SpringBoot
SpringBoot
SpringBoot介绍
1.SpringBoot是Spring的全家桶,SpringBoot是用来简便Spring应用开发的,约定大于配置,去繁从简,just run就能创建一个独立的,产品级别的应用
2.背景:J2EE笨重的开发、繁多的配置、低下的开发效率、复杂的部署流程、第三方技术集成难度大,所以现在程序员都是用SpringBoot开发,简化了很多很多步骤,和配置文件和依赖
3.优点
快速搭建项目,简化spring开发
内嵌了tomcat服务器,无序程序员手动部署
自定义启动器,完成自动装配
大量的自动配置
无xml配置文件,使用yaml格式的文件处理效果好
SpringBoot入门程序
创建一个SpringBoot工程
1.创建maven工程,勾选webapp骨架
2.导入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
3.编写主类
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloSpringBootApplicatio(){
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(HelloSpringBootApplication,args);
}
}
4.运行,通过浏览器测试
使用IDEA创建SpringBoot工程
1.勾选想要的模块
2.手动创建源码文件夹、配置文件夹、测试类文件夹
SpringBoot加载原理
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootTest{
public static void main (String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTest.class,args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication是一个主启动类注解:
1.@SpringBootConfiguration配置类
1.1@Configuration用这个注解修饰的类是SpringBoot的配置类
2.@EnableAutoConfiguration
2.1@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({Register.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage{
String[] basePackages()default{}; //这代表了当前主启动类下面的子包都会被扫描,主类必须高于所有子包一级
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() defalut{};}
2.2@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)}导入了一个自动配置选择器
2.2.1AutoConfigurationImportSelector
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> getAutoConfigurationImportFilters() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportFilter.class, this.beanClassLoader);
}
//这个类下的属性FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION的值就是你当前需要加载的类
public final class SpringFactoriesLoader{
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
}
//这个文件位置:
E:\mavenlocal\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-autoconfigure\2.6.1\spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.6.1.jar!\META-INF\spring.factories
这个文件中有很多类,以下只是一小部分:
webMvc的自动装配,这个类中实例化处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器不需要手动配置类,自动配置org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.webMvcAutoConfiguration
如果后期我们要拓展一个 interceptor,那我们就要拓展这个类,在这个类的基础上继续添加内容。
字符集的自动配置,在之前Springmvc时候需要在web.xml中配置字符集过滤器,现在不用了,org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "server.servlet.encoding",
value = {"enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
private final Encoding properties;
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties.getServlet().getEncoding();
}
}
ServerProperties:这个类就是springboot默认的配置参数,自动装配默认参数
@ConfigurationProperties( 这个注解修饰的类可以将配置文件的内容直接赋值给类的属性
prefix = "server",
ignoreUnknownFields = true
)
public class ServerProperties {
private Integer port;
private InetAddress address;
}
这个类是SpringMVC的前台控制器,无需配置在web.xml中了,SpringBoot已经帮助我们配置好了 org.springframework.boot.autocconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
3.@ComponentScan 扫描器
SpringBoot的依赖传递
我们在开发时需要导入这个依赖,这个依赖下有子依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.6.1version>
<relativePath/>
parent>
子依赖,这个依赖下包含了所有SpringBoot默认的依赖,如果不够用,再自行导入
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>2.6.1version>
parent>
这些starters几乎涵盖了javaee所有常用场景,SpringBoot对这些场景依赖的jar也做了严格的测试与版本控制,我们不必担心jar版本合适度问题
SpringBoot的配置文件
SpringBoot支持两种全局配置文件:功能是一模一样的,就是写法不同,可视化不同
1.application.properties(默认的)
server.port=8081
server.address=192.168.200.128
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/haha
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter.enabled=true
2.aplication.yaml(新格式)yml格式的缩进必须加空格
#配置tomcat服务器的端口号
server:
port: 8081 #这个必须加空格
#配置 springmvc的 RESTful 风格的请求方式
#spring:
# mvc:
# hiddenmethod:
# filter:
# enabled: true
3.配置好后,运行springboot:
2021-12-02 14:47:20.176 INFO 9100 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8081 (http) with context path ''
2021-12-02 14:47:20.204 INFO 9100 --- [ main] com.oracle.Springboot02Application : Started Springboot02Application in 5.62 seconds (JVM running for 11.552)
YAML的语法结构
1.YAML基本语法
- 使用缩进表示
- 缩进时不允许使用tab键,只允许使用空格
- 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
- 大小写敏感
例如:
spring:
#配置数据库连接参数
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306?mysql?characterEncoding=UTF8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
Person.java
package com.oracle.pojo;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.*;
/**
* spring的依赖注入有几种方式?
