python-OpenCV轻松入门-凸包
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、凸包是什么?
- 二、使用步骤
-
- 1.获取凸包
- 2.凸包缺陷检测(图缺陷)
- 3.测试轮廓是否是凸型的
- 总结
前言
随着人工智能的不断发展,OpenCV这门技术也越来越重要,很多人都开启了学习OpenCV,本文就介绍了OpenCV的基础内容。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、凸包是什么?
凸包(Convex Hull)是一个计算几何(图形学)中的概念,它的严格的数学定义为:在一个向量空间V中,对于给定集合X,所有包含X的凸集的交集S被称为X的凸包。
在图像处理过程中,我们常常需要寻找图像中包围某个物体的凸包。凸包跟多边形逼近很像,只不过它是包围物体最外层的一个凸集,这个凸集是所有能包围这个物体的凸集的交集。
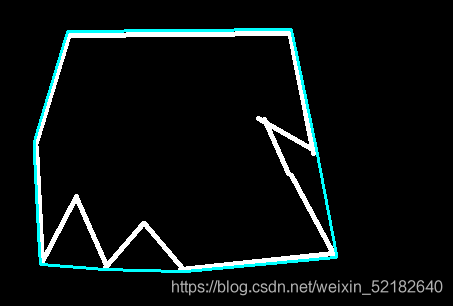
凸包示意图如下:
二、使用步骤
1.获取凸包
hull = cv2.convexHull( points[,clockwise[,returnPoints]] )
代码如下(示例):
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#author:Kong DeXing
#案例:Fu Xianjun. All Rights Reserved.
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('contours2.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#阈值处理
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,0)
#查找轮廓
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
hull = cv2.convexHull(contours[0])
cv2.polylines(img,[hull],True,(255,255,0),2)
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
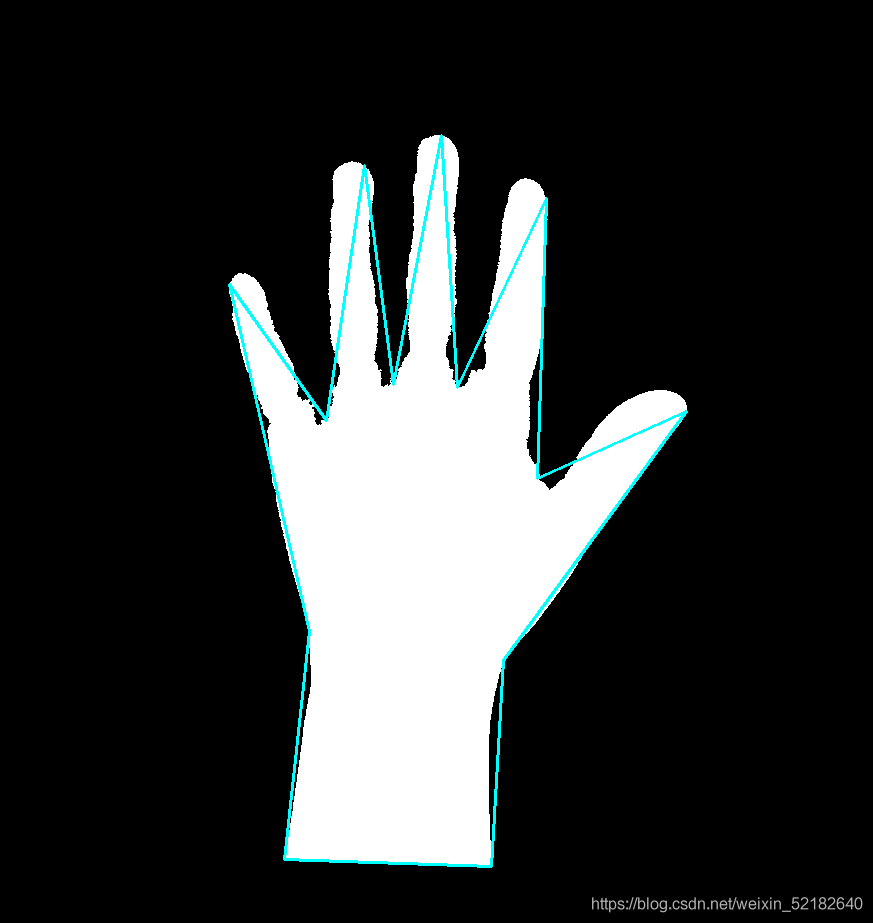
2.凸包缺陷检测(图缺陷)
convexityDefects = cv2.convexityDefects( contour, convexhull)
代码如下(示例):
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#author:Kong DeXing
#案例:Fu Xianjun. All Rights Reserved.
