springcloud--Sentinel(服务容错)
目录
1.什么是Sentinel
2.为什么使用sentinel
3.服务雪崩效应
3.1.什么是服务雪崩效应
3.2.如何解决雪崩效应
3.2.1.超时处理
3.2.2.舱壁模式
3.2.3.熔断降级
3.2.4.流量控制
4.常见的容错组件
4.1.hystrix
4.2.sentinel
4.3.hystrix 组件和sentinel组件的比较
5.安装Sentinel控制台
5.1.下载sentinel
5.2.启动sentinel
5.3.访问sentinel
5.4.修改sentinel的端口号
5.5.修改账号和密码
6.微服务整合Sentinel
6.1.引入sentinel依赖
6.2.修改配置文件
6.3.访问微服务的任意点,触发sentinel监控
7.簇点链路
7.1.流控规则
7.1.1.流控规则入门案例
7.1.2.jemeter
7.2.流控模式
7.2.1.流控模式-关联模式
7.2.2.流控模式-关联模式例子
7.2.3.测试 jemeter
7.2.4.流控模式-链路模式
7.2.5. 流控模式-链路模式的例子
7.2.6.测试jmeter
7.2.7.流控模式有哪些
7.3.流控效果
7.3.1.流控效果-warm up
7.3.2.流控效果-warm up的例子
7.3.3.测试jmeter
7.3.4.流控效果-排队等待
7.3.5.流控效果-排队等待的例子
7.3.6.测试jmeter
7.3.7.流控效果有哪些?
8.热点规则
8.1.什么是热点参数限流
8.2.热点参数限流的例子
8.2.1.设置热点规则
8.2.2.测试
9.隔离和降级
9.1.openFeign整合Sentinel
9.1.1.修改OrderService的application文件,开启Feign的Sentinel功能
9.1.2.编写失败后的降级逻辑
9.2.线程隔离
9.2.1.线程隔离方式实现
9.2.2. 线程池隔离与信号量隔离的区别
9.2.3.在添加限流规则时,可以选择两种阈值
9.2.4.线程隔离(舱壁模式)的列子
9.3.熔断降级
9.3.1.断路器熔断策略--慢调用
9.3.2.熔断策略-异常比例、异常数、
9.3.3.Sentinel熔断降级的策略有哪些?
9.3.4.自定义异常
10.Sentinel规则持久化
10.1.Sentinel的控制台规则管理有三种模式
10.2.规则管理模式-原始模式
10.3.规则管理模式-pull模式
10.4.规则管理模式-push模式
10.5. 实现pull模式
10.5.1.编写配置类
10.5.2.添加配置
10.5.3.运行
1.什么是Sentinel
Sentinel (分布式系统的流量防卫兵) 是阿里开源的一套用于服务容错的综合性解决方案。它以流量为切入点, 从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度来保护服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 分为两个部分:
核心库(Java 客户端 微服务) 不依赖任何框架/库,能够运行于所有 Java 运行时环境,同时对 Dubbo /Spring Cloud 等框架也有较好的支持。
控制台(Dashboard==sentinel服务)基于 Spring Boot 开发,打包后可以直接运行,不需要额外的 Tomcat 等应用容器。
2.为什么使用sentinel
在微服务架构中,我们将业务拆分成一个个的服务,服务与服务之间可以相互调用,但是由于网络原因或者自身的原因,服务并不能保证服务的100%可用,如果单个服务出现问题,调用这个服务就会出现网络延迟,此时若有大量的网络涌入,会形成任务堆积,最终导致服务瘫痪