* 1.构造器注入
* 2.setter 方法注入
* 3.p命名空间注入
* 4.c命名空间注入
*/
@Component //将Person 加载到Ioc容器中
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "person"
)
public class Person {
private Integer pid;
public Integer getPid() {
return pid;
}
public void setPid(Integer pid) {
this.pid = pid;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"pid=" + pid +
'}';
}
}
application.yml:
person:
pid: 1
lastName: "admin"
age: 23
address: 哈尔滨
birth: 1999/09/08
pet:
name: 大黄
age: 2
hobbys:
- 篮球
- 羽毛球
- 台球
list:
- 李四
- 王五
set: [1,2,3,4,5,56]
map: {1: v1,2: v2}
单元测试:
@SpringBootTest
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02ApplicationTests {
//自动注入Person实体,直接输出person对象,会在控制台上打印Person的toString方法
//你会观察到,配置文件中的数据,赋值到了Person对象的属性中
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
Pet pet = person.getPet();
System.out.println(pet);
}
}
运行结果:
Person{pid=1, lastName='admin', age=23, address='哈尔滨', birth=Wed Sep 08 00:00:00 CST 1999, hobbys=[篮球, 羽毛球, 台球], list=[李四, 王五], set=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 56], map={1=v1, 2=v2}}
Pet{name='大黄', age=2}
总结:application.yml,application.properties都是通过属性的setter方法给实体赋值的;给实体类赋值的话,要在实体类上面加上@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person“)注解。要是给单个属性赋值用@Value。
@Value和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
| @ConfigurationProperties | @Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件中的值给实体的属性 | 一个一个的指定 |
| 松散绑定(松散语法) | 支持 | 支持 |
| SpEL表达式(Spring Expression Language) | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR303数据校验 就是一批注解 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂数据类型,List,Set,Pet, Map | 支持 | 不支持 |
@Component //将当前的Person类放到spring的Ioc容器
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "person"
)
@Validated
public class Person {
//@Value("${person.pid}")
private Integer pid;
//@Value("${person.last-name}")
private String lastName;
//@Value("#{2*4}")
private Integer age;
@Email //JSR303 数据校验
private String email; //必须是邮箱格式
}
@PropertySource注解:这个注解的作用是用来加载指定配置文件的,但是application.yml优先级高
只支持xxx.properties文件,不支持person.yml文件(无效)
@PropertySource(Value= {"classpath:person.properties"})//只针对xxx.properties文件有效
public class Person{
}
@ImportResource:默认情况下SpringBoot是没有xml配置文件的,但是他可以引入那个需要这个注解
@ImportResource(location = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
public class Person{}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.oracle.serviceImpl.UserServiceImpl">bean>
beans>
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserServiceImpl userService;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
userService.login();
}
}
SpringBoot默认是不推荐使用xml格式添加需求的,他推荐你使用给容器添加组件的方式添加功能,其实就是全注解形式
1.编写配置类@Configuration—>替换Spring的beans.xml配置文件
2.使用@Bean注解给容器添加组件
@Configuration //替换spring的beans.xml配置文件吗
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public UserServiceImpl userService(){
System.out.println("配置类@Bean给容器添加了自定义的组件~~~");
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
//如果springboot需要整合持久层框架,需要用到数据源的化,通过@Bean形式添加进去即可
@Bean
public DruidDataSource dataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
运行结果:
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v2.6.1)
2021-12-03 10:41:34.085 INFO 1056 --- [ main] c.o.SpringbootConfigApplicationTests : Starting SpringbootConfigApplicationTests using Java 1.8.0_77 on DESKTOP-AF2G3H5 with PID 1056 (started by If_You in C:\Users\GaoYuanze\IdeaProjects\springboot_config)
2021-12-03 10:41:34.087 INFO 1056 --- [ main] c.o.SpringbootConfigApplicationTests : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
****配置类@Bean给容器添加了自定义的组件~~~**** 这里说明了我们springboot容器启动时就直接加载了
2021-12-03 10:41:36.225 INFO 1056 --- [ main] c.o.SpringbootConfigApplicationTests : Started SpringbootConfigApplicationTests in 3.293 seconds (JVM running for 6.937)
Person{pid=1, lastName='Tom', age=23, address='±³¾°', birth=null, email='null', hobbys=null, list=null, set=null, map=null}
我是登录方法
配置文件的占位符
1.随机数:SpringBoot配置文件中支持随机数
${random.uuid} ,${random.int(10)} 10以内的随机数
