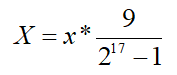人工智能-遗传算法
1.编码
采用的是二进制编码,用一个二进制编码序列表示一条染色体。
首先需要确定序列的长度。区间是 [0,9],区间长度为9-0=9,精确到小数点后4位,所以至少需要把区间分为![]() 等份,
等份,
然后是将解码后的数归一化到规定区间 [0,9] 内,转化公式如下:
解码代码如下:
double decoding(int *a) //解码
{
double x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chromosome_size; i++) {
x += a[i] * pow_2[chromosome_size - i - 1];
}
return x * 9.0 / (pow_2[chromosome_size] - 1);
}2.适应度函数
3.遗传算子
一开始我采用的是轮盘赌选择算子,但是由于我直接把目标函数当成适应度函数,所以适应度函数值可能会得出负的,导致概率也是负的。然后换了一种选择算子,采用了锦标赛选择算子,即在种群中随机抽取n个个体,让他们竞争,从中抽取最优的个体,我选取的n是2。
使用锦标赛选择算子,使代码也简化了许多,不需要记录总的适应度函数值,也不需要计算适应度函数值所占的比例。
选择函数代码如下:
void selection(int &cnt) //选择
{
int t1 = rand() % population_size;
int t2 = rand() % population_size;
while (t1 == t2) {
t2 = rand() % population_size;
}
if (now_population[t1].fitness >= now_population[t2].fitness) {
next_population[cnt] = now_population[t1];
} else {
next_population[cnt] = now_population[t2];
}
cnt++;
}4.参数设置
#define population_size 200 //种群规模
#define generation_size 100 //进化代数
#define chromosome_size 17 //染色体长度
#define cross_rate 0.8 //交叉概率
#define mutate_rate 0.01 //变异概率5.数据结构
在解码时会不断用到2的幂次,而最高幂次只有17,所以我直接定义了数组存放2的幂次。
int pow_2[] = {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536, 131072, 262144};
目标函数中只有一个自变量,所以只需要一个染色体,定义一个结构体,存放染色体的基因数组、对应的十进制数、以及该染色体的适应度函数。
struct chromosome {
int gene[chromosome_size];
double value; //编码对应的值
double fitness; //对应的适应度函数
};
总代码如下:
#include
#define population_size 200 //种群规模
#define generation_size 100 //进化代数
#define chromosome_size 17 //染色体长度
#define cross_rate 0.8 //交叉概率
#define mutate_rate 0.01 //变异概率
using namespace std;
int pow_2[] = {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536, 131072, 262144};
struct chromosome {
int gene[chromosome_size];
double value; //编码对应的值
double fitness; //对应的适应度函数
};
struct chromosome now_population[population_size]; //当前种群
struct chromosome next_population[population_size]; //新种群
double ans = 0.0;
double Fitness(double x) { //适应值函数
return x + 10 * sin(5 * x) + 7 * cos(4 * x);
}
double decoding(int *a) //解码
{
double x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chromosome_size; i++) {
x += a[i] * pow_2[chromosome_size - i - 1];
}
return x * 9.0 / (pow_2[chromosome_size] - 1);
}
void init_population() //初始化种群+计算适应值+计算适应值占的比值
{
for (int i = 0; i < population_size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chromosome_size; j++) {
now_population[i].gene[j] = rand() % 2;
}
now_population[i].value = decoding(now_population[i].gene);
now_population[i].fitness = Fitness(now_population[i].value);
}
}
void selection(int &cnt) //选择
{
int t1 = rand() % population_size;
int t2 = rand() % population_size;
while (t1 == t2) {
t2 = rand() % population_size;
}
if (now_population[t1].fitness >= now_population[t2].fitness) {
next_population[cnt] = now_population[t1];
} else {
next_population[cnt] = now_population[t2];
}
cnt++;
}
void crossover(int &cnt) //交叉
{
int rate = rand() % 10;
if (rate < cross_rate * 10) {
int chromosome1 = rand() % population_size;
int chromosome2 = rand() % population_size;
int cross_position = rand() % (chromosome_size - 1) + 1;
next_population[cnt] = now_population[chromosome1];
for (int i = cross_position; i < chromosome_size; i++) {
next_population[cnt].gene[i] = now_population[chromosome2].gene[i];
}
next_population[cnt].value = decoding(next_population[cnt].gene);
next_population[cnt].fitness = Fitness(next_population[cnt].value);
if(next_population[cnt].value>=0&&next_population[cnt].value<=9){
cnt++;
}
}
}
void mutation(int &cnt) //变异
{
int rate = rand() % 100;
if (rate < 100 * mutate_rate) {
int chromosome = rand() % population_size;
int mutate_position = rand() % chromosome_size;
if (now_population[chromosome].gene[mutate_position] == 1)
next_population[cnt].gene[mutate_position] = 0;
if (now_population[chromosome].gene[mutate_position] == 0)
next_population[cnt].gene[mutate_position] = 1;
next_population[cnt].value = decoding(next_population[cnt].gene);
next_population[cnt].fitness = Fitness(next_population[cnt].value);
if(next_population[cnt].value >= 0 && next_population[cnt].value <= 9){
cnt++;
}
}
}
void reproduction() //复制
{
for (int i = 0; i < population_size; i++) {
now_population[i] = next_population[i];
}
memset(&next_population, 0, sizeof(next_population));
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned) time(NULL));
init_population();
for (int i = 0; i < generation_size; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt < population_size) {
selection(cnt);
crossover(cnt);
mutation(cnt);
}
reproduction();
}
for (int j = 0; j < population_size; j++) {
if (now_population[j].fitness > ans)ans = now_population[j].fitness;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}