MMRotate:旋转框检测实现过程
MMRotate:旋转框检测实现过程
MMRotate地址:https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmrotate
文档地址:https://mmrotate.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
一、环境搭建
1.创建虚拟环境
conda create --name mmdet2 python=3.8 -y
激活虚拟环境:
conda activate openmmlab
2.安装pytorch、torchvision
根据自己的配置安装相应版本
pip install torch==1.7.1+cu101 torchvision==0.8.2+cu101 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
3.安装mmcv-full
下载mmcv-full 1.4.5
pip install mmcv-full==1.4.5 --user -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
4.下载mmdet 2.22.0
pip install mmdet==2.22.0 --user -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
5.下载mmrotate
git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmrotate.git
6.编译mmrotate
cd mmrotate
pip install -r requirements/build.txt -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
python setup.py develop
6.制作数据集
使用工具:rolabelimg
git clone GitHub - cgvict/roLabelImg: Label Rotated Rect On Images for training
安装相关依赖库:
pip install pyqt5-tools
pip install lxml
进入rolabelimg目录
pyrcc5 -o resources.py
resources.qrc python roLabelImg.py
进入rolabelimg方式:
./roLabelImg.py
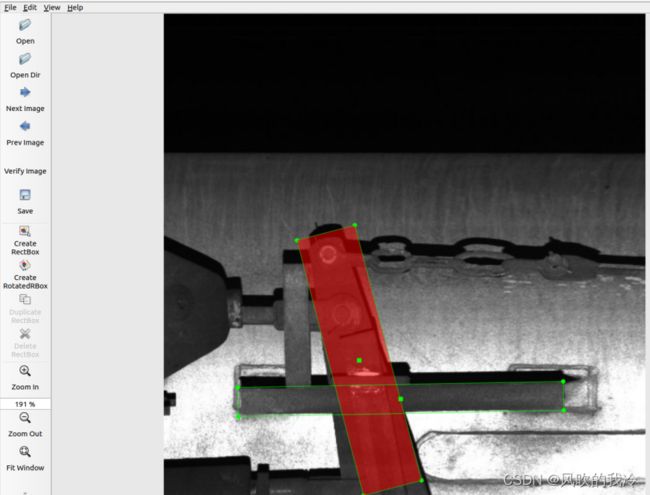
切换旋转框模式
旋转框标记
标记完数据后需将xml改为dota格式,运行如下代码:
import os
import glob
import math
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import json
from base64 import b64encode
from json import dumps
import cv2
def rotatePoint(xc, yc, xp, yp, theta):
xoff = xp - xc
yoff = yp - yc
cosTheta = math.cos(theta)
sinTheta = math.sin(theta)
pResx = cosTheta * xoff + sinTheta * yoff
pResy = - sinTheta * xoff + cosTheta * yoff
return str(int(xc + pResx)), str(int(yc + pResy))
def get(root, name):
return root.findall(name)
# 检查读取xml文件是否出错
def get_and_check(root, name, length):
vars = root.findall(name)
if len(vars) == 0:
raise NotImplementedError('Can not fing %s in %s.' % (name, root.tag))
if length > 0 and len(vars) != length:
raise NotImplementedError('The size of %s is supposed to be %d, but is %d.' % (name, length, len(vars)))
if length == 1:
vars = vars[0]
return vars
def convert(xml_file, save_dir, name, data):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file) # 读取xml文件
root = tree.getroot()
size = get_and_check(root, 'size', 1) # 读取xml中<>size<>字段中的内容
img = cv2.imread(data)
# 当标注中有多个目标时全部读取出来
txtname = name + '.txt'
txt_file = os.path.join(save_dir, txtname)
category_list=[]
with open(txt_file, "w+", encoding='UTF-8') as out_file:
for obj in get(root, 'object'):