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('hand.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(gray,60,255,0)
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
n=len(contours)
contoursImg=[]
x=0
for i in range(n):
area = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
if area>10000:
print(f"轮廓{i}的面积: \n{area}")
x = i
#获取凸包
cnt = contours[x]
hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt,returnPoints=False)
defects = cv2.convexityDefects(cnt,hull)
for i in range(defects.shape[0]):
s,e,f,d = defects[i,0]
start = tuple(cnt[s][0])
end = tuple(cnt[e][0])
far = tuple(cnt[f][0])
cv2.line(img,start,end,(255,255,0),1)
cv2.circle(img,far,5,(0,255,0),1)
print(defects)
#显示图片
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3.测试轮廓是否是凸型的
retval = cv2.isContourConvex( contours)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#author:Kong DeXing
#案例:Fu Xianjun. All Rights Reserved.
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('binaryhand.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#阈值处理
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,0)
#查找轮廓
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
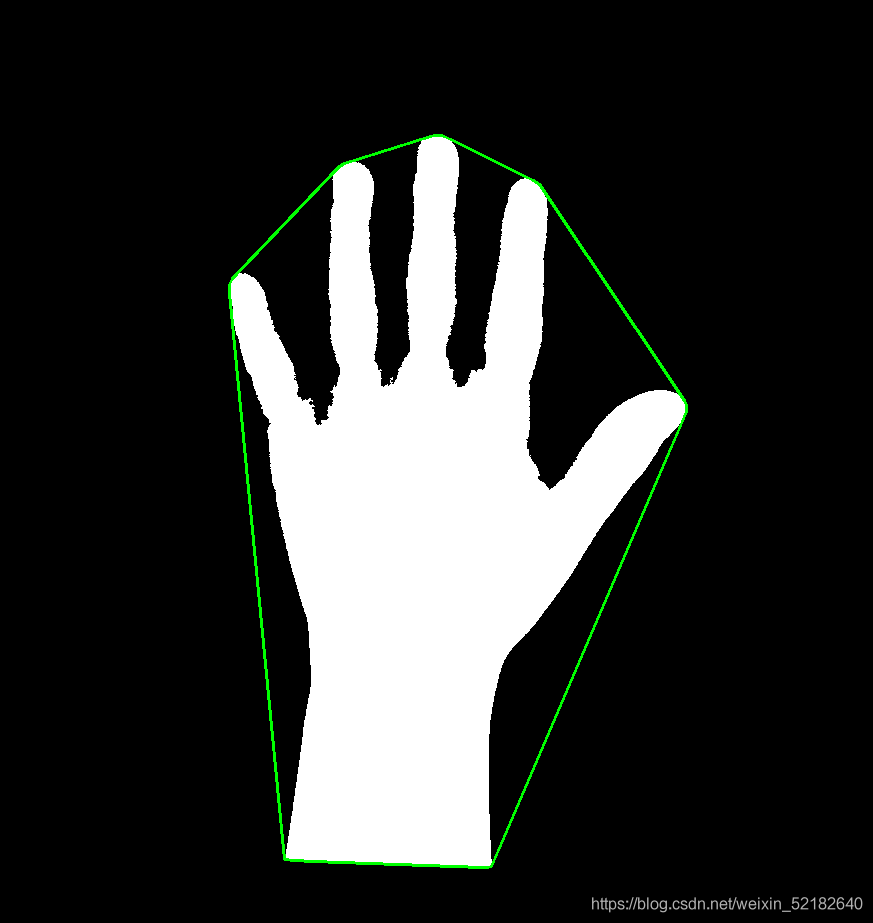
#---------------凸包-----------------
img1 = img.copy()
hull = cv2.convexHull(contours[0])
cv2.polylines(img1,[hull],True,(0,255,0),2)
print("使用函数cv2.convexHull()构造的多边形是否是凸型的:",cv2.isContourConvex( hull ))
cv2.imshow('img1',img1)
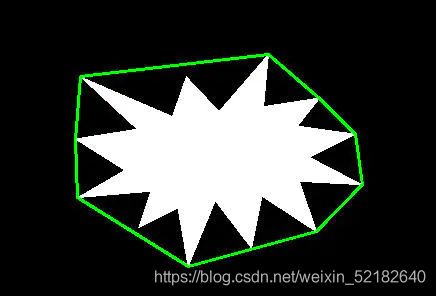
#-----------逼近多边形----------------
img2 = img.copy()
epsilon = 0.01*cv2.arcLength(contours[0],Ture)
approx1 = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[0],epsilon ,True)#拟合精确度
img1 =cv2.polylines(img2,[approx1],True,(255,255,0),2)
print("使用函数cv2.approxPolyDP()构造的多边形是否是凸型的:",cv2.isContourConvex( approx1 ))
cv2.imshow('approxPolyDP1',img2)
#-----------释放窗口--------------
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
使用函数cv2.convexHull()构造的多边形是否是凸型的: True
使用函数cv2.approxPolyDP()构造的多边形是否是凸型的: False
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了OpenCV凸包的使用,而凸包提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。