卷积神经网络(CNN)实现MNIST手写数字识别
目录
- 准备阶段
-
- 1.设置GPU(没有GPU可跳过)
- 2.数据准备(使用mnist数据集)
- 3.归一化
- 4.图片可视化
- 5.更改图片格式
-
-
- 构建CNN网络模型
- 编译模型
- 训练模型
- 预测
准备阶段
编译器:jupyter notebook
深度学习环境:tensorflow2
1.设置GPU(没有GPU可跳过)
import tensorflow as tf
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
if gpus:
gpu0 = gpus[0] #如果有多个GPU,仅使用第0个GPU
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu0, True) #设置GPU显存用量按需使用
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpu0],"GPU")
2.数据准备(使用mnist数据集)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, models
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入mnist数据,依次分别为训练集图片、训练集标签、测试集图片、测试集标签
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
3.归一化
# 将像素的值标准化至0到1的区间内。(对于灰度图片来说,每个像素最大值是255,每个像素最小值是0,也就是直接除以255就可以完成归一化。)
train_images, test_images = train_images / 255.0, test_images / 255.0
# 查看数据维数信息
train_images.shape,test_images.shape,train_labels.shape,test_labels.shape
"""
输出:((60000, 28, 28), (10000, 28, 28), (60000,), (10000,))
"""
4.图片可视化
# 将数据集前20个图片数据可视化显示
# 进行图像大小为20宽、10长的绘图(单位为英寸inch)
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
# 遍历MNIST数据集下标数值0~49
for i in range(20):
# 将整个figure分成5行10列,绘制第i+1个子图。
plt.subplot(2,10,i+1)
# 设置不显示x轴刻度
plt.xticks([])
# 设置不显示y轴刻度
plt.yticks([])
# 设置不显示子图网格线
plt.grid(False)
# 图像展示,cmap为颜色图谱,"plt.cm.binary"为matplotlib.cm中的色表
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
# 设置x轴标签显示为图片对应的数字
plt.xlabel(train_labels[i])
# 显示图片
plt.show()
5.更改图片格式
#调整数据到我们需要的格式
train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1))
test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1))
train_images.shape,test_images.shape,train_labels.shape,test_labels.shape
"""
输出:((60000, 28, 28, 1), (10000, 28, 28, 1), (60000,), (10000,))
"""
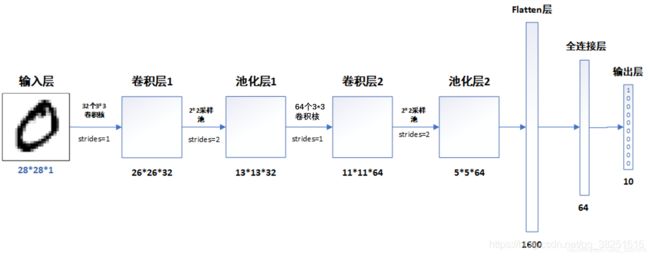
构建CNN网络模型
# 创建并设置卷积神经网络
# 卷积层:通过卷积操作对输入图像进行降维和特征抽取
# 池化层:是一种非线性形式的下采样。主要用于特征降维,压缩数据和参数的数量,减小过拟合,同时提高模型的鲁棒性。
# 全连接层:在经过几个卷积和池化层之后,神经网络中的高级推理通过全连接层来完成。
model = models.Sequential([
# 设置二维卷积层1,设置32个3*3卷积核,activation参数将激活函数设置为ReLu函数,input_shape参数将图层的输入形状设置为(28, 28, 1)
# ReLu函数作为激活励函数可以增强判定函数和整个神经网络的非线性特性,而本身并不会改变卷积层
# 相比其它函数来说,ReLU函数更受青睐,这是因为它可以将神经网络的训练速度提升数倍,而并不会对模型的泛化准确度造成显著影响。
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
#池化层1,2*2采样
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
# 设置二维卷积层2,设置64个3*3卷积核,activation参数将激活函数设置为ReLu函数
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'),
#池化层2,2*2采样
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
layers.Flatten(), #Flatten层,连接卷积层与全连接层
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'), #全连接层,特征进一步提取,64为输出空间的维数,activation参数将激活函数设置为ReLu函数
layers.Dense(10) #输出层,输出预期结果,10为输出空间的维数
])
# 打印网络结构
model.summary()
编译模型
"""
这里设置优化器、损失函数以及metrics
"""
# model.compile()方法用于在配置训练方法时,告知训练时用的优化器、损失函数和准确率评测标准
model.compile(
# 设置优化器为Adam优化器
optimizer='adam',
# 设置损失函数为交叉熵损失函数(tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy())
# from_logits为True时,会将y_pred转化为概率(用softmax),否则不进行转换,通常情况下用True结果更稳定
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
# 设置性能指标列表,将在模型训练时监控列表中的指标
metrics=['accuracy'])
训练模型
"""
这里设置输入训练数据集(图片及标签)、验证数据集(图片及标签)以及迭代次数epochs
"""
history = model.fit(
# 输入训练集图片
train_images,
# 输入训练集标签
train_labels,
# 设置10个epoch,每一个epoch都将会把所有的数据输入模型完成一次训练。
epochs=10,
# 设置验证集
validation_data=(test_images, test_labels))
预测
输入一张图片,将会得到一组数,这组代表这张图片上的数字为0~9中每一个数字的几率,out数字越大可能性越大。
- 输入层:用于将数据输入到训练网络
- 卷积层:使用卷积核提取图片特征
- 池化层:进行下采样,用更高层的抽象表示图像特征
- Flatten层:将多维的输入一维化,常用在卷积层到全连接层的过渡
- 全连接层:起到“特征提取器”的作用
- 输出层:输出结果
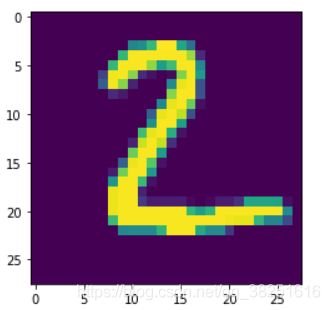
plt.imshow(test_images[1])
pre = model.predict(test_images) # 对所有测试图片进行预测
pre[1] # 输出第一张图片的预测结果