深度学习TF—14.WGAN原理及实战
文章目录
-
-
- 一、WGAN原理
-
- 1.JS散度的缺陷
- 2.Wasserstein 距离
- 3.损失函数
- 二、WGAN实战
-
- 1.数据集的加载
- 2.构建网络
- 3.全部代码
-
一、WGAN原理
WGAN 算法从理论层面分析了GAN 训练不稳定的原因,并提出了有效的解决方法。那么是什么原因导致了GAN 训练如此不稳定呢?WGAN 提出是因为JS 散度在不重叠的分布和上的梯度曲面是恒定为0 的。当分布和不重叠时,JS 散度的梯度值始终为0,从而导致此时GAN 的训练出现梯度弥散现象,参数长时间得不到更新,网络无法收敛。
1.JS散度的缺陷
下面通过一个简单的分布实例来解释JS 散度的缺陷。考虑完全不重叠( ≠ 0)的两个分布和
分布为:∀(, ) ∈ p, = 0, ∼ U(0,1)
分布为:∀(, ) ∈ , = , ∼ U(0,1)
其中 ∈ ,当 = 0时,分布和重叠,两者相等;当 ≠ 0时,分布和不重叠。
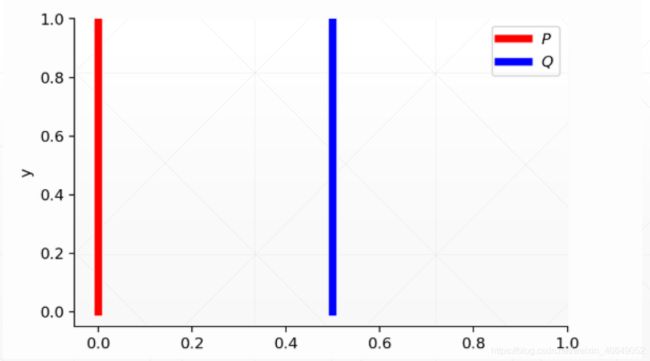
我们分析上述分布和之间的JS 散度随的变化情况。
根据KL 散度与JS 散度的定义,计算 = 0时的JS 散度(||):
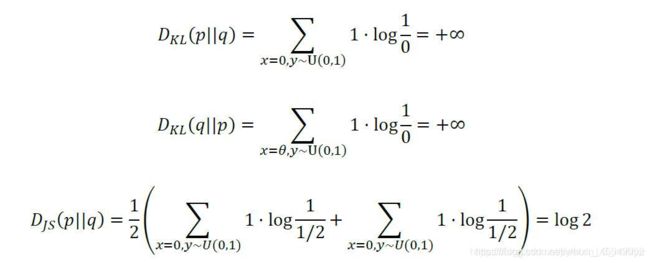
当 = 0时,两个分布完全重叠,此时的JS 散度和KL 散度都取得最小值0

(||)随的变化趋势为:
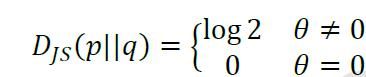
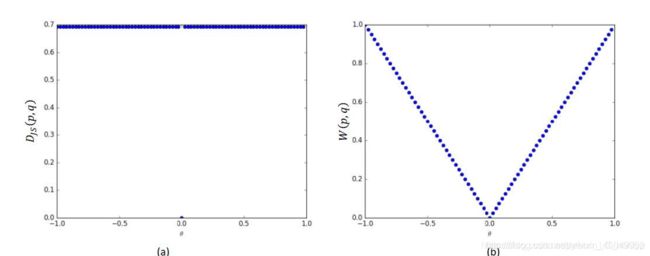
也就是说:当两个分布完全不重叠时,无论分布之间的距离远近,JS 散度为恒定值log2,此时JS 散度将无法产生有效的梯度信息;当两个分布出现重叠时,JS 散度才会平滑变动,产生有效梯度信息;当完全重合后,JS 散度取得最小值0。

由图可知:由于p分布与q分布不重叠,随着q的移动,生成样本位置处的梯度值始终为0,无法更新生成网络的参数,从而出现网络训练困难的现象。因此,JS 散度在分布和不重叠时是无法平滑地衡量分布之间的距离,从而导致此位置上无法产生有效梯度信息,出现GAN 训练不稳定的情况。要解决此问题,需要使用一种更好的分布距离衡量标准,使得它即使在分布和不重叠时,也能平滑反映分布之间的真实距离变化。
2.Wasserstein 距离
WGAN 论文发现了JS 散度导致GAN 训练不稳定的问题,并引入了一种新的分布距离度量方法:Wasserstein 距离,它表示了从一个分布变换到另一个分布的最小代价,定义为:
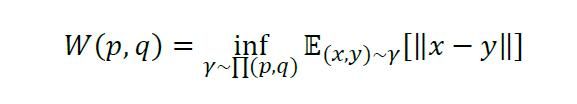
其中Π(, )是分布和组合起来的所有可能的联合分布的集合,对于每个可能的联合分布 ∼ Π(, ),计算距离‖ − ‖的期望(,)∼[‖ − ‖],其中(, )采样自联合分布。不同的联合分布有不同的期望(,)∼[‖ − ‖],这些期望中的下确界即定义为分布和的Wasserstein 距离。
绘制出 JS 散度和EM 距离的曲线,如图所示,可以看到,JS 散度在 = 0处不连续,其他位置导数均为0,而EM 距离总能够产生有效的导数信息,因此EM 距离相对于JS 散度更适合指导GAN 网络的训练。
3.损失函数
前面是EM距离,后面是GP惩罚项
其中̂来自于与的线性差值:
̂ = + (1 − ) , ∈ [0,1]
判别器 D 的目标是最小化上述的误差ℒ(, ),即迫使生成器G 的分布与真实分布之间EM 距离∼[()]−∼ [()]项尽可能小,‖̂(̂)‖2逼近于1。
WGAN 的生成器G 的训练目标为:
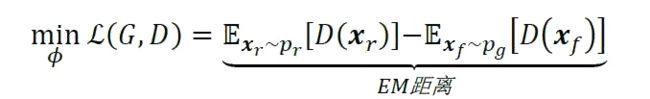
即使得生成器的分布与真实分布之间的EM 距离越小越好。考虑到∼[()]一项与生成器无关,因此生成器的训练目标简写为:

从实现来看,判别网络D 的输出不需要添加Sigmoid 激活函数,这是因为原始版本的判别器的功能是作为二分类网络,添加Sigmoid 函数获得类别的概率;而WGAN 中判别器作为EM 距离的度量网络,其目标是衡量生成网络的分布和真实分布之间的EM 距离,属于实数空间,因此不需要添加Sigmoid 激活函数。在误差函数计算时,WGAN 也没有log 函数存在。在训练WGAN 时,WGAN 作者推荐使用RMSProp 或SGD 等不带动量的优化器。