# 定义图片的标注信
category = get_and_check(obj, 'name', 1).text # 读取当前目标的类别
if category not in category_list:
category_list.append(category)
bndbox = get_and_check(obj, 'robndbox', 1)
cx = float(get_and_check(bndbox, 'cx', 1).text)
cy = float(get_and_check(bndbox, 'cy', 1).text)
w = float(get_and_check(bndbox, 'w', 1).text)
h = float(get_and_check(bndbox, 'h', 1).text)
angle = float(get_and_check(bndbox, 'angle', 1).text)
x0, y0 = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx - w / 2, cy - h / 2, -angle)
x1, y1 = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx + w / 2, cy - h / 2, -angle)
x2, y2 = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx + w / 2, cy + h / 2, -angle)
x3, y3 = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx - w / 2, cy + h / 2, -angle)
dict = {y0: x0, y1: x1, y2: x2, y3: x3}
list = find_topLeftPopint(dict)
if list[0] == x0:
list_xy = [x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3]
elif list[0] == x1:
list_xy = [x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x0, y0]
elif list[0] == x2:
list_xy = [x2, y2, x3, y3, x0, y0, x1, y1]
else:
list_xy = [x3, y3, x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2]
# 在原图上画矩形 看是否转换正确
cv2.line(img, (int(list_xy[0]), int(list_xy[1])), (int(list_xy[2]), int(list_xy[3])), color=(255, 0, 0),thickness=3)
cv2.line(img, (int(list_xy[2]), int(list_xy[3])), (int(list_xy[4]), int(list_xy[5])), color=(255, 0, 0),thickness=3)
cv2.line(img, (int(list_xy[4]), int(list_xy[5])), (int(list_xy[6]), int(list_xy[7])), color=(255, 0, 0),thickness=3)
cv2.line(img, (int(list_xy[6]), int(list_xy[7])), (int(list_xy[0]), int(list_xy[1])), color=(255, 0, 0),thickness=3)
points = str(list_xy[0]) + " " + str(list_xy[1]) + " " + str(list_xy[2]) + " " + str(list_xy[3]) +" " + str(list_xy[4]) + " " + str(list_xy[5]) + " " + str(list_xy[6]) +" " + str(list_xy[7]) + " "
points = points + category + " " + "0" + "\n"
out_file.write(points)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(saved_path, name + '.png'), img)
return category_list
def find_topLeftPopint(dict):
dict_keys = sorted(dict.keys()) # y值
temp = [dict[dict_keys[0]], dict[dict_keys[1]]]
minx = min(temp)
if minx == temp[0]:
miny = dict_keys[0]
else:
miny = dict_keys[1]
return [minx, miny]
def do_transformation(xml_dir, save_path, img):
cnt = 0
list1 = []
for fname in os.listdir(xml_dir):
name = fname.split(".")[0] # 获取图片名字
endwith = fname.split(".")
path = os.path.join(xml_dir, fname) # 文件路径
for img_name in os.listdir(img):
end = img_name.split('.')