${random.long}
person:
pid: 1
last-name: admin${random.uuid}
age: ${random.int(11)}
SpringBoot多文件配置profies
SpringBoot支持在不同场景下加载不同的配置文件,从而达到最终的效果,有开发模式、测试模式(对程序的要求极其严格)、上线模式。
编写配置文件格式,命名方式为:application-自定义.properties/yaml,其中一定要含有一个住配置文件
1.例如:
properites格式
application-dev.properties 开发模式
application-test.properties 测试模式
application-run.properties; 上线模式
spring.profiles.active=dev 激活需要指定的配置文件即可 ,激活开发模式的配置文件
2.yml格式
#第一行相当于主配置文件
#默认是8080
server:
port: 8080
spring:
prfiles:
active: dev #主配置文件激活想要激活的环境配置文件
---
server:
port: 8081
#开发环境
spring:
profiles: dev #定义为那个环境的配置
---
server:
port: 8082
# 测试环境
spring:
profiles: test #定义为哪个环境 ,测试环境
多文件所在的位置
SpringBoot在启动时会扫描以下位置的application.properties文件或application.yml的文件作为SpringBoot的默认配置文件
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener implements EnvironmentPostProcessor , SmartApplicationListener ,Ordered{
private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS="classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";
}
-file:./config/
-file:./
-classpath:./config/
-classpath:./
以上就是SpringBoot配置文件优先级加载顺序,从高到低,优先级高的会覆盖优先级低的配置
SpringBoot整合Web
web资源是SpringBoot自动整合,因为他是自动装配,就是SpringBoot自动配置的jar包中的spring.factories文件中配置了WebMvcAutoConfiguration,其中jar包中xxxAutoConfiguration就是帮助我们向容器中添加组件
处理器映射器:
@Bean
@Primary
public ReqeustMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping(@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager, @Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService, @Qualifier("mvcResourceUrlProvider") ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider){
return super.requestMappingHandlerMapping(contentNegotiationManager, conversionService, resourceUrlProvider);}
处理器适配器:
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter requestMappingHandlerAdapter(@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager, @Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService, @Qualifier("mvcValidator") Validator validator) {
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter adapter = super.requestMappingHandlerAdapter(contentNegotiationManager, conversionService, validator);
adapter.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.mvcProperties == null || this.mvcProperties.isIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect());
return adapter;
}
视图解析器:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public InternalResourceViewResolver defaultViewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getPrefix());
resolver.setSuffix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getSuffix());
return resolver;
}
一上类使用@Bean注解,将各个类添加到spring的Ioc容器中
|—EnableWebMvcConfiguration 开启mvc的配置文件 静态内部类
|—WebMvcProperties::日期格式化 xxxProperties这个类是为了封装配置文件的内容
|-- WebProPerties: xxxProperties这个类是为了封装配置文件的内容
|–Resources
public static class Resources {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS =
new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/","classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
创建SpringBoot的Web项目
一、创建工程是需要选中的依赖
1.devTools开发工具
2.congfiguration-process
3.springWeb
4.Thymeleaf
二、导入静态资源
css,js,jquert内容存放在static文件夹下,html页面放在template
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ThymeleafProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnClass({TemplateMode.class, SpringTemplateEngine.class})
@AutoConfigureAfter({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class})
public class ThymeleafAutoConfiguration {
public ThymeleafAutoConfiguration() {
}
}
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/";
private String suffix = ".html";
}
SpringBoot多静态资源的映射规则
1.默认情况下加载本地文件,就是static文件夹下的
2.SpringBoot支持webjars映射,这是WebMvcAutoConfiguration类
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
this.addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
this.addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (this.servletContext != null) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, "/");
registration.addResourceLocations(new Resource[]{resource});
}
});
