PyTorch笔记 - Vision Transformer(ViT)
Transformer包含Encoder和Decoder,核心是Multi-Head Self-Attention(空间融合),FeedForward Nerual Network(通道融合)。
Encoder和Decoder的交互信息:Memory-base Multi-Head Cross-Attention
注入位置信息Position Embedding
数据量的要求与 归纳偏置(Inductive Bias) 的引入成反比,上限很高,数据量要求也很高。
归纳法、演绎法,归纳偏置(Inductive Bias),将人类的经验带入模型的设计当中。
Transformer的使用场景:
- Encoder Only:BERT、分类任务、非流式任务
- Decoder Only:GPT系列、语言建模、自回归生成任务、流式任务
- Encoder-Decoder:机器翻译、语言识别
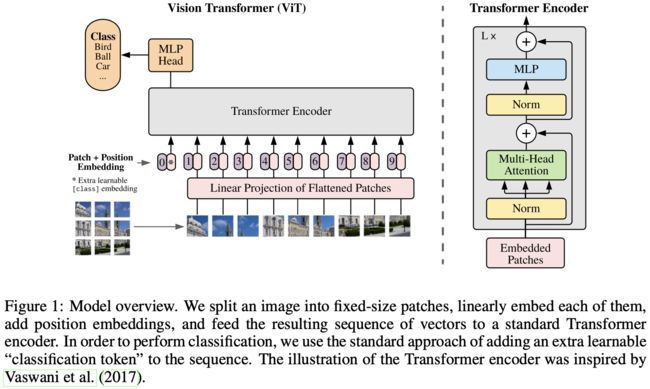
Vision Transformer(ViT):
- DNN perspective(视角): Image2Patch、Patch2Embedding
- CNN perspective(视角): 2D Convolution over image
- Class Token Embedding,占位符
- Position Embedding: Interpolation(插入) when inference
- Transformer Encoder
- Classification Head
Paper: An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale
Classification Token:起到Query的作用
Linear Projection of Flattened Patches -> Patch + Position Embedding -> Transformer Encoder -> MLP Head
Patch + Position Embedding,先从左到右,再从上到下,拉成序列形状
实现Image2Embedding,TransformerEncoder由PyTorch封装
- torch.nn.functional.unfold: 取出patch卷积区域
- torch.nn.TransformerEncoder
ViT:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# step1 convert image to embedding vector sequence
def image2emb_naive(image, patch_size, weight):
"""
使用unfold生成patch
"""
# image shape: bs*channel*h*w
# 没有交叠,stride=patch_size,直接生成patch
patch = F.unfold(image, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
patch = patch.transpose(2, 1)
# (bs, patch_depth(patch_size*patch_size*ic), num_patch)
print(f'patch: {patch.shape}')
patch_embedding = patch @ weight # 输出的embeding
print(f'patch_embedding: {patch_embedding.shape}')
return patch_embedding
def image2emb_conv(image, kernel, stride):
"""
使用conv生成patch
"""
conv_output = F.conv2d(image, kernel, stride=stride) # bs*oc*oh*ow
bs, oc, oh, ow = conv_output.shape
patch_embedding = conv_output.reshape((bs, oc, oh*ow)).transpose(2, 1)
print(f'patch_embedding: {patch_embedding.shape}')
return patch_embedding
# test code for image2emb
bs, ic, image_h, image_w = 1, 3, 8, 8
patch_size = 4
model_dim = 8 # embedding dim
max_num_token = 16
num_classes = 10
label = torch.randint(10, (bs,))
patch_depth = patch_size*patch_size*ic
# 分块方法得到embedding
torch.manual_seed(42)
image = torch.randn((bs, ic, image_h, image_w)) # 生成图像
weight = torch.randn((patch_depth, model_dim)) # patch_depth -> model_dim, model_dim是输出通道数目
print(f'weight: {weight.shape}')
patch_embedding_naive = image2emb_naive(image, patch_size, weight)
print(f'patch_embedding_naive: \n{patch_embedding_naive}')
# 二维卷积方法得到embedding
# kernel的形状,oc*ic*k_h*k_w
kernel = weight.transpose(1, 0).reshape((model_dim, ic, patch_size, patch_size))
patch_embedding_conv = image2emb_conv(image, kernel, stride=patch_size)
print(f'patch_embedding_conv: \n{patch_embedding_conv}')
# step2 prepend CLS token embedding
cls_token_embedding = torch.randn((bs, 1, model_dim), requires_grad=True)
token_embedding = torch.cat([cls_token_embedding, patch_embedding_conv], dim=1)
print(f'token_embedding: {token_embedding.shape}')
# step3 add position embedding
position_embedding_table = torch.randn((max_num_token, model_dim), requires_grad=True)
seq_len = token_embedding.shape[1]
# 复制 position_embedding 操作
position_embedding = torch.tile(position_embedding_table[:seq_len], [token_embedding.shape[0], 1, 1])
token_embedding += position_embedding
print(f'token_embedding: {token_embedding.shape}')
# step4 pass embedding to Transformer Encoder
encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=model_dim, nhead=8)
transformer_encoder = nn.TransformerEncoder(encoder_layer, num_layers=6)
encoder_output = transformer_encoder(token_embedding)
# step5 do classification
cls_token_output = encoder_output[:, 0, :]
linear_layer = nn.Linear(model_dim, num_classes)
logits = linear_layer(cls_token_output)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss = loss_fn(logits, label)
print(f'loss: {loss}')