, (err) =>
this._notificationService.warn(err)
);
}
}
}
主要是找到 keybinding 对应的 command 并执行,_getResolver 方法会拿到已注册的 keybinding,然后通过 resolve 方法找到对应的 keybinding 及 command 信息。而执行 command 则会从 CommandsRegistry 中找到对应已注册的 command,然后执行 command 的 handler 函数(即keybinding 的回调函数)。
6.卸载
先看看一开始的例子中的代码:
const onClick = () => {
actionDispose?.dispose();
window.alert('已卸载');
};
卸载过程如下:
回到刚开始注册时:setActionDispose(editorIns.addAction(action)),addAction 方法会返回一个 disposable 对象,setActionDispose 将该对象保存了起来。通过调用该对象的 dispose 方法:actionDispose.dispose(),便可卸载该 action,对应的 command 和 keybinding 便都会被卸载。
四、结语
对 Monaco Editor 的 Keybinding 机制进行简单描述,就是通过监听用户的键盘输入,找到对应注册的 keybinding 和 command,然后执行对应的回调函数。但仔细探究的话,每个过程都有很多处理逻辑,本文也只是对其做了一个大体的介绍,实际上还有许多相关的细节没有讲到,感兴趣的同学可以探索探索。
以上就是详解Monaco Editor中的Keybinding机制的详细内容,更多关于Monaco Editor Keybinding的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!