}
}
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjarsgroupId>
<artifactId>jqueryartifactId>
<version>3.4.1version>
dependency>
index.html
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="author" content="">
<title>Signin Template for Bootstraptitle>
<link href="@{asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="@{webjars\jquery\3.4.1\jquery.js}" rel="stylesheet">
head>
Thymeleaf模板引擎
jsp(java Server Pag)Java服务页面,属于动态页面,通过EL表达式,JSTL标签库从后台获取数据值,但是SpringBoot不推荐使用jsp,因为性能不是很好,加载速度慢,每次加载页面都需要重新渲染,但是模板引擎不用。
模板引擎种类:
JSP,Velocity(Apache研发),Freemarker(个人研发),Thymeleaf(SpringBoot推荐)
1.引入Thymeleaf依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
2.在HTML页面中引入头信息
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
......
html>
3.Thymeleaf语法:表达式写法
@{ } 超链接,或者跳转路径
${ } 获取变量的,无论是文本变量还是对象变量${user.nalme}
*{ } 当前对象,变量属性 可以省略对象*{uname
#{ } 国际话内容
~{ }片段引入,页面布局
UserController
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(Model model){
User user = new User();
user.setUid(1);
user.setUname("Tom");
user.setPassword("123");
user.setAge(23);
user.setAddress("哈尔滨");
user.setGender(0);
model.addAttribute("user",user);
model.addAttribute("uname","admin");
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(new User(1,"张三","123"));
list.add(new User(2,"李四","123"));
list.add(new User(3,"王五","123"));
list.add(new User(4,"赵六","123"));
list.add(new User(5,"王二麻子","123"));
list.add(new User(6,"刘备","123"));
model.addAttribute("users",list);
return "test";
}
}
test.html:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
获取文本: <div th:text="${uname}">div>
<br/>
获取对象: <div th:object="${user}">
用户编号:
<div>[[${user.uid}]]div>
地址:
<div th:text="*{address}">div>
姓名:
<div>[[${user.uname}]]div>
年龄:
<div th:text="${user.age}">div>
性别: <div th:if="${user.gender} == 1">男div>
<div th:if="${user.gender} == 0">女div>
div>
<br/>
<a th:href="@{/index}">跳转登录页面a>
<br/>
遍历的集合List:
<table>
<tr>
<th>用户idth>
<th>用户姓名th>
<th>用户密码th>
tr>
<tr th:each="user : ${users}">
<td th:text="${user.uid}">td>
<td th:text="${user.uname}">td>
<td th:text="${user.password}">td>
tr>
table>
body>
html>
登录案例
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="author" content="">
<title>Signin Template for Bootstraptitle>
<link href="asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="asserts/css/signin.css" th:href="@{asserts/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet">
head>
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html" th:action="@{/login}">
<img class="mb-4" th:src="@{asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" src="asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal">Please sign inh1>
<label class="sr-only">Usernamelabel>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="uname" placeholder="Username" required="" autofocus="">
<label class="sr-only">Passwordlabel>
<input type="password" class="form-control" name="password" placeholder="Password" required="">
<div class="checkbox mb-3">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"> Remember me
label>
div>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit">Sign inbutton>
<p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018p>
<a class="btn btn-sm">中文a>
<a class="btn btn-sm">Englisha>
form>
body>
html>
UserController:
package com.oracle.controller;
import com.oracle.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("uname") String uname,
@RequestParam("password") String password,
Model model){
User user = new User();
user.setUname(uname);
user.setPassword(password);
System.out.println(user);
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "dashboard";
}
}
dashboard.html:
<a class="navbar-brand col-sm-3 col-md-2 mr-0" href="http://getbootstrap.com/docs/4.0/examples/dashboard/#">欢迎 [[${user.uname}]] 登录a>
页面抽取
th:insert:代表插入
~{全路径::fragment名字}
th:include:代表包含,值包含内容
~{全路径::fragment名字}
th:replace:代表替代
~{全路径::fragment名字}
<footer th:fragment="copy"> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Groceryfooter>
<body> ...