if name == end[0]:
data = img + name + '.' + end[1] # xml文件对应的图片路径
list = convert(path, save_path, name, data)
for i in list:
if i not in list1:
list1.append(i)
print(list1)
cnt += 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
data_path = "/home/work/mjt/xuanzhuan_train/data/" # json文件夹路径
saved_path = "/home/work/mjt/xuanzhuan_train/train_data" # xml保存路径
xml_path = "/home/work/mjt/xuanzhuan_train/resizexml"
txt_path = saved_path + '/trainval1/annfiles'
if not os.path.exists(txt_path):
os.makedirs(txt_path)
files = os.listdir(xml_path)
files = [i.replace("\\", "/").split("/")[-1].split(".xml")[0] for i in files]
print(files)
img = "/home/work/mjt/xuanzhuan_train/data/" # xml对应图片文件夹
save_dota_path = "/home/work/mjt/xuanzhuan_train/dota/" # 存放json文件夹
if not os.path.exists(save_dota_path):
os.makedirs(save_dota_path)
do_transformation(xml_path, save_dota_path, img)
数据格式:
datasets
--trainval
--images #存放图片
--annfiles #对应的txt文件(上图代码生成的)
--test
--images
--annfiles
7.修改config文件
(1)下载预训练权重
地址:mmrotate/model_zoo.md at main · open-mmlab/mmrotate · GitHubOpenMMLab Rotated Object Detection Toolbox and Benchmark - mmrotate/model_zoo.md at main · open-mmlab/mmrotate![]() https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmrotate/blob/main/docs/zh_cn/model_zoo.md(2)修改./configs/rotated_faster_rcnn/rotated_faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_data_le90.py
https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmrotate/blob/main/docs/zh_cn/model_zoo.md(2)修改./configs/rotated_faster_rcnn/rotated_faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_data_le90.py
如下图修改文件中的num_classes
(3)修改./mmrotate/datasets/dota.py 中的类别名称
修改文件中CLASSES
(4)修改 ./configs/_base_/datasets/dotav1.py 文件
修改文件中的data_root、可根据训练集尺寸更img_scale
(5)修改./configs/_base_/default_runtime.py文件
修改文件中的预训练模型
(6)一些其他设置
8.训练
修改./tool/train.py文件
- -config: 使用的模型文件 ; - -work-dir:训练得到的模型及配置信息保存的路径。
9.测试
可用./tool/test.py进行测试,也可运行下面代码
from argparse import ArgumentParser
from mmdet.apis import inference_detector, init_detector, show_result_pyplot
import os
import time
import mmrotate
def parse_args():
parser = ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('img', help='Image file')
parser.add_argument('config', help='Config file')
parser.add_argument('checkpoint', help='Checkpoint file')
parser.add_argument(
'--device', default='cuda:0', help='Device used for inference')
parser.add_argument(
'--palette',
default='dota',
choices=['dota', 'sar', 'hrsc', 'hrsc_classwise', 'random'],
help='Color palette used for visualization')
parser.add_argument(
'--score-thr', type=float, default=0.3, help='bbox score threshold')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def main(args):
file_name = os.listdir(args.img)
model = init_detector(args.config, args.checkpoint, device=args.device)
for image in file_name:
images = os.path.join(args.img, image)
start = time.time()
result = inference_detector(model, images)
end = time.time()
show_result_pyplot(
model,
images,
result,
palette=args.palette,
score_thr=args.score_thr,
out_file=os.path.join("/home/work/预言故障图/1111/旋转", image))
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
main(args)
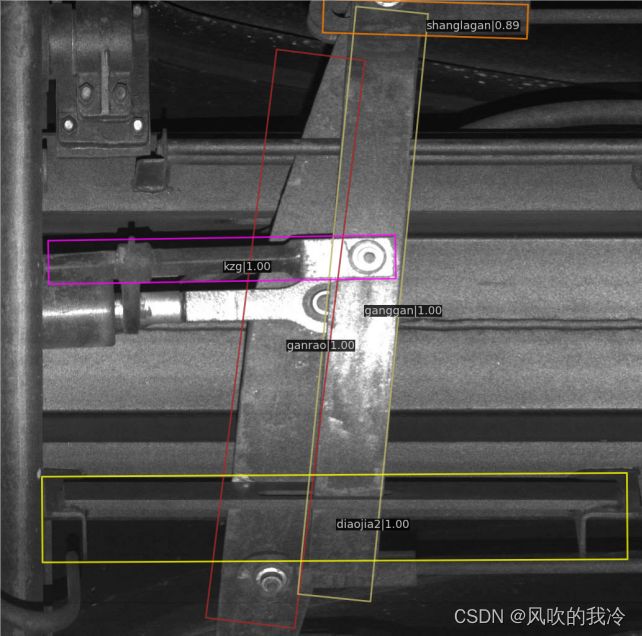
9.结果展示