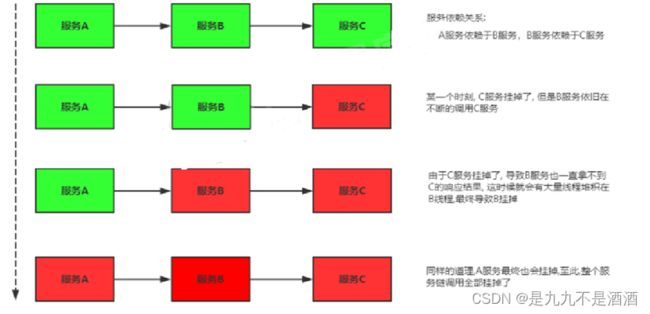
3.服务雪崩效应
3.1.什么是服务雪崩效应
在分布式系统中,由于网络原因或自身的原因,服务一般无法保证 100% 可用。如果一个服务出现了问题,调用这个服务就会出现线程阻塞的情况,此时若有大量的请求涌入,就会出现多条线程阻塞等待,进而导致服务瘫痪。由于服务与服务之间的依赖性,故障会传播,会对整个微服务系统造成灾难性的严重后果,这就是服务故障的 “雪崩效应”
雪崩发生的原因多种多样,有不合理的容量设计,或者是高并发下某一个方法响应变慢,亦或是某台机器的资源耗尽。我们无法完全杜绝雪崩源头的发生,只有做好足够的容错,保证在一个服务发生问题,不会影响到其它服务的正常运行。也就是"雪落而不雪崩"
3.2.如何解决雪崩效应
解决雪崩问题的常见方式有四种
3.2.1.超时处理
设定超时时间,请求超过一定时间没有相应就返回错误有信息,不会无休止等待
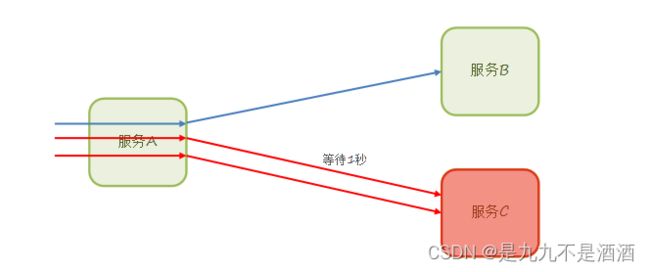
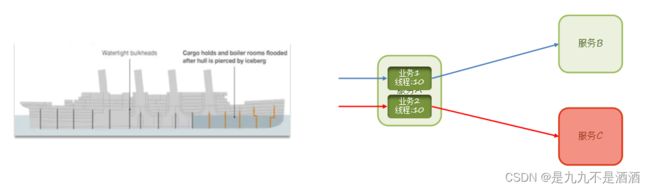
3.2.2.舱壁模式
限定每个业务能使用的线程数,避免耗尽整个tomcat的资源,因此也叫线程隔离。
3.2.3.熔断降级
由断路器统计业务执行的异常比例,如果超出阈值则会熔断该业务,拦截访问该业务的一切请求。
3.2.4.流量控制
限制业务访问的QPS,避免服务因流量的突增而故障。
前三个方法是避免因服务故障引起的雪崩问题,最后一个是避免因瞬间高并发流量而导致服务故障
4.常见的容错组件
4.1.hystrix
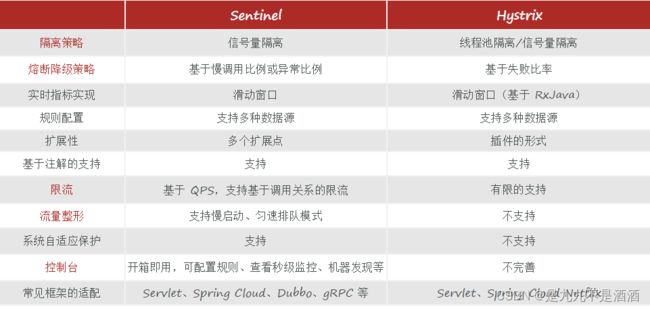
Hystrix是由Netflix开源的一个延迟和容错库,用于隔离访问远程系统、服务或者第三方库,防止级联失败,从而提升系统的可用性与容错性
4.2.sentinel
Sentinel 是阿里巴巴开源的一款断路器实现,本身在阿里内部已经被大规模采用,非常稳定。
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
完备的实时监控:Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展接口。您可以通过实现扩展接口来快速地定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等。
4.3.hystrix 组件和sentinel组件的比较
5.安装Sentinel控制台
5.1.下载sentinel
sentinel官方提供了UI控制台,方便我们对系统做限流设置。大家可以在GitHub下载。不用解压
5.2.启动sentinel
找到自己下载的位置,在路径上输入cmd 打开黑窗口
java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.1.jar
5.3.访问sentinel
5.4.修改sentinel的端口号
java -Dserver.port=端口号 -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.1.jar
5.5.修改账号和密码
6.微服务整合Sentinel
6.1.引入sentinel依赖
com.alibaba.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel
6.2.修改配置文件
#指定sentinel控制台的地址
spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.dashboard=localhost:80806.3.访问微服务的任意点,触发sentinel监控
