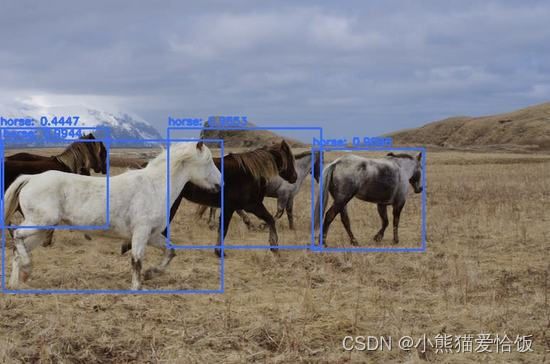
用python+opencv实现目标检测
前言
opencv是什么可能很多人都不清楚,那么这个时候咱们就可以打开百度输入opencv是什么。

这不就有了吗,然后点击进去。

这不就完美的解决了opencv是干啥的了吗,不过估计还是有很多人是看不明白的那么接下来咱们就来实现它当中的一个功能吧,非常强大,好好看好好学。
正文
在此篇文章中主要讲的是
展示如何使用Python和OpenCV实现简单的对象检测。
我们需要初始化虚拟环境:
python3 -m venv env
source env/bin/activate
mkdir weights
cp [darknet directory]/cfg/coco.names weights/
cp [darknet directory]/cfg/yolov3.cfg weights/
cp [darknet directory]/yolov3.weights
安装
接下来,我们需要安装示例所需的库,创建一个“requirements.txt”文件并添加以下内容:
# requirements.txt
opencv-python
argparse
numpy
然后通过以下方式安装:
pip install -r requirements.txt
编写源代码
首先,我们需要导入所需的模块:
import numpy as np
import argparse
import cv2
接下来声明必要的变量并初始化网络模型:
LABELS_FILE = "weights/coco.names"
CONFIG_FILE = "weights/yolov3.cfg"
WEIGHTS_FILE = "weights/yolov3.weights"
CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.3 python学习交流群:660193417
LABELS = open(LABELS_FILE).read().strip().split("\n")
np.random.seed(4)
COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 255, size = (len(LABELS), 3), dtype = "uint8")
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(CONFIG_FILE, WEIGHTS_FILE)
下面的函数循环遍历在图像中找到的检测到的对象,检查置信度是否高于最小阈值,如果是,则将该框与检测到的坐标一起添加到box数组中。
然后,它检查以确保有一个以上的检测,如果是这样,它将框连同对象标签和置信度一起绘制到图像上。
最后,修改后的图像显示在屏幕上。
def drawBoxes (image, layerOutputs, H, W):
boxes = []
confidences = []
classIDs = []
for output in layerOutputs:
for detection in output:
scores = detection[5:]
classID = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classID]
if confidence > CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD:
box = detection[0:4] * np.array([W, H, W, H])
(centerX, centerY, width, height) = box.astype("int")
x = int(centerX - (width / 2))
y = int(centerY - (height / 2))
boxes.append([x, y, int(width), int(height)])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
classIDs.append(classID)
idxs = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD, CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD)
# Ensure at least one detection exists
if len(idxs) > 0:
for i in idxs.flatten():
(x, y) = (boxes[i][0], boxes[i][1])
(w, h) = (boxes[i][2], boxes[i][3])
color = [int(c) for c in COLORS[classIDs[i]]]
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
text = "{}: {:.4f}".format(LABELS[classIDs[i]], confidences[i])
cv2.putText(image, text, (x, y - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
# Display the image
cv2.imshow("output", image)
下一个函数从提供的路径中读取一个图像文件,从图像中创建一个blob并设置网络输入。
然后,我们获得层输出,然后将必要的变量传递给上面定义的函数。
def detectObjects (imagePath):
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
(H, W) = image.shape[:2]
ln = net.getLayerNames()
ln = [ln[i - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1 / 255.0, (416, 416), swapRB = True, crop = False)
net.setInput(blob)
layerOutputs = net.forward(ln)
drawBoxes(image, layerOutputs, H, W)
最后,我们当然需要main函数,我们使用argparse从命令行读取文件路径,调用上面的函数,然后等待用户按任意键。
完成之后
if __name__ == "__main__":
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required = True, help = "Path to input file")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
detectObjects(args["image"])
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行程序
该程序可以通过以下命令执行:
python main.py -i horses.png
结语
到这里咱们就完成了。是不是非常简单但又很好用。
有什么python相关报错解答自己不会的、或者源码资料/模块安装/女装大佬精通技巧 都可以来这里:(https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=2Q3YTfym)或者文末私号问我