PyTorch 学习笔记 3 —— DATASETS & DATALOADERS & TRANSFORMS
文章目录
- 1. 下载数据集
- 2. 数据集的迭代与可视化
- 3. 读取自己的数据集
- 4. DataLoader
- 5. TRANSFORMS
数据读取是深度学习的第一步,PyTorch 提供了 torch.utils.data.DataLoader 和 torch.utils.data.Dataset 两个 Module 让我们读取在线的数据集以及自己的数据集。
PyTorch 提供了很多预加载的数据集,如 FashionMNIST,他们都是 torch.utils.data.Dataset 的子类,可以在这里找到它们: Image Datasets, Text Datasets, and Audio Datasets
1. 下载数据集
Fashion-MNIST 是一个服装图像的数据集,包含 60000 张训练样本和 10000 张测试样本,每一个样本是大小为 28 × 28 28 \times 28 28×28 的灰度图,一共包含 10 类图像,加载数据集需要指定以下参数:
rootis the path where the train/test data is stored,trainspecifies training or test dataset,download=Truedownloads the data from the internet if it’s not available at root.transformandtarget_transformspecify the feature and label transformations
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
training_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root='data',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root='data',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
print(len(training_data)) # 60000
2. 数据集的迭代与可视化
得到的数据集是 torchvision.datasets.mnist.FashionMNIST 对象,支持像 list 一样的方式进行迭代:training_data[index]
print(type(training_data))
print(len(training_data)) # 60000
X, y = training_data[0]
print(f'img[0].shape = {X.shape}') # torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
print(f'label[0] = {y}') # 9
使用下面的方法迭代 training_data 的元素:
for i in range(len(training_data)):
X, y = training_data[i]
for X, y in training_data:
pass
使用 matplotlib 对数据集可视化:
labels_map = {
0: "T-Shirt",
1: "Trouser",
2: "Pullover",
3: "Dress",
4: "Coat",
5: "Sandal",
6: "Shirt",
7: "Sneaker",
8: "Bag",
9: "Ankle Boot",
}
X, y = training_data[0]
print(f'img[0].shape = {X.shape}')
print(f'label[0] = {y}')
figure = plt.figure()
cols, rows = 4, 4
for i in range(1, cols * rows + 1):
sample_index = torch.randint(
low=0,
high=len(training_data),
size=(1,)).item()
img, label = training_data[sample_index]
# print(img.shape) # torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
figure.add_subplot(rows, cols, i)
plt.title(labels_map[label])
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(img.squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.show()
其中,torch.squeeze(input, dim) 可以将输入的 tensor 的1的维度删除,dim 默认为所有维度,指定 dim 后,若 dim 维大小为 1,则删除,否则不删除,如:
t = torch.randint(0, 10, size=(1, 28, 1, 28))
print(f't.shape = {t.shape}')
print(f't.squeeze().shape = {t.squeeze().shape}')
print(f't.squeeze(dim=2).shape = {t.squeeze(dim=2).shape}')
print(f'torch.squeeze(input=t, dim=1).shape = {torch.squeeze(input=t, dim=1).shape}')
# t.shape = torch.Size([1, 28, 1, 28])
# t.squeeze().shape = torch.Size([28, 28])
# t.squeeze(dim=2).shape = torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
# torch.squeeze(input=t, dim=1).shape = torch.Size([1, 28, 1, 28])
由于从 training_data 中读取到的 X 的 shape 为 torch.Size([1, 28, 28]),无法用 pyplot 绘制,使用 squeeze 后 shape 变成 torch.Size([28, 28]),则可以用 pyplot 绘制,得到的结果如下:
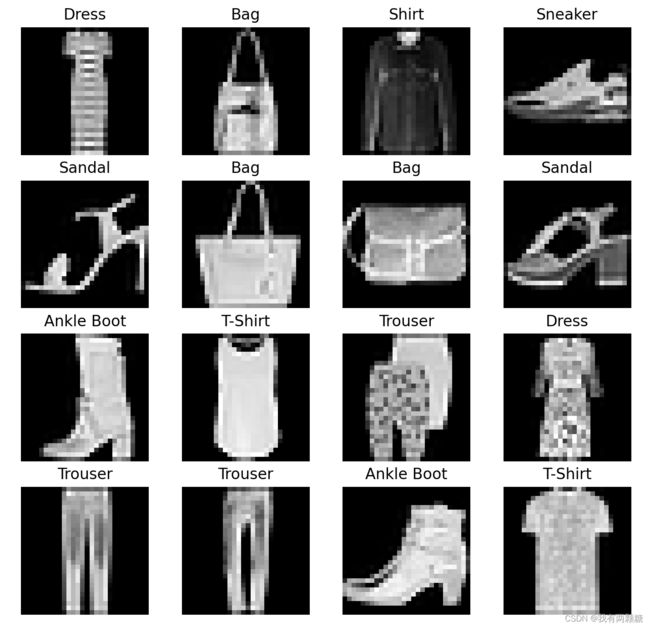