WGAN 从理论层面发现了原始GAN 容易出现训练不稳定的原因,并给出了一种新的距离度量标准和工程实现解决方案,取得了较好的效果。WGAN 还在一定程度上缓解了模式崩塌的问题,使用WGAN 的模型不容易出现模式崩塌的现象。需要注意的是,WGAN一般并不能提升模型的生成效果,仅仅是保证了模型训练的稳定性。当然,保证模型能够稳定地训练也是取得良好效果的前提。
二、WGAN实战
1.数据集的加载
# 加载数据集的函数
import multiprocessing
import tensorflow as tf
def make_anime_dataset(img_paths, batch_size, resize=64, drop_remainder=True, shuffle=True, repeat=1):
@tf.function
def _map_fn(img):
img = tf.image.resize(img, [resize, resize])
img = tf.clip_by_value(img, 0, 255)
img = img / 127.5 - 1
return img
dataset = disk_image_batch_dataset(img_paths,
batch_size,
drop_remainder=drop_remainder,
map_fn=_map_fn,
shuffle=shuffle,
repeat=repeat)
img_shape = (resize, resize, 3)
len_dataset = len(img_paths) // batch_size
return dataset, img_shape, len_dataset
def batch_dataset(dataset,
batch_size,
drop_remainder=True,
n_prefetch_batch=1,
filter_fn=None,
map_fn=None,
n_map_threads=None,
filter_after_map=False,
shuffle=True,
shuffle_buffer_size=None,
repeat=None):
# set defaults
if n_map_threads is None:
n_map_threads = multiprocessing.cpu_count()
if shuffle and shuffle_buffer_size is None:
shuffle_buffer_size = max(batch_size * 128, 2048) # set the minimum buffer size as 2048
# [*] it is efficient to conduct `shuffle` before `map`/`filter` because `map`/`filter` is sometimes costly
if shuffle:
dataset = dataset.shuffle(shuffle_buffer_size)
if not filter_after_map:
if filter_fn:
dataset = dataset.filter(filter_fn)
if map_fn:
dataset = dataset.map(map_fn, num_parallel_calls=n_map_threads)
else: # [*] this is slower
if map_fn:
dataset = dataset.map(map_fn, num_parallel_calls=n_map_threads)
if filter_fn:
dataset = dataset.filter(filter_fn)
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=drop_remainder)
dataset = dataset.repeat(repeat).prefetch(n_prefetch_batch)
return dataset
def memory_data_batch_dataset(memory_data,
batch_size,
drop_remainder=True,
n_prefetch_batch=1,
filter_fn=None,
map_fn=None,
n_map_threads=None,
filter_after_map=False,
shuffle=True,
shuffle_buffer_size=None,
repeat=None):
"""Batch dataset of memory data.