<div th:insert="footer :: copy">div>
<div th:replace="footer :: copy">div>
<div th:include="footer :: copy">div>
body>
<body> ...
<div>
<footer> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery footer>
div>
<footer> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery footer>
<div> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery div>
body>
SpringBoot国际化
- 什么是国际化
国际化(Internationalztion)简称i18n,其中i和n分别为首字符和尾字符,18是一共字符数,是软件开发时具备多种语言的支持,也可以理解为中英文切换。
通常以下有3步:
1.编写国际化配置文件,在项目中的resources中
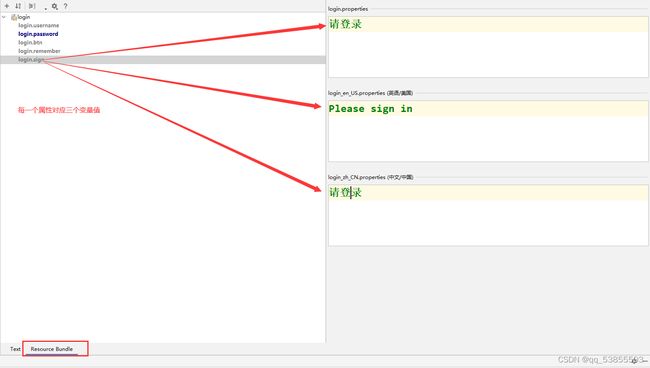
2.SpringBoot使用MessageSourceAutoConfiguration类对ResourceBundleMessageSource类管理国际化资源文件提供了默认配置
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483648)
@Conditional({MessageSourceAutoConfiguration.ResourceBundleCondition.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
private static final Resource[] NO_RESOURCES = new Resource[0];
public MessageSourceAutoConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.messages"
)
public MessageSourceProperties messageSourceProperties() {
return new MessageSourceProperties();
}
=====================================================================
public class MessageSourceProperties {
private String basename = "messages";
private Charset encoding;
因此我们必须在配置文件中配置:
spring:
thymeleaf:
cache: false
#国际化配置
messages:
basename: i18n.login #在配置文件中 必须设置i18n的 基础名
encoding: UTF-8
3.在页面获取国际化的数据
在页面上点超链接来手动切换语言
配置页面
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index(a='zh_CN')}">中文a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index(a='en_US')}">Englisha>
拓展springMvc的功能:添加一个自定义区域信息解析器
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
//zh_CN
String a = request.getParameter("a");
//设置默认的区域信息解析器
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
//不等于 空
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(a)){
//把字符串 zh_CN 截取
String[] s = a.split("_");
//zh language 语言, CN country 国家
locale = new Locale(s[0], s[1]);
}
return locale;
}
把加载到组件中:定义一个配置类,Myconfig
/**
* 设置MyConfig 是一个配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
//添加一个组件给Ioc容器 ,这个方法名是容器中的 id 属性 localeResolver
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
== 需要用rhymeleaf模板引擎的#{}来完成国际化的取值操作==
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="author" content="">
<title>Signin Template for Bootstraptitle>
<link href="asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="asserts/css/signin.css" th:href="@{asserts/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet">
head>
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html" th:action="@{/login}">
<img class="mb-4" th:src="@{asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" src="asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal">[[#{login.sign}]]h1>
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.username}">Usernamelabel>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="uname" placeholder="Username" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus="">
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.password}">Passwordlabel>
<input type="password" class="form-control" name="password" placeholder="Password" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required="">
<div class="checkbox mb-3">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"> [[#{login.remember}]]
label>
div>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.btn}">Sign inbutton>
<p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2021-2022p>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index(a='zh_CN')}">中文a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index(a='en_US')}">Englisha>
form>
body>
html>
SpringBoot定制SpringMvc(拓展)