3. 读取自己的数据集
读取自定义的数据集需要定义三个函数__init__,__len__, 和 __getitem__,将 FashionMNIST 图像存储在 img_dir, 标签存储在 CSV 文件 annotations_file 中:
import os
import pandas as pd
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torchvision.io import read_image
class CustomImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, annotations_file, img_dir, transform=None, target_transform=None):
# initialize the directory containing the images, the annotations file, and both transforms
self.img_labels = pd.read_csv(annotations_file)
self.img_dir = img_dir
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
def __len__(self):
# returns the number of samples in our dataset.
return len(self.img_labels)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
# loads and returns a sample from the dataset at the given index idx
img_path = os.path.join(self.img_dir, self.img_labels.iloc[idx, 0])
image = read_image(img_path)
label = self.img_labels.iloc[idx, 1]
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
if self.target_transform:
label = self.target_transform(label)
return image, label
(1) __init__ 初始化数据集的目录、标签文件以及 transform,labels.csv 文件如下:
tshirt1.jpg, 0
tshirt2.jpg, 0
......
ankleboot999.jpg, 9
(2)__len__ 返回数据集包含的样本数量
(3)__getitem__ 实现了通过索引获取数据集中样本的 image 和 label
4. DataLoader
DataLoader 可以将数据集划分为若干个 minibatch,可以指定是否使用随机打乱 shuffle
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_dataloader = DataLoader(training_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
for X, y in test_dataloader:
print(f'Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: {X.shape}') # torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
print(f'Shape of y: {y.shape} {y.dtype}') # torch.Size([64])
DataLoader 返回的对象是可迭代的:
# Display image and label.
train_features, train_labels = next(iter(train_dataloader))
print(f"Feature batch shape: {train_features.size()}") # torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
print(f"Labels batch shape: {train_labels.size()}") # torch.Size([64])
# show image[0]
img = train_features[0].squeeze()
label = train_labels[0]
plt.imshow(img, cmap="gray")
plt.show()
print(f"Label: {label}")
5. TRANSFORMS
transforms 可以将数据集的格式转换成便于训练的格式,TorchVision 的数据集都有两个参数:用来修改特征的 -transform ,以及用于修改标签的 -target_transform
import torch
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor, Lambda
ds = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor(),
target_transform=Lambda(lambda y: torch.zeros(10, dtype=torch.float).scatter_(0, torch.tensor(y), value=1))
)
其中,ToTensor 可以将 PIL 图像或 numpy 矩阵转换成 FloatTensor,并将图像的灰度值转换到 [0. 1] 范围内;
target_transform 指定使用自定义的 lambda transforms,下面的代码将标签从一个整数转换乘了 one-hot 编码形式的标签(scatter_ 将 label y 对应的位置变成 1):
target_transform = Lambda(lambda y: torch.zeros(
10, dtype=torch.float).scatter_(dim=0, index=torch.tensor(y), value=1))
REDERENCE:
1 . https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/basics/data_tutorial.html
2 . torch.utils.data API
3 . TRANSFORMS
更多 PyTorch 入门学习笔记参考 PyTorch 学习笔记