Parameters
----------
memory_data : nested structure of tensors/ndarrays/lists
"""
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(memory_data)
dataset = batch_dataset(dataset,
batch_size,
drop_remainder=drop_remainder,
n_prefetch_batch=n_prefetch_batch,
filter_fn=filter_fn,
map_fn=map_fn,
n_map_threads=n_map_threads,
filter_after_map=filter_after_map,
shuffle=shuffle,
shuffle_buffer_size=shuffle_buffer_size,
repeat=repeat)
return dataset
def disk_image_batch_dataset(img_paths,
batch_size,
labels=None,
drop_remainder=True,
n_prefetch_batch=1,
filter_fn=None,
map_fn=None,
n_map_threads=None,
filter_after_map=False,
shuffle=True,
shuffle_buffer_size=None,
repeat=None):
"""Batch dataset of disk image for PNG and JPEG.
Parameters
----------
img_paths : 1d-tensor/ndarray/list of str
labels : nested structure of tensors/ndarrays/lists
"""
if labels is None:
memory_data = img_paths
else:
memory_data = (img_paths, labels)
def parse_fn(path, *label):
img = tf.io.read_file(path)
img = tf.image.decode_png(img, 3) # fix channels to 3
return (img,) + label
if map_fn: # fuse `map_fn` and `parse_fn`
def map_fn_(*args):
return map_fn(*parse_fn(*args))
else:
map_fn_ = parse_fn
dataset = memory_data_batch_dataset(memory_data,
batch_size,
drop_remainder=drop_remainder,
n_prefetch_batch=n_prefetch_batch,
filter_fn=filter_fn,
map_fn=map_fn_,
n_map_threads=n_map_threads,
filter_after_map=filter_after_map,
shuffle=shuffle,
shuffle_buffer_size=shuffle_buffer_size,
repeat=repeat)
return dataset
2.构建网络
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
class Generator(keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
# z: [b,100] => [b,3*3*512] => [b,3,3,512] => [b,64,64,3]
self.fc = layers.Dense(3 * 3 * 512)
# 参数选择的经验,channel从大往小,feturesize从小往大,kernel_size一般1~6,strides,padding需要精细控制满足最后输出为[b,64,64,3]
# 这样正好可以与下面的Discriminator相衔接
self.conv1 = layers.Conv2DTranspose(256, kernel_size=3, strides=3, padding='valid')
self.bn1 = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.conv2 = layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding='valid')
self.bn2 = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.conv3 = layers.Conv2DTranspose(3, kernel_size=4, strides=3, padding='valid')
# 定义前向传播
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
# [z,100] => [z,3*3*512]
x = self.fc(inputs)
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 3, 3, 512])
x = tf.nn.leaky_relu(x)
#
x = tf.nn.leaky_relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x), training=training))
x = tf.nn.leaky_relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x), training=training))
x = self.conv3(x)
# 范围是[-1,1]
x = tf.tanh(x)
return x
# 包含三个卷积层和一个全连接层
class Discriminator(keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
# [b,64,64,3] => [b,1]
self.conv1 = layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=5, strides=3, padding='valid')
self.conv2 = layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=5, strides=3, padding='valid')
self.bn2 = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.conv3 = layers.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=5, strides=3, padding='valid')
self.bn3 = layers.BatchNormalization()
# [b,h,w,3] => [b,-1] 打平
self.flatten = layers.Flatten()
# 分类
self.fc = layers.Dense(1)
# 定义前向传播
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
# tf.nn.leaky_relu表示非线性的激活函数
x = tf.nn.leaky_relu(self.conv1(inputs))
# 由于BatchNormalization层的train与test行为是不一样的,所以有必要将状态信息告诉BatchNormalization
x = tf.nn.leaky_relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(inputs), training=training))
x = tf.nn.leaky_relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(inputs), training=training))
# [b,h,w,3] => [b,-1]
x = self.flatten(x)
# [b,-1] => [b,1]
logits = self.fc(x)
return logits
# 测试网络-测试基本功能正常
def main():
d = Discriminator()
g = Generator()
x = tf.random.normal([2, 64, 64, 3])
z = tf.random.normal([2, 100])
prob = d(x)
print(prob)