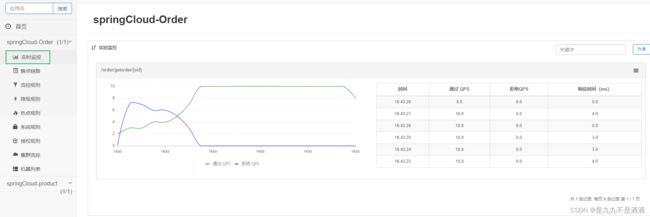
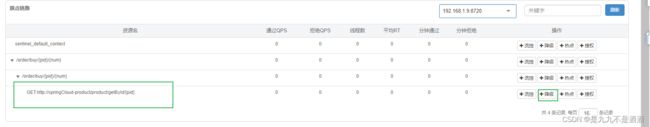
7.簇点链路
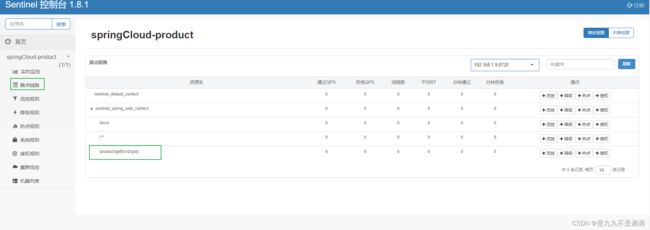
簇点链路:就是项目内的调用链路,链路中被监控的每个接口就是一个资源.默认情况下sentinel会监控SpringMVC的每一个端点(Endpoint)因此SpringMVC的每一个端点(Endpoint)就是调用链路中的一个资源。流控、熔断等都是针对簇点链路中的资源来设置的,因此我们可以点击对应资源后面的按钮来设置规则
7.1.流控规则
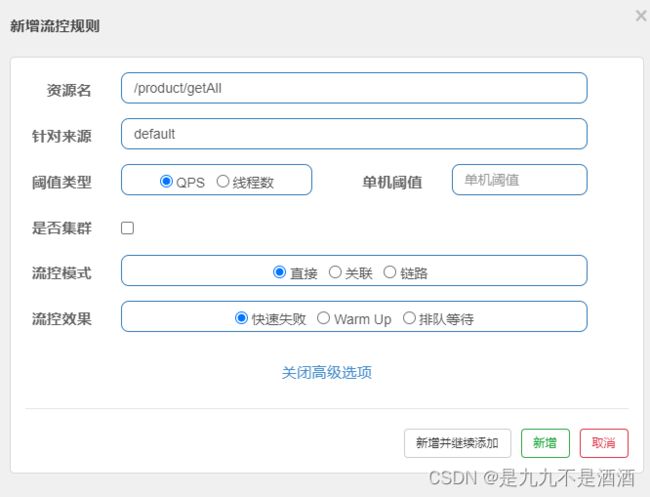
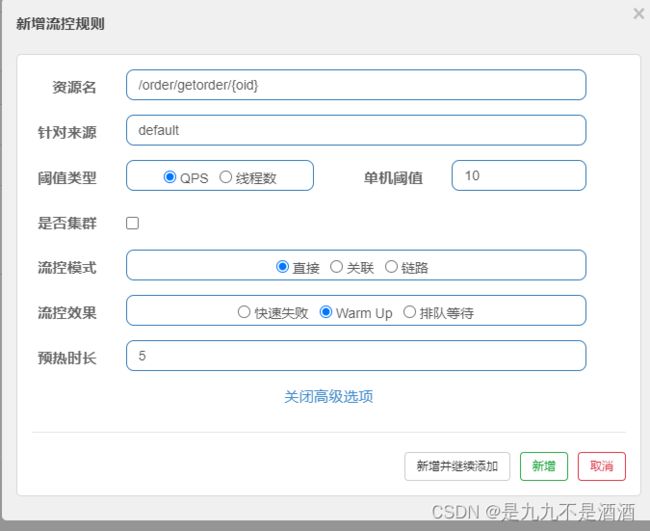
点击资源后面的流控按钮,就可以弹出表单。表单中可以添加流控规则,如下图所示:
其含义是限制/product/getById/{pid}这个资源的单机QPS为1,即每秒只允许1次请求,超出的请求会被拦截并报错。
7.1.1.流控规则入门案例
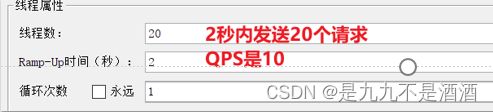
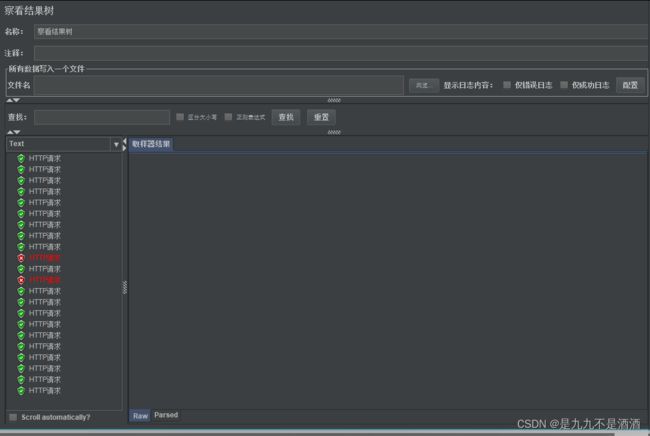
需求:给 /product/getById/{pid}这个资源设置流控规则,QPS不能超过 5。然后利用jemeter测试。
![]()
 7.1.2.jemeter
7.1.2.jemeter
启动jemeter
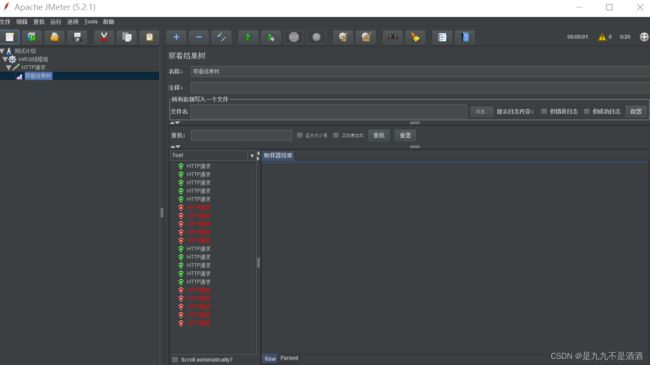 7.2.流控模式
7.2.流控模式
在添加限流规则时,点击高级选项,可以选择三种流控模式:
直接:统计当前资源的请求,触发阈值时对当前资源直接限流,也是默认的模式
关联:统计与当前资源相关的另一个资源,触发阈值时,对当前资源限流
链路:统计从指定链路访问到本资源的请求,触发阈值时,对指定链路限流
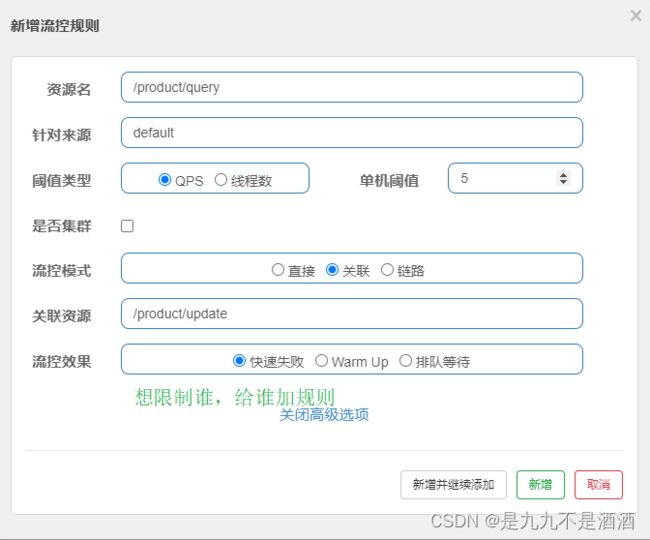
7.2.1.流控模式-关联模式
关联模式:统计与当前资源相关的另一个资源,触发阈值时,对当前资源限流
使用场景:比如用户支付时需要修改订单状态,同时用户要查询订单。查询和修改操作会争抢数据库锁,产生竞争。业务需求是有限支付和更新订单的业务,因此当修改订单业务触发阈值时,需要对查询订单业务限流
满足下面条件可以使用关联模式:
1.两个有竞争关系的资源
2.一个优先级较高,一个优先级较低
7.2.2.流控模式-关联模式例子
在Controller新建两个端点:/product/query和/product/update,无需实现业务
配置流控规则,当/product/ update资源被访问的QPS超过5时,对/order/query请求限流
@GetMapping("/query")
public String query(){
return "查询商品信息";
}
@GetMapping("/update")
public String update(){
return "修改商品信息";
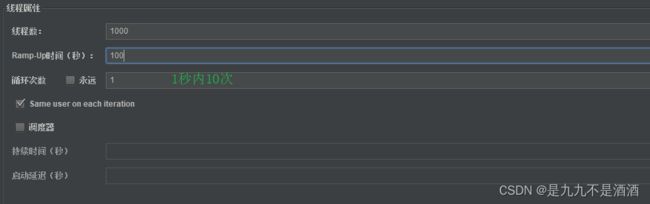
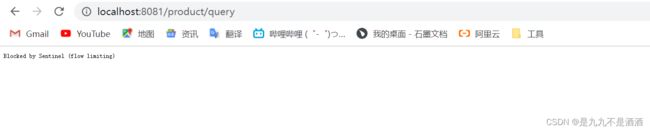
}7.2.3.测试 jemeter
运行的时候我们在浏览器上重新运行一下/product/update发现限流了
7.2.4.流控模式-链路模式
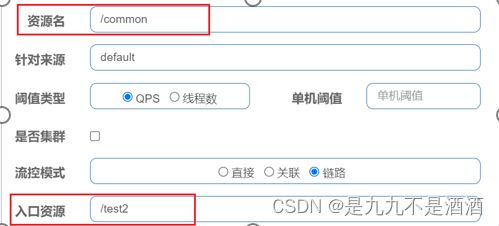
