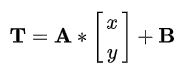opencv仿射变换:平移,缩放和旋转
目录
仿射变换原理
opencv中仿射变换实现
使用getAffineTransform()函数求仿射变换矩阵
使用 getRotationMatrix2D()函数获取仿射矩阵
使用仿射矩阵对图像做仿射变换warpAffine
仿射变换原理
仿射变换(Affine Transformation或 Affine Map),又称仿射映射,是指在几何中,一个向量空间进行一次线性变换并接上一个平移,变换为另一个向量空间的过程。它保持了二维图形的“平直性”(即:直线经过变换之后依然是直线)和“平行性”(即:二维图形之间的相对位置关系保持不变,平行线依然是平行线,且直线上点的位置顺序不变)。
一个任意的仿射变换都能表示为乘以一个矩阵(线性变换)接着再加上一个向量(平移)的形式。可以表示为线性变换和平移变换的叠加
我们能够用仿射变换来表示如下三种常见的变换形式:
- 旋转,rotation (线性变换)
- 平移,translation(向量加)
- 缩放,scale(线性变换)
如果进行更深层次的理解,仿射变换代表的是两幅图之间的一种映射关系。
仿射变换的数学表示是先乘以一个线形变换矩阵再加上一个平移向量,其中线性变换矩阵为2×2的矩阵,平移向量为2×1的向量
假设我们存在一个线性变换矩阵 A 和平移矩阵B ,两者与输入的M矩阵之间的关系如式
根据旋转矩阵 A和平移矩阵B 以及图像像素值![]() ,仿射变换的数学原理可以用式
,仿射变换的数学原理可以用式
仿射变换又称为三点变换,如果知道变换前后两张图像中三个像素点坐标的对应关系,就可以求得仿射变换中的变换矩阵 .
点1, 2 和 3 (在图一中形成一个三角形) 与图二中三个点一一映射, 仍然形成三角形, 但形状已经大大改变. 如果我们能通过这样两组三点求出仿射变换 (你能选择自己喜欢的点), 接下来我们就能把仿射变换应用到图像中所有的点.。
而我们通常使用2 x 3的矩阵来表示仿射变换。
opencv中仿射变换实现
要求出图像的仿射变换(旋转缩放等),首先要求出仿射变换矩阵。
使用getAffineTransform()函数求仿射变换矩阵
上文提到过,已知变换前后两张图像中三个像素点坐标的对应关系,就可以求得仿射变换中的变换矩阵。OpenCV 4提供了利用三个对应像素点来确定 矩阵的函数getAffineTransform()
函数原型:
CV_EXPORTS Mat getAffineTransform( const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[] );Calculates an affine transform from three pairs of the corresponding points.
The function calculates the matrix of an affine transform so that:where
@param src Coordinates of triangle vertices in the source image.
@param dst Coordinates of the corresponding triangle vertices in the destination image.
- src[]:原图像中的三个像素坐标。
- dst[]:目标图像中的三个像素坐标。
使用 getRotationMatrix2D()函数获取仿射矩阵
函数原型:
CV_EXPORTS_W Mat getRotationMatrix2D(Point2f center, double angle, double scale);
/** @sa getRotationMatrix2D */
CV_EXPORTS Matx23d getRotationMatrix2D_(Point2f center, double angle, double scale);
inline
Mat getRotationMatrix2D(Point2f center, double angle, double scale)
{
return Mat(getRotationMatrix2D_(center, angle, scale), true);
}@brief Calculates an affine matrix of 2D rotation.
The function calculates the following matrix:以此得出仿射矩阵:
where
The transformation maps the rotation center to itself. If this is not the target, adjust the shift.
@param center Center of the rotation in the source image.
@param angle Rotation angle in degrees. Positive values mean counter-clockwise rotation (the
coordinate origin is assumed to be the top-left corner).
@param scale Isotropic scale factor.