SpringBoot抛弃了原始的SpringMvc的xml配置文件,通过配置类的形式添加额外功能;SpringBoot对SpringMvc的自动配置可以满足我们绝大多数的需求,但是我们也可以在SpringBoot的基础上,自定义配置类的形式,来添加额外的共能,例如@Configuration修饰类,并实现一个WebMvcConfigurer,例如;拦截器,视图控制器…
拓展SpringMvc
/**
* 设置MyConfig 是一个配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//向现有的视图控制器 添加额外的 映射 ,我们可以通过这个三个路径,访问同一个页面
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
}
//添加一个组件给Ioc容器 ,这个方法名是容器中的 id 属性 localeResolver
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
全面接管:取消SpringBoot对SpringMvc的全部自动配置,有程序员自己完全接管SpringMvc
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc //完全结管SpringMvc, 取消了SpringBoot的默认配置
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
}
总结:如果使用了EnableWebMvc注解,那就是取消了SpringBoot的自动配置,由程序员完全接管了Springmvc,这样所有的SpringBoot默认都将失效,例如:SpringBoot对静态资源的映射。
SpringBoot拦截器
SpringBoot使用拦截器步骤
1.定义拦截器
/**
* HandlerInterceptor 这个类 在SpringMvc 拦截器的时候用过
*/
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//内容需要自己手写 ,就是设置拦截规则
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//获取session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//判断user是否为null
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
//如果 user 是null 说明 没登录过
if(user == null){
session.setAttribute("msg","您没有权限,请先登录!");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index").forward(request,response);
//跳转到 登录页面后 就拦截了
return false;
}
//如果 user 不是 null 那么就直接放行
return true; //return false 拦截 ,return true 是放行
}
}
2.注册拦截器:注册拦截器相当于给SpringBoot添加一个组件
3.设置拦截规则:拦截时,静态资源可能也会被拦截,要注意静态资源放行
/**
* 设置MyConfig 是一个配置类
*/
@Configuration
//@EnableWebMvc //完全结管SpringMvc, 取消了SpringBoot的默认配置
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//向现有的视图控制器 添加额外的 映射
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
}
/**
* 拓展功能
* 添加一个拦截器
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// 我们注册完了 拦截器后,需要拦截哪些 路径 /** 拦截所有请求,默认包含静态资源的
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**") //拦截所有请求,默认包含静态资源的
.excludePathPatterns("/","/index","/index.html","/login",
"/asserts/css/**","/asserts/js/**","/asserts/img/**");
//第一次请求时,放行登录请求,和静态资源
}
//添加一个组件给Ioc容器 ,这个方法名是容器中的 id 属性 localeResolver
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
index.html:
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal">[[#{login.sign}]]h1>
<p style="color:red" th:text="${session.msg}" th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(session.msg)}">p>
SpringBoot持久层框架整合
SpringBoot和Mybatis整合
1.创建工程
2.配置maven
3.给idea添加lombok插件
package com.oracle.pojo;
import lombok.*;
//@Getter
//@Setter
//@ToString
//@EqualsAndHashCode
@Data
public class User {
private Integer uid;
private String uname;
private String password;
}
4.引入依赖
mysql驱动包,druid数据源,mybatis-spring依赖,PageHelper分页插件的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjarsgroupId>
<artifactId>jqueryartifactId>
<version>3.4.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.46version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.2.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.4.1version>
dependency>
5.mapper接口
@Mapper
public interface ProductMapper {
//查询
public List<Product> getProductList();
//删除
public int deleteProductByPid(Integer pid);
//修改
public int updateProductByPid(Product product);
//添加
public int insertProduct(Product product);
//根据 id 查询product实体
public Product getProductByPid(Integer pid);
}
6.mapper.xml:
<mapper namespace="com.oracle.mapper.ProductMapper">
<select id="getProductList" resultType="product">
select * from product
select>
<insert id="insertProduct">
insert into product(pid,pname,price,remark,img)
values (null,#{pname},#{price},#{remark},#{img})
insert>
<update id="updateProductByPid">
update product set pname = #{pname} , price = #{price},