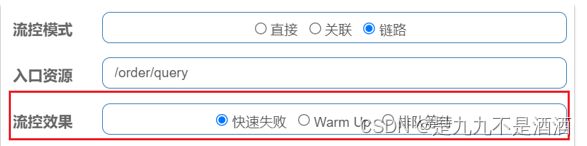
链路模式:只针对从指定链路访问到本资源的请求做统计,判断是否超过阈值。
例如有两条请求链路:
/test1 /common /test2 /common
如果只希望统计从/test2进入到/common的请求,则可以这样配置:
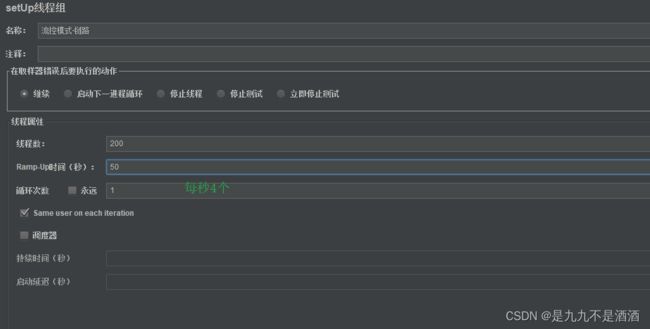
7.2.5. 流控模式-链路模式的例子
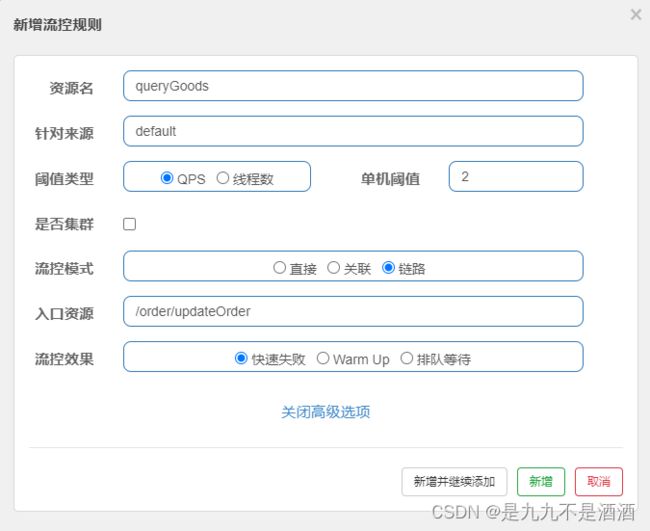
需求:有查询订单和创建订单业务,两者都需要查询商品。针对从查询订单进入到查询商品的请求统计,并设置限流。
步骤:
在OrderService中添加一个queryGoods方法,不用实现业务
在OrderController中,改造/order/query端点,调用OrderService中的queryGoods方法
在OrderController中添加一个/order/save的端点,调用OrderService的queryGoods方法
给queryGoods设置限流规则,从/order/query进入queryGoods的方法限制QPS必须小于2
controller
@GetMapping("/queryOrder")
public String query(){
String query= orderService.queryGoods();
return "查询信息";
}
@GetMapping("/updateOrder")
public String update(){
String update= orderService.queryGoods();
return "修改信息";
}Sentinel默认只标记Controller中的方法为资源,如果要标记其它方法,需要利用@SentinelResource注解
@SentinelResource("queryGoods")
public String queryGoods() {
return null;
}修改配置文件--Sentinel默认会将Controller方法做context整合,导致链路模式的流控失效,需要修改application.yml
#关闭上下文件 spring.cloud.sentinel.web-context-unify=false
运行一下自己刚刚写的方法
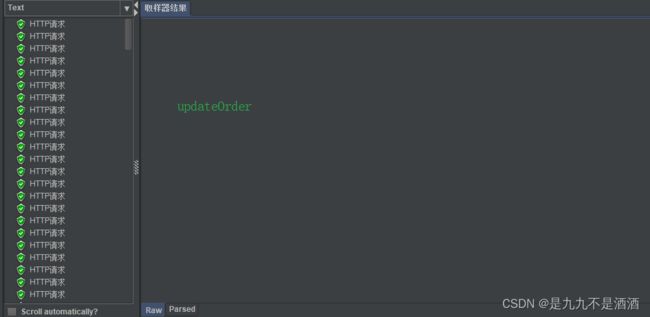
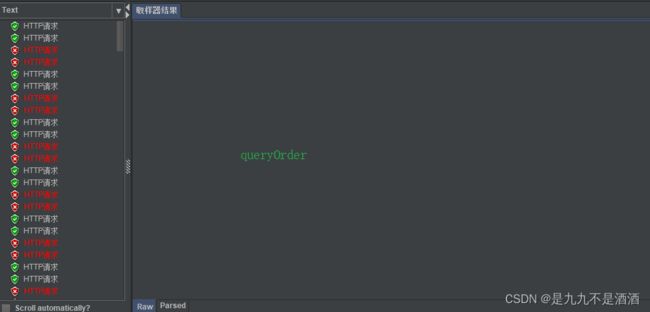
7.2.6.测试jmeter
写连个http请求我们可以看到queryOrder每秒执行两个,被限流了,而updateOrder没有限流
7.2.7.流控模式有哪些
直接:对当前资源限流
关联:高优先级资源触发阈值,对低优先级资源限流。
链路:阈值统计时,只统计从指定资源进入当前资源的请求,是对请求来源的限流
7.3.流控效果
流控效果是指请求达到流控阈值时应该采取的措施,包括三种:
快速失败:达到阈值后,新的请求会被立即拒绝并抛出FlowException异常。是默认的处理方式。
warm up:预热模式,对超出阈值的请求同样是拒绝并抛出异常。但这种模式阈值会动态变化,从一个较小值逐渐增加到最大阈值。
排队等待:让所有的请求按照先后次序排队执行,两个请求的间隔不能小于指定时长
7.3.1.流控效果-warm up
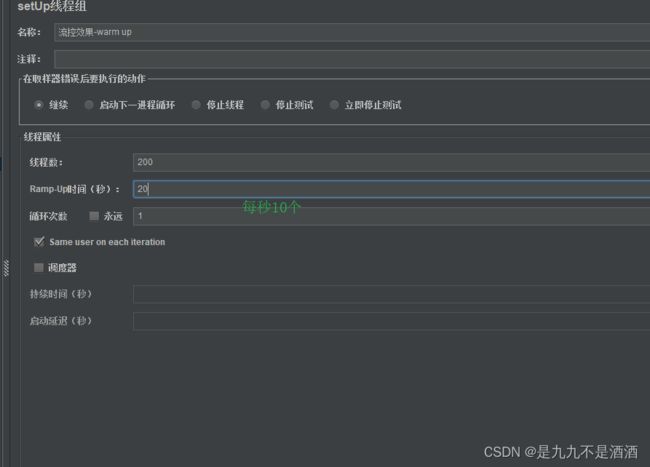
warm up也叫预热模式,是应对服务冷启动的一种方案。请求阈值初始值是 threshold / coldFactor,持续指定时长后,逐渐提高到threshold值。而coldFactor的默认值是3.
