中南林业科技大学Java实验报告十:常用实用类
文章目录
- 实验10 常用实用类
-
- 10.1 实验目的
- 10.2 实验内容
-
- 10.2.1 编写一个正则表达式,自己定义一个String类型的字符验证是否满足该正则表达式。(比如可以验证字符串是否以a开头,以b结尾的字符串,其正则表达式为:regx=a.*b)
- 10.2.2 利用Pattern类和Matcher类以及其类中的方法,统计字符串str1,在str2中出现的次数。
- 10.2.3 编写一个计算纪念日提醒的Java程序,具有倒计时功能,以及到期提醒功能(如离某某人生日还有多少天,今天是某某人生日),以及距离某一个日期已经多少天,多少小时等(如已经进入中南林业科技大学2年X月X天,注意:最少精确到天)。
- 10.2.4 新建一个Student类,属性为姓名,年龄,学号,声明一个Student的对象数组,分别按照年龄和学号进行排序并输出结果。
实验10 常用实用类
10.1 实验目的
- 理解String类的特性,熟练掌握String类的常用方法。
- 掌握正则表达式的使用方法。
- 能用日期类创建对象,熟练掌握日期类的常用方法。
- Arrays类的常用方法使用。
10.2 实验内容
10.2.1 编写一个正则表达式,自己定义一个String类型的字符验证是否满足该正则表达式。(比如可以验证字符串是否以a开头,以b结尾的字符串,其正则表达式为:regx=a.*b)
【前提引入】
1️⃣ 字符匹配符 —— “ . ”
| 符号 | 名称 | 示例 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | 匹配出\n以外的任何字符 | a…b | 以a开头,b结尾,中间包括2个任意字符的长度为4的字符串 |
| [] | 可接收的字符列表 | [efgh] | 是 e、f、g、h 中的任意一个字符 |
2️⃣ 选择匹配符 —— " * "
| 符号 | 名称 | 示例 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| * | 指定字符重复0次或多次 | (abc)* | 仅包含任意个 abc 的字符串出现0或多次 |
| + | 指定字符重复1次或多次 | m+abc | 以至少一个m开头后接abc |
3️⃣ 定位符
| 符号 | 名称 | 示例 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ^ | 指定起始开始字符 | ^a+[a-z]$ | 以至少一个a开头,后接任意个小写字母的字符串 |
| $ | 指定结束字符 | ^[0-9]+c$ | 以至少一个数字开头,后接字母c结尾的字符串 |
那怎样写以 a 开头,以 b 结尾的字符串呢?
- 以a开头:
^a - 以b结尾:
b$ - 中间字符串任意对应
.,有或没有都可以 对应*,因此组合起来是:.*
所以组合起来就是:^a.*b$
3️⃣ String类中具有判断功能的 matches 方法
解读:public boolean matches(String regex)
该方法是进行整体匹配,相当自带 ^ 和 $
既然自带了,那么以a开头,以b结尾的字符串就可以由原来的 ^a.*b$ 写为 a.*b
当然,如果你写的是 matches(“^a.*b$”) 这也是对的,完全等价于 matches(“a.*b”)。
【核心代码】
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RegxTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描器对象
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//通过键盘输入字符串
String str = scanner.next();
//进行正则匹配,调用 matches 方法
if(str.matches("a.*b")){
System.out.println("匹配成功");
}else{
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
}
【运行流程】
10.2.2 利用Pattern类和Matcher类以及其类中的方法,统计字符串str1,在str2中出现的次数。
【前提引入】
1️⃣ Pattern类
Pattern类对象是一个正则表达式对象。Pattern类没有公共的构造的方法:
因此要创建一个 Pattern 类对象,需要调用其公共的静态方法compile,它会返回一个Pattern对象。该方法接收一个正则表达式作为它的第一个参数,看下该方法的源码:
/**
* Compiles the given regular expression into a pattern.