x_hat = g(z)
print(x_hat.shape)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3.全部代码
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from scipy.misc import toimage
import glob
from gan import Generator, Discriminator
from dataset import make_anime_dataset
tf.random.set_seed(22)
np.random.seed(22)
# 将多张图片合并成一张图片
def save_result(val_out, val_block_size, image_path, color_mode):
def preprocess(img):
img = ((img + 1.0) * 127.5).astype(np.uint8)
# img = img.astype(np.uint8)
return img
preprocesed = preprocess(val_out)
final_image = np.array([])
single_row = np.array([])
for b in range(val_out.shape[0]):
# concat image into a row
if single_row.size == 0:
single_row = preprocesed[b, :, :, :]
else:
single_row = np.concatenate((single_row, preprocesed[b, :, :, :]), axis=1)
# concat image row to final_image
if (b+1) % val_block_size == 0:
if final_image.size == 0:
final_image = single_row
else:
final_image = np.concatenate((final_image, single_row), axis=0)
# reset single row
single_row = np.array([])
if final_image.shape[2] == 1:
final_image = np.squeeze(final_image, axis=2)
toimage(final_image).save(image_path)
# 计算真的损失
def celoss_ones(logits):
# [b,1]
loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=tf.ones_like(logits.shape))
return tf.reduce_mean(loss)
# 计算假的损失
def celoss_zeros(logits):
# [b,1]
loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=tf.zeros_like(logits.shape))
return tf.reduce_mean(loss)
# 完成discriminator计算的函数
def d_loss_fn(generator,discriminator,batch_z,batch_x,is_training):
# 1.treat real image as real
# 2.treat generated image as fake
# 假的image
fake_image = generator(batch_z,is_training)
d_fake_logits = discriminator(fake_image,is_training)
d_real_logits = discriminator(batch_x,is_training)
d_loss_real = celoss_ones(d_real_logits)
d_loss_fake = celoss_zeros(d_fake_logits)
loss = d_loss_fake + d_loss_real
return loss
def g_loss_fn(generator,discriminator,batchsz,is_training):
fake_image = generator(batchsz, is_training)
d_fake_logitis = discriminator(fake_image, is_training)
loss = celoss_ones(d_fake_logitis)
return loss
def main():
# 超参数
z_dim = 100
epochs = 3000000
batch_size = 512
learning_rate = 0.002
is_training = True
# 数据集的加载
# glob函数给定一个路径,会把当前路径下所有符合条件的图片都筛选出来
# 确定路径
img_path = glob.glob(r'路径')
# 加载图片
dataset,img_shape,_ = make_anime_dataset(img_path,batch_size)
print(dataset,img_shape)
sample = next(iter(dataset))
print(sample.shape,tf.reduce_max(sample).numpy(),tf.reduce_min(sample).numpy())
# 无限次采样
dataset = dataset.repeat()
db_iter = iter(dataset)
generator = Generator()
generator.build(input_shape = (None, z_dim))
discriminator = Discriminator()
discriminator.build(input_shape=(None,64,64,3))
g_optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate,beta_1=0.5)
d_optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate,beta_1=0.5)
for epoch in range(epochs):
batch_z = tf.random.uniform([batch_size,z_dim],minval=-1.,maxval=1.)
batch_x = next(db_iter)
# train D
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
d_loss = d_loss_fn(generator,discriminator,batch_z,batch_x,is_training)
grads = tape.gradient(d_loss,discriminator.trainable_variables)
d_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads,discriminator.trainable_variables))
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
g_loss = g_loss_fn(generator,discriminator,batch_size,is_training)
grads = tape.gradient(g_loss,generator.trainable_variables)
g_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, generator.trainable_variables))
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print(epoch, 'd-loss:', float(d_loss), 'g-loss:', float(g_loss))
z = tf.random.uniform([100,z_dim])
fake_image = generator(z, training= False)
img_path = os.path.join('image', 'gan-%d.png'%epoch)
save_result(fake_image.numpy(), 10, img_path, color_mode='P')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
如果对您有帮助,麻烦点赞关注,这真的对我很重要!!!如果需要互关,请评论留言!
![]()