例如,我设置QPS的threshold为10,预热时间为5秒,那么初始阈值就是 10 / 3 ,也就是3,然后在5秒后逐渐增长到10
7.3.2.流控效果-warm up的例子
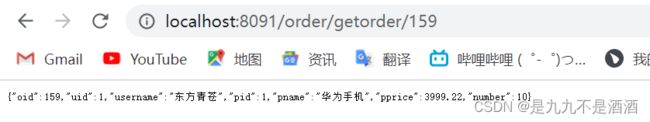
需求:给/getorder/{orId}这个资源设置限流,最大QPS为10,利用warm up效果,预热时长为5秒
controller
@GetMapping("/getorder/{oid}")
public Order getOrder(@PathVariable Integer oid){
return orderService.findId(oid);
}serviceimpl
@Override
public Order findId(Integer oid) {
return orderMapper.selectById(oid);
}在浏览器访问自己写的方法
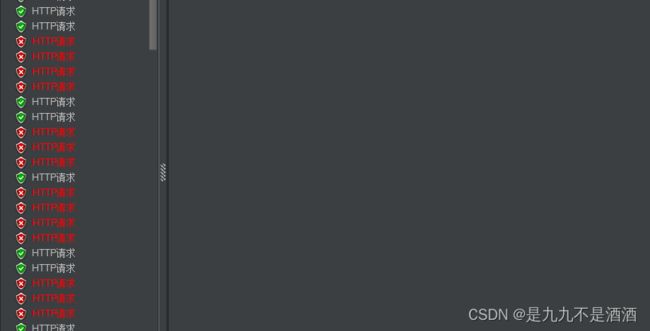
7.3.3.测试jmeter
7.3.4.流控效果-排队等待
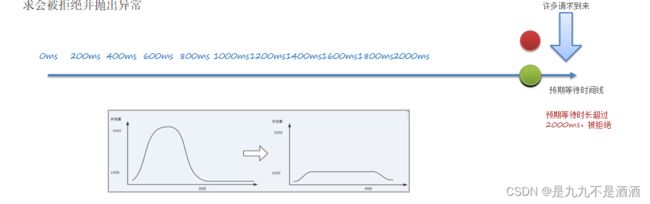
当请求超过QPS阈值时,快速失败和warm up 会拒绝新的请求并抛出异常。而排队等待则是让所有请求进入一个队列中,然后按照阈值允许的时间间隔依次执行。后来的请求必须等待前面执行完成,如果请求预期的等待时间超出最大时长,则会被拒绝。
例如:QPS = 5,意味着每200ms处理一个队列中的请求;timeout = 2000,意味着预期等待超过2000ms的请求会被拒绝并抛出异常
7.3.5.流控效果-排队等待的例子
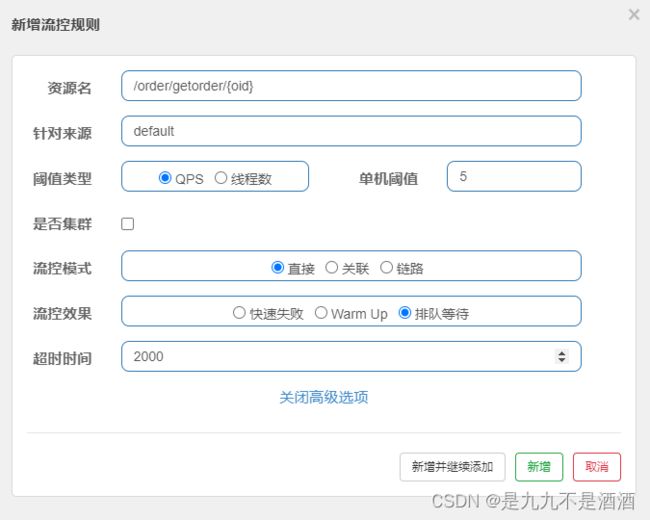
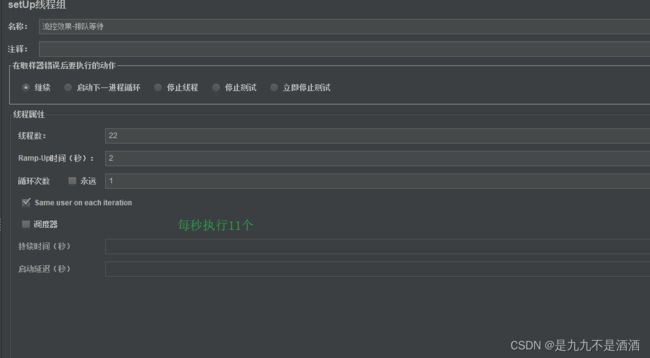
给/order/{orderId}这个资源设置限流,最大QPS为5,利用排队的流控效果,超时时长设置为2s
7.3.6.测试jmeter
我们在sentinel那边设置的每秒执行5个,然后我们又延迟了2秒,相当于2秒执行10次,我们在jmeter中设置的22次,会先执行sentinel10次,在加上jmeter中设置2秒,在执行10次,一共是20次,会有两个报错
7.3.7.流控效果有哪些?
快速失败:QPS超过阈值时,拒绝新的请求
warm up:QPS超过阈值时,拒绝新的请求;QPS阈值是逐渐提升的,可以避免冷启动时高并发导致服务宕机。
排队等待:请求会进入队列,按照阈值允许的时间间隔依次执行请求;如果请求预期等待时长大于超时时间,直接拒绝
8.热点规则
8.1.什么是热点参数限流
之前的限流是统计访问某个资源的所有请求,判断是否超过QPS阈值。而热点参数限流是分别统计参数值相同的请求,判断是否超过QPS阈值。
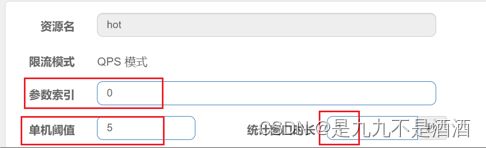
代表的含义是:对hot这个资源的0号参数(第一个参数)做统计,每1秒相同参数值的请求数不能超过5
在热点参数限流的高级选项中,可以对部分参数设置例外配置:
代表的含义:结合上一个配置,这里的含义是对0号的long类型参数限流,每1秒相同参数的QPS不能超过5,有两个例外:
如果参数值是100,则每1秒允许的QPS为10 如果参数值是101,则每1秒允许的QPS为15
8.2.热点参数限流的例子
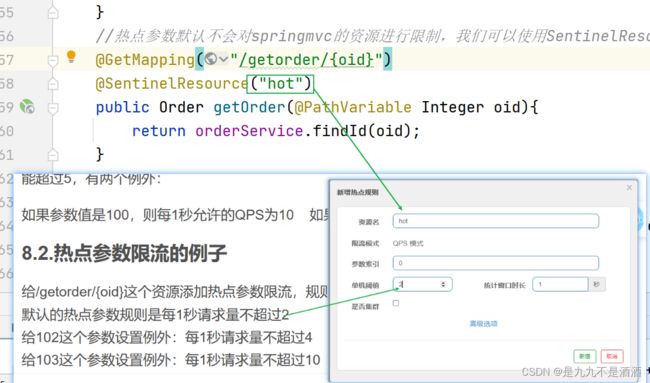
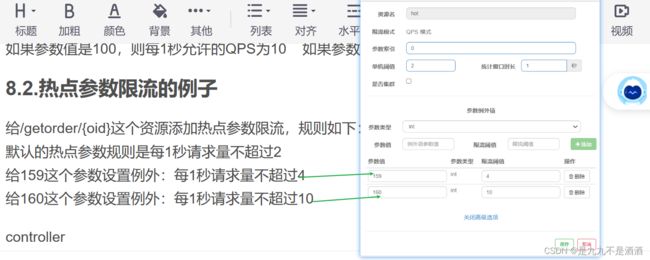
给/getorder/{oid}这个资源添加热点参数限流,规则如下:
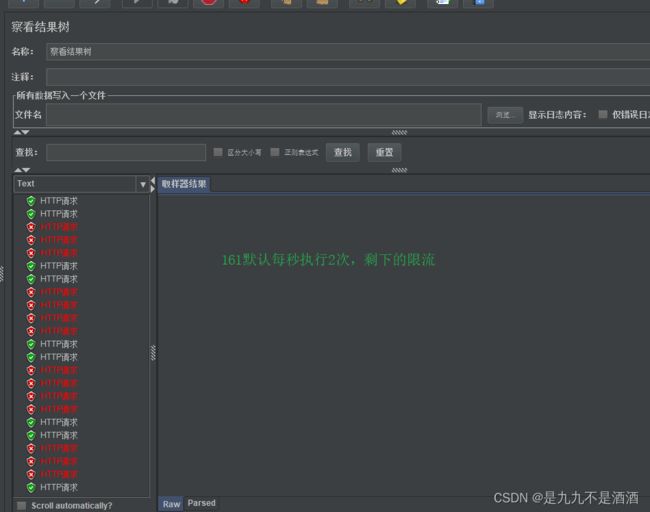
默认的热点参数规则是每1秒请求量不超过2
给159这个参数设置例外:每1秒请求量不超过4
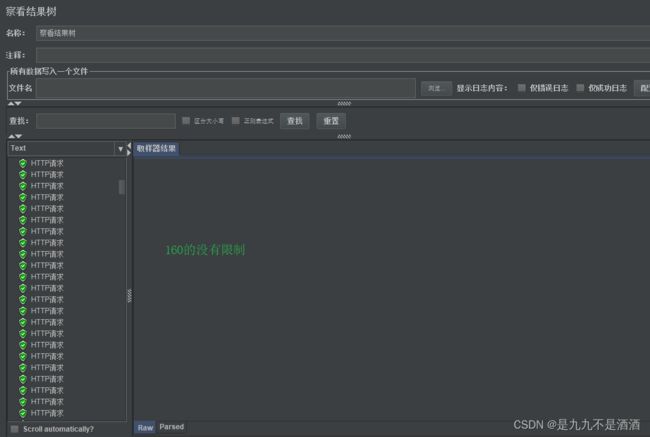
给160这个参数设置例外:每1秒请求量不超过10
controller
//热点参数默认不会对springmvc的资源进行限制,我们可以使用SentinelResource自定义资源
@GetMapping("/getorder/{oid}")
@SentinelResource("hot")
public Order getOrder(@PathVariable Integer oid){
return orderService.findId(oid);
}8.2.1.设置热点规则
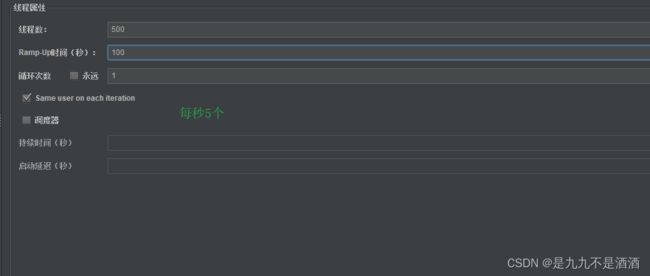
8.2.2.测试
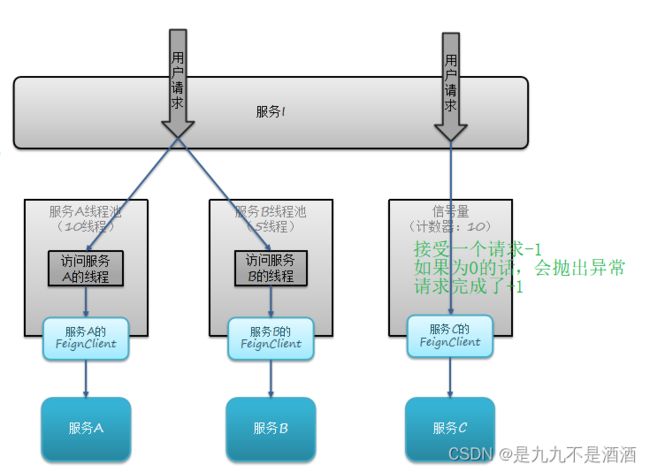
9.隔离和降级
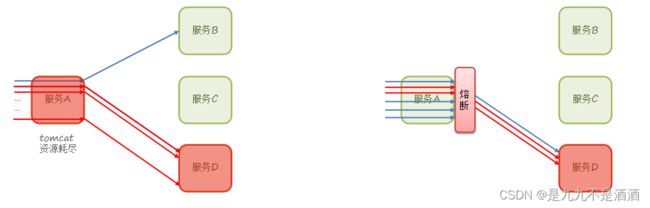
虽然限流可以尽量避免因高并发而引起的服务故障,但服务还会因为其它原因而故障。而要将这些故障控制在一定范围,避免雪崩,就要靠线程隔离(舱壁模式)和熔断降级手段了。
不管是线程隔离还是熔断降级,都是对客户端(调用方)的保护。
9.1.openFeign整合Sentinel
SpringCloud中,微服务调用都是通过openFeign来实现的,因此做客户端保护必须整合Feign和Sentinel。
9.1.1.修改OrderService的application文件,开启Feign的Sentinel功能
#开启feign和sentinel整合
feign.sentinel.enabled=true9.1.2.编写失败后的降级逻辑
方式一:FallbackClass,无法对远程调用的异常做处理
方式二:FallbackFactory,可以对远程调用的异常做处理,我们选择这种
//交于容器管理
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ProductFeignFactory implements FallbackFactory {
@Override
public FeignProduct create(Throwable throwable) {
//返回FeignProduct类型--接口new的话编程匿名内部类
FeignProduct feignProduct=new FeignProduct() {
@Override
public Product product(Integer pid) {
log.error("远程调用商品出现问题");
Product product=new Product();
product.setPname("服务器正忙,请稍后在访问");
return product;
}
};
return feignProduct;
}
}
修改被调用的接口
//调用微服务 (value="被调用的微服务的名称")
@FeignClient(value = "springCloud-product",fallbackFactory =ProductFeignFactory.class)9.2.线程隔离
9.2.1.线程隔离方式实现
线程池隔离
信号量隔离(Sentinel默认采用)
9.2.2. 线程池隔离与信号量隔离的区别
信号量隔离
优点: 轻量级,无额外开销
缺点: 不支持主动超时 不支持异步调用
使用场景: 高频调用 高扇出
线程池隔离
优点: 支持主动超时 支持异步调用
缺点: 线程的额外开销比较大