*
* @param regex
* The expression to be compiled
* @return the given regular expression compiled into a pattern
* @throws PatternSyntaxException
* If the expression's syntax is invalid
*/
public static Pattern compile(String regex) {
return new Pattern(regex, 0);
}
2️⃣ Matcher类
Matcher类对象是对输入字符串进行解释和匹配的引擎。与Pattern类一样,Matcher也没有公共的构造方法,需要调用Pattern对象的matcher方法来获得一个Matcher对象。
/*
input:要匹配的字符序列
*/
public Matcher matcher(CharSequence input) {
if (!compiled) {
synchronized(this) {
if (!compiled)
compile();
}
}
Matcher m = new Matcher(this, input);
return m;
}
一个常用方法:
public boolean find():部分匹配,找到一个匹配的子串,则返回true,并将定位移动到下次匹配的位置。
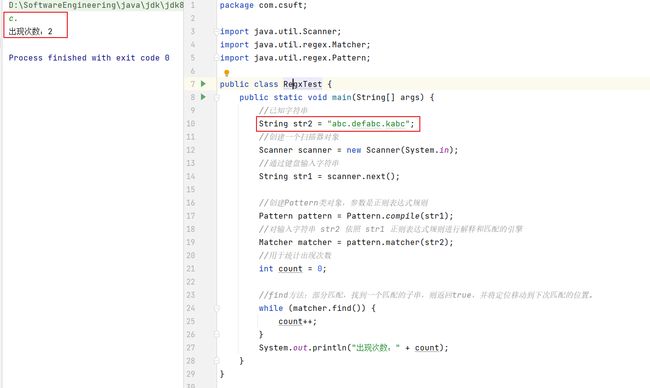
【核心代码】
public class RegxTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//已知字符串
String str2 = "abc.defabc.kabc";
//创建一个扫描器对象
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//通过键盘输入字符串
String str1 = scanner.next();
//创建Pattern类对象,参数是正则表达式规则
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(str1);
//对输入字符串 str2 依照 str1 正则表达式规则进行解释和匹配的引擎
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str2);
//用于统计出现次数
int count = 0;
//find方法:部分匹配,找到一个匹配的子串,则返回true,并将定位移动到下次匹配的位置。
while (matcher.find()) {
count++;
}
System.out.println("出现次数:" + count);
}
}
【运行流程】
10.2.3 编写一个计算纪念日提醒的Java程序,具有倒计时功能,以及到期提醒功能(如离某某人生日还有多少天,今天是某某人生日),以及距离某一个日期已经多少天,多少小时等(如已经进入中南林业科技大学2年X月X天,注意:最少精确到天)。
【前提引入】
| 所在类 | 是否静态方法 | 方法 | 返回值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LocalDate | 静态 | now() | LocalDate | 获取当前时间LocalDate对象,包括年月日 |
| LocalDate | 静态 | getYear() | int | 获取对象的年份 |
| LocalDate | 静态 | parse(String dateStr) | LocalDate | 将一个日期字符串dateStr解析转为LocalDate对象 |
| LocalDate | 非静态 | isBefore(LocalDate localDate) | boolean | 判断对象时间是否在localDate时间之前 |
| LocalDate | 非静态 | isAfter(LocalDate localDate) | boolean | 判断对象时间是否在localDate时间之后 |
| LocalDate | 非静态 | until(LocalDate localDate,ChronoUnit.DAYS) | long | 返回locaDate与对象天数差 |
| LocalDate | 静态 | Period.between(start, end) | Period | 两个时间相差的年月日Period对象 |
| Period | 非静态 | getYears | int | period对象存储的年份 |
| Period | 非静态 | getMonths | int | period对象存储的月份 |
| Period | 非静态 | getDays | int | period对象存储的天数 |
【核心代码】
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
public class DateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//得到当前时间(年月日)
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
//定义某人生日时间
String birthday = "11-05";
//获取当前年份
int nowYear = now.getYear();
//获取今年的生日时间
LocalDate birthdayDate1 = LocalDate.parse(nowYear + "-" + birthday);
//如果当前时间在今年生日时间之前
if (now.isBefore(birthdayDate1)) {
//那么可以直接计算时间差
System.out.println("距离生日还有:" + now.until(birthdayDate1, ChronoUnit.DAYS));
} else if (now.isAfter(birthdayDate1)) {
//如果当前时间在今年生日时间之后,说明生日已过,那么计算距离明年生日的天数
//获取明年的生日时间