remark = #{remark} ,img = #{img} where pid = #{pid}
update>
<delete id="deleteProductByPid">
delete from product where pid = #{pid}
delete>
<select id="getProductByPid" resultType="product">
select * from product where pid =#{pid}
select>
mapper>
7.serviceImpl:
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductMapper productMapper;
@Override
public PageInfo getProductWithPage() {
PageHelper.startPage(1,5);
List<Product> products = productMapper.getProductList();
//将数据存储到PageInfo对象中
PageInfo pageInfo = new PageInfo(products);
return pageInfo;
}
@Override
public int deleteProductByPid(Integer pid) {
return productMapper.deleteProductByPid(pid);
}
@Override
public int updateProductByPid(Product product) {
return productMapper.updateProductByPid(product);
}
@Override
public int insertProduct(Product product) {
return productMapper.insertProduct(product);
}
@Override
public Product getProductByPid(Integer pid) {
return productMapper.getProductByPid(pid);
}
}
8.controller
@Controller
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@RequestMapping("/productList")
public String productList(Model model){
System.out.println("商品列表");
PageInfo page = productService.getProductWithPage();
model.addAttribute("page",page);
return "productList";
}
@RequestMapping("/deleteProduct/{pid}")
public String deleteProduct(@PathVariable("pid") String pid){
System.out.println(pid);
productService.deleteProductByPid(Integer.parseInt(pid));
//删除后 重定向到上面 查询列表
return "redirect:/productList";
}
@RequestMapping("/getProductByPid")
public String getProductByPid(@RequestParam("pid") String pid,
Model model){
Product product = productService.getProductByPid(Integer.parseInt(pid));
model.addAttribute("product",product);
return "updateProduct";
}
@RequestMapping("/updateProduct")
public String updateProduct(Product product){
productService.updateProductByPid(product);
return "redirect:/productList";
}
@RequestMapping("/toAddPage")
public String toAddPage(){
return "addProduct";
}
@RequestMapping("/addProduct")
public String addProduct(Product product){
productService.insertProduct(product);
//重定向到添加页面
return "redirect:/productList";
}
}
SpringBoot和SpringDataJPA整合(了解)
SpringBoot JDBC —>Jdbc Template
SpringBoot JPA —>Hibernate框架
实际上就是对目前淘汰掉的Hibernate进行了二次封装,变成了SpringDataJPA的框架,SpringBoot对持久层操作做了很多支持
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
springboot data jpa 启动器 里面集成了 hibernate框架的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernategroupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-coreartifactId>
<version>5.6.1.Finalversion>
dependency>
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.47version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.2.6version>
dependency>
2.编写yaml配置文件
#配置Spring的数据源
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: root
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#配置spring Data JPA的参数
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true #显示sql语句
3.编写代码
实体类:User
package com.oracle.pojo;
import lombok.*;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "t_user")
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class User {
@Id //代表主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //主键生成测率,主键自增
@Column(name="uid") //与哪个表进行映射
private Integer uid;
@Column(name = "username")
private String username;
@Column(name = "password")
private String password;
}
Dao接口:
/**
* JpaRepository
* 参数一 : T 泛型的第一个参数是需要映射的实体
* 参数二 : ID 泛型的第二个参数是实体中主键的uid类型
*/
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> {
/**
* 自己拓展 他没有的功能 (不好使)
*
* 这个语句 是 hql 语句 不是 sql语句
* update 实体名
*/
// @Query("update User set username=? where uid=?")