使用场景: 低扇出
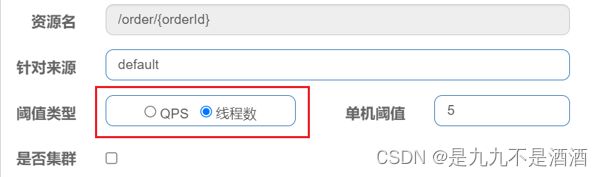
9.2.3.在添加限流规则时,可以选择两种阈值
QPS:就是每秒的请求数
线程数:是该资源能使用用的tomcat线程数的最大值。也就是通过限制线程数量,实现舱壁模式。
9.2.4.线程隔离(舱壁模式)的列子
9.3.熔断降级
熔断降级是解决雪崩问题的重要手段。其思路是由断路器统计服务调用的异常比例、慢请求比例,如果超出阈值则会熔断该服务。即拦截访问该服务的一切请求;而当服务恢复时,断路器会放行访问该服务的请求。
9.3.1.断路器熔断策略--慢调用
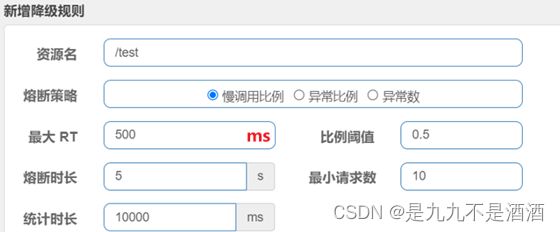
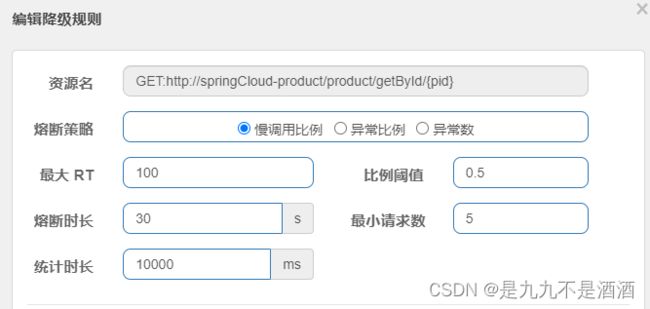
慢调用:业务的响应时长(RT)大于指定时长的请求认定为慢调用请求。在指定时间内,如果请求数量超过设定的最小数量,慢调用比例大于设定的阈值,则触发熔断。例如:
解读:RT超过500ms的调用是慢调用,统计最近10000ms内的请求,如果请求量超过10次,并且10次中慢调用比例不低于0.5,则触发熔断,熔断时长为5秒。然后进入half-open状态,放行一次请求做测试。
提示:为了触发慢调用规则,我们需要修改controller中的业务,增加业务耗时:
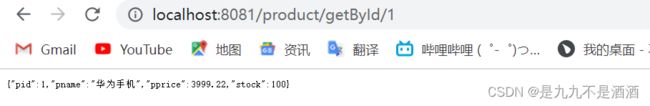
@GetMapping("/getById/{pid}")
public Product product(@PathVariable Integer pid){
if (pid == 1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return productService.findById(pid);
}下面是半开状态
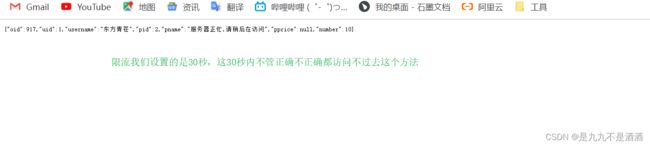
30秒之后--访问一个正确的--断路器关闭
30秒之后--访问一个错误的--断路器开启
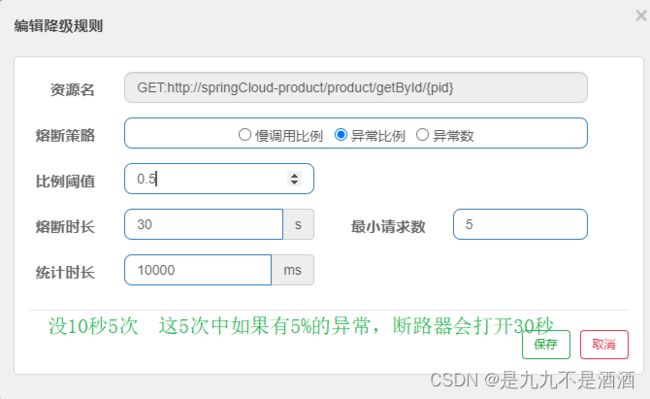
9.3.2.熔断策略-异常比例、异常数、
异常比例或异常数:统计指定时间内的调用,如果调用次数超过指定请求数,并且出现异常的比例达到设定的比例阈值(或超过指定异常数),则触发熔断。例如:
![]()
解读:统计最近1000ms内的请求,如果请求量超过10次,并且异常比例不低于0.5,则触发熔断,熔断时长为5秒。然后进入half-open状态,放行一次请求做测试。
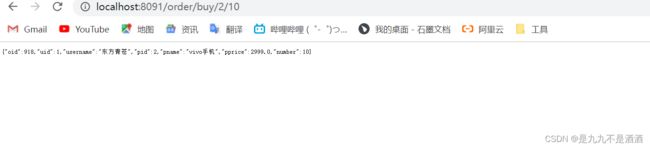
提示:为了触发异常统计,我们需要修改controller中的业务,抛出异常:
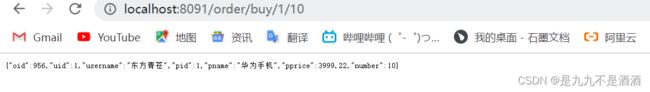
@GetMapping("/getById/{pid}")
public Product product(@PathVariable Integer pid){
if (pid == 1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
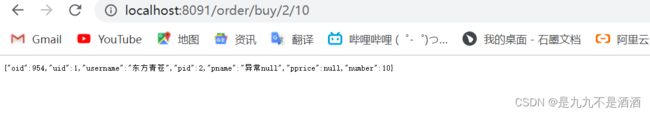
}else if (pid == 2) {
throw new RuntimeException("故意抛出异常");
}
return productService.findById(pid);
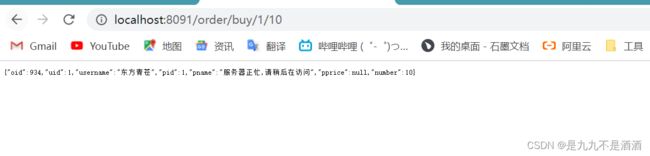
}30秒之后
9.3.3.Sentinel熔断降级的策略有哪些?