LocalDate birthdayDate2 = LocalDate.parse(nowYear + 1 + "-" + birthday);
//计算天数差
System.out.println("距离生日还有:" + now.until(birthdayDate2, ChronoUnit.DAYS));
}else{
//说明恰好是今天
System.out.println("今天是雨浪的生日");
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------");
//定义进校时间
LocalDate intoSchoolDate = LocalDate.parse("2021-09-10");
//得到现在与进校时间的时间差:年、月、日
Period period = Period.between(intoSchoolDate, now);
//输出时间差
System.out.println("现在与进校时间相差:" + period.getYears() + " 年 " +
period.getMonths() + " 月 " + period.getDays() + " 日");
}
}
【运行流程】
10.2.4 新建一个Student类,属性为姓名,年龄,学号,声明一个Student的对象数组,分别按照年龄和学号进行排序并输出结果。
【前提引入】
Arrays类:包含了一系列的静态方法,用于管理或操作数组(比如排序和搜索)
Arrays.sort方法:因为数组是引用类型,所以通过 sort 排序后会直接影响到数组本身。sort是重载的,也可以通过传入一个接口 Comparator 实现定制排序规则,调用定制排序时,传入两个参数:
-
排序的数组arr
-
实现了Comparator接口的匿名内部类,要求重写compare方法,通过返回值的正负情况决定了排序规则。
这充分体现了 接口编程 + 动态绑定 + 匿名内部类 的综合使用。
这里我们通过一个简单模拟来该方法的实现(对于理解Arrays的sort方法很重要):
public class ArraysTest {
/**
* 使用 冒泡排序 + 匿名内部类 来简单模拟 Arrays.sort 方法的实现
* 也就是说,我们在这里自定义一个sort方法
*
* @param arr 待排序的数组
* @param c 实现Comparator接口的类 对象
*/
public static void sort(int[] arr, Comparator c) {
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
//数组排序由 c.compare(arr[j], arr[j + 1])返回的值决定
//如果返回正数则进行交换,否则不交换
if (c.compare(arr[j], arr[j + 1]) > 0) {
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5,3,2,8,7};
//从小到大排序
sort(arr,new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
//value1 代表 arr[j] 的值
int value1 = (Integer)o1;
//value2 代表 arr[j+1] 的值
int value2 = (Integer)o2;
//如果返回正数,即arr[j]比arr[j+1]大时,在sort方法中会将这两个位置上的值进行交换
//则说明了我们指定的是从小到大进行排序
return value1-value2;
}
});
//使用 Arrays.toString方法 打印数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
【核心代码】
-
Student类(为了演示方便,这里把属性的修饰符定为 public )
package com.csuft; public class Student { public String name; public int age; public int studentId; public Student(String name, int age, int studentId) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.studentId = studentId; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", studentId=" + studentId + '}'; } } -
ArraysTest类
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class ArraysTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Student[] students = new Student[] { new Student("雨浪",18,20212819), new Student("夜莺",16,20212850), new Student("狐狸半面添",17,20212880) }; System.out.println("-------------依照年龄对数组进行 升序 排序------------"); Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return o1.age-o2.age; } }); for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student); } System.out.println("-------------依照学号对数组进行 降序 排序------------"); Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return o2.studentId-o1.studentId; } }); for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student); } } }
【运行流程】