// @Modifying
// public int updateUserByUid(String username,Integer uid);
}
测试
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootDataJpaApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
public void delete(){
userDao.deleteById(5);
}
@Test
public void update(){
User user = new User();
user.setUid(3);
user.setUsername("貂蝉");
user.setPassword("0987");
userDao.saveAndFlush(user);
//userDao.updateUserByUid("刘备",5);
}
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<User> all = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : all) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
@Test
void add(){
User user =new User();
user.setUsername("张三");
user.setPassword("123");
userDao.save(user);
System.out.println("添加成功");
}
}
SpringBoot和RedisTemplate整合
Spring使用jedis连接redis服务器,但是SpringBoot整合,redis内置的客户端时lettuce。
jedis:采用的是直连,在多线程操作的话,是不安全的
lettuce:lettuce中又实用了netty框架,netty用以快速开发高性能、高可靠性的网络服务器和客户端程序。也就是说,netty是一个基于NIO的客户、服务器端的编程框架,lettuce解决在多个线程共享,不存在线程安全问题,所以lettuce比jedis性能好,高效而安全。
依赖配置:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
引入了lettuce 作为客户端
<dependency>
<groupId>io.lettucegroupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-coreartifactId>
<version>6.1.5.RELEASEversion>
<scope>compilescope>
dependency>
源码分析
|-- RedisAutoConfiguration
|--RedisProperties
内酯类很多redis的基本参数
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.redis"
)
public class RedisProperties {
private int database = 0;
private String url;
private String host = "localhost";
private String username;
private String password;
private int port = 6379;
}
配置文件
#springboot 整合 reids
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.200.128 # 默认是localhost 但是我链接的是 Linux的
port: 6379 #默认端口号
database: 3 #选择第三个数据库
# lettuce:
# pool:
# max-active: 8
# max-idle: 3
# jedis: 不要用这个
# pool:
# max-active:
单元测试
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootRedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
// RedisConnectionFactory redis = redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory();
// RedisConnection connection = redis.getConnection();
// System.out.println(connection);
//redisTemplate调用方法
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();//就是操作字符串
ops.set("uname","admin");
Object uname = ops.get("uname");
System.out.println(uname);
// redisTemplate.opsForList(); //操作列表的
// redisTemplate.opsForHash(); //操作hash
// redisTemplate.opsForSet(); //操作set
// redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); //操作zset
}
}
自定义RedisTemplate
首先我们先看一下,SpringBoot对RedisTemplate默认的序列化的方式有几种:我们并不像用它默认的序列化方式,所以我们自定义一个RedisTemplae的序列化方式,这时它就不会使用SpringBoot默认的RedisTemplate了;
RedisConfig
package com.oracle.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.jsontype.impl.LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* 修改了SpringBoot默认的redisTemplate序列化,自定义了一个序列化方式
* @param redisConnectionFactory
* @return redisTemplate
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
//采用json序列化并对其做出配置
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
//Jackson ObjectMapper 中的 enableDefaultTyping 方法由于安全原因,从 2.10.0 开始标记为过期,建议用 activateDefaultTyping 方法代替
//om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
om.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
//创建一个String类型的序列化对象
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
//key 采用的String 的序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
//hashde key 也采用String的序列化方式
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
//value 序列化方式采用jackson
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//hash 的 value序列化方式采用jackson
template.setHashKeySerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
RedisUtil二次封装:
package com.oracle.util;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 把这个工具类放到容器中
* redisTemplate的方法 ,都在这里进行二次封装
*/
@Component
public class RedisUtil {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 向redis中设置缓存
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean set(String key, Object value){
try{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,value);
return true;
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 获取redis中的缓存
* @param key
* @return
*/
public Object get(String key){
return key == null ? null : redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
}
public long incr(String key,long value){
if(value < 0){
throw new RuntimeException();
}
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, value);
}
}
ServiceImpl:
package com.oracle.serviceImpl;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
//@Autowired
//private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil;
@Override
public User login(String uname, String password) {
//这行代码是从数据库查询出来的 , 查询以后应该加入缓存
//userMapper.getUserByUnameAndPassword(uname, password);
User user = new User();
user.setUid(3);
user.setUname("张三");
user.setPassword("123");
//user 支持不支持 序列化啊
Gson gson = new Gson();
String s = gson.toJson(user);
//如何加到redis中啊
redisUtil.set("user",s);
return null;
}
}
单元测试:
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootRedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil;
@Test
void testRedis(){
userService.login("","");
}
@Test
void getUser(){
String str = (String) redisUtil.get("user");
//{"uid":3,"uname":"张三","password":"123"}
System.out.println(str);
}
}