慢调用比例:超过指定时长的调用为慢调用,统计单位时长内慢调用的比例,超过阈值则熔断
异常比例:统计单位时长内异常调用的比例,超过阈值则熔断
异常数:统计单位时长内异常调用的次数,超过阈值则熔断
9.3.4.自定义异常
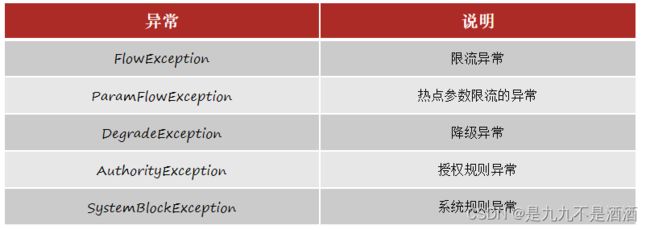
而BlockException包含很多个子类,分别对应不同的场景:
@Component
public class MyException implements BlockExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, BlockException e) throws Exception {
String msg = "未知异常";
int status = 429;
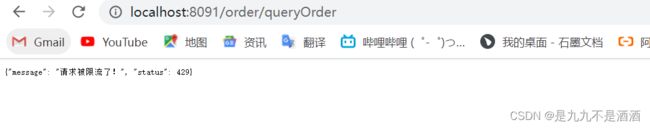
if (e instanceof FlowException) {
msg = "请求被限流了!";
} else if (e instanceof DegradeException) {
msg = "请求被降级了!";
} else if (e instanceof ParamFlowException) {
msg = "热点参数限流!";
} else if (e instanceof AuthorityException) {
msg = "请求没有权限!";
status = 401;
}
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setStatus(status);
httpServletResponse.getWriter().println("{\"message\": \"" + msg + "\", \"status\": " + status + "}");
}
}10.Sentinel规则持久化
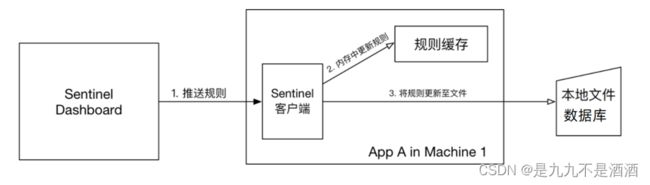
通过前面的讲解,我们已经知道,可以通过Dashboard来为每个Sentinel客户端设置各种各样的规则,但是这里有一个问题,就是这些规则默认是存放在内存中,极不稳定,所以需要将其持久化。本地文件数据源会定时轮询文件的变更,读取规则。这样我们既可以在应用本地直接修改文件来更新规则,也可以通过 Sentinel 控制台推送规则
10.1.Sentinel的控制台规则管理有三种模式
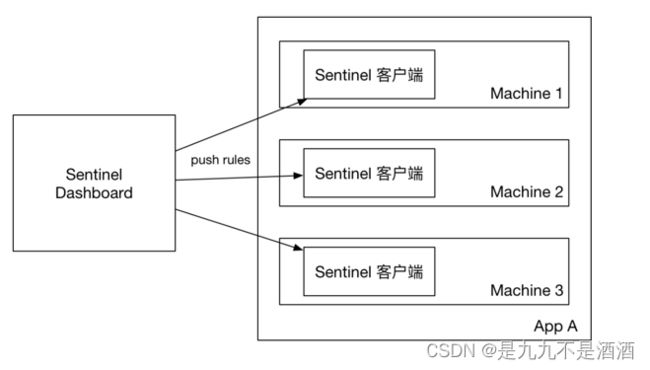
10.2.规则管理模式-原始模式
原始模式:控制台配置的规则直接推送到Sentinel客户端,也就是我们的应用。然后保存在内存中,服务重启则丢失
10.3.规则管理模式-pull模式
ull模式:控制台将配置的规则推送到Sentinel客户端,而客户端会将配置规则保存在本地文件或数据库中。以后会定时去本地文件或数据库中查询,更新本地规则。
10.4.规则管理模式-push模式
push模式:控制台将配置规则推送到远程配置中心,例如Nacos。Sentinel客户端监听Nacos,获取配置变更的推送消息,完成本地配置更新。
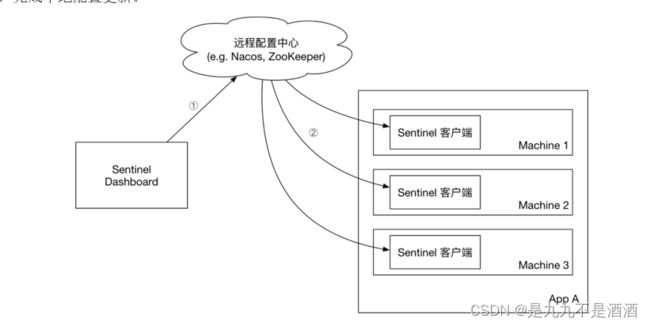 10.5. 实现pull模式
10.5. 实现pull模式
10.5.1.编写配置类
package com.ykq.config;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.*;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List
public class FilePersistence implements InitFunc {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String appcationName;
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
String ruleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + "/sentinel-rules/" + appcationName;
String flowRulePath = ruleDir + "/flow-rule.json";
String degradeRulePath = ruleDir + "/degrade-rule.json";
String systemRulePath = ruleDir + "/system-rule.json";
String authorityRulePath = ruleDir + "/authority-rule.json";
String paramFlowRulePath = ruleDir + "/param-flow-rule.json";
this.mkdirIfNotExits(ruleDir);
this.createFileIfNotExits(flowRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(degradeRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(systemRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(authorityRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(paramFlowRulePath);
// 流控规则
ReadableDataSource> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
flowRuleListParser
);
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS);
// 降级规则
ReadableDataSource> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
degradeRuleListParser
);
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS);
// 系统规则
ReadableDataSource> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
systemRuleListParser
);
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS);
// 授权规则
ReadableDataSource> authorityRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
authorityRuleListParser
);
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> authorityRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authorityRuleWDS);
// 热点参数规则
ReadableDataSource> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
paramFlowRuleListParser
);
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS);
}
private Converter> flowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> degradeRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> systemRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> authorityRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private Converter> paramFlowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference>() {
}
);
private void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
private void createFileIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
}
private String encodeJson(T t) {
return JSON.toJSONString(t);
}
}
10.5.2.添加配置
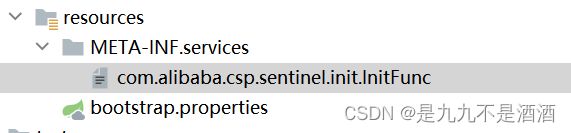
在resources下创建配置目录 META-INF
![]()
在META-INF文件中闯将services文件
然后添加文件com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc
然后添加配置文件中添加内容
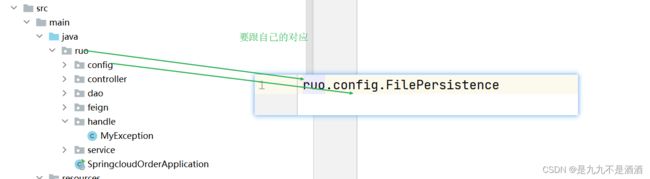
ruo.config.FilePersistence
10.5.3.运行
设置限流
![]()