- 第一个参数,Point2f类型的center,表示源图像的旋转中心。
- 第二个参数,double类型的angle,旋转角度。角度为正值表示向逆时针旋转(坐标原点是左上角)。
- 第三个参数,double类型的scale,缩放系数。
getRotationMatrix2D函数源代码:
cv::Mat cv::getRotationMatrix2D( Point2f center,double angle, double scale )
{
angle *= CV_PI/180;
double alpha = cos(angle)*scale;
double beta = sin(angle)*scale;
Mat M(2, 3, CV_64F);//生成一个2*3的矩阵
double* m = (double*)M.data;
//按照上文公式填充内容
m[0] = alpha;
m[1] = beta;
m[2] = (1-alpha)*center.x - beta*center.y;
m[3] = -beta;
m[4] = alpha;
m[5] = beta*center.x + (1-alpha)*center.y;
return M;
}
使用仿射矩阵对图像做仿射变换warpAffine
warpAffine函数原型:
CV_EXPORTS_W void warpAffine( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
InputArray M, Size dsize,
int flags = INTER_LINEAR,
int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT,
const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());@brief Applies an affine transformation to an image.
The function warpAffine transforms the source image using the specified matrix:依据如下式子,对图像做仿射变换
when the flag #WARP_INVERSE_MAP is set. Otherwise, the transformation is first inverted
with #invertAffineTransform and then put in the formula above instead of M. The function cannot
operate in-place.@param src input image.
@param dst output image that has the size dsize and the same type as src .
@param M transformation matrix.
@param dsize size of the output image.
@param flags combination of interpolation methods (see #InterpolationFlags) and the optional
flag #WARP_INVERSE_MAP that means that M is the inverse transformation (
).
@param borderMode pixel extrapolation method (see #BorderTypes); when
borderMode=#BORDER_TRANSPARENT, it means that the pixels in the destination image corresponding to
the "outliers" in the source image are not modified by the function.
@param borderValue value used in case of a constant border; by default, it is 0.
- 第一个参数,InputArray类型的src,输入图像,即源图像,填Mat类的对象即可。
- 第二个参数,OutputArray类型的dst,函数调用后的运算结果存在这里,需和源图片有一样的尺寸和类型。
- 第三个参数,InputArray类型的M,2×3的变换矩阵。
- 第四个参数,Size类型的dsize,表示输出图像的尺寸。
- 第五个参数,int类型的flags,插值方法的标识符。此参数有默认值INTER_LINEAR(线性插值),可选的插值方式如下:
- INTER_NEAREST - 最近邻插值
- INTER_LINEAR - 线性插值(默认值)
- INTER_AREA - 区域插值
- INTER_CUBIC –三次样条插值
- INTER_LANCZOS4 -Lanczos插值
- CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS - 填充所有输出图像的象素。如果部分象素落在输入图像的边界外,那么它们的值设定为 fillval.
- CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP –表示M为输出图像到输入图像的反变换,即 。因此可以直接用来做象素插值。否则, warpAffine函数从M矩阵得到反变换。
- 第六个参数,int类型的borderMode,边界像素模式,默认值为BORDER_CONSTANT。
- 第七个参数,const Scalar&类型的borderValue,在恒定的边界情况下取的值,默认值为Scalar(),即0。
使用两种方式进行仿射变换:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
Mat img = imread("5.jpg");
if (img.empty())
{
cout << "请确认图像文件名称是否正确" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat rotation0, rotation1, img_warp0, img_warp1;
double angle = 30; //设置图像旋转的角度
Size dst_size(img.rows, img.cols); //设置输出图像的尺寸
Point2f center(img.rows / 2.0, img.cols / 2.0); //设置图像的旋转中心
rotation0 = getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1); //计算放射变换矩阵
warpAffine(img, img_warp0, rotation0, dst_size); //进行仿射变换
imshow("img_warp0", img_warp0);
//根据定义的三个点进行仿射变换
Point2f src_points[3];
Point2f dst_points[3];
src_points[0] = Point2f(0, 0); //原始图像中的三个点
src_points[1] = Point2f(0, (float)(img.cols - 1));
src_points[2] = Point2f((float)(img.rows - 1), (float)(img.cols - 1));
//放射变换后图像中的三个点
dst_points[0] = Point2f((float)(img.rows)*0.11, (float)(img.cols)*0.20);
dst_points[1] = Point2f((float)(img.rows)*0.15, (float)(img.cols)*0.70);
dst_points[2] = Point2f((float)(img.rows)*0.81, (float)(img.cols)*0.85);
rotation1 = getAffineTransform(src_points, dst_points); //根据对应点求取仿射变换矩阵
warpAffine(img, img_warp1, rotation1, dst_size); //进行仿射变换
imshow("img_warp1", img_warp1);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
实验效果:
参考文章:
【从零学习OpenCV 4】图像仿射变换
【OpenCV入门教程之十八】OpenCV仿射变换 & SURF特征点描述合辑