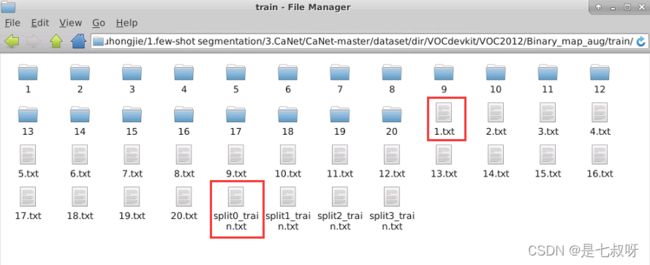
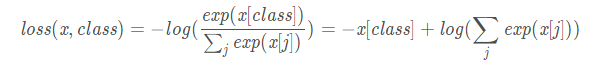CaNet-master装载图片数据和mask(index对应单张图片序号)
使用三个txt(15cls)训练,另外1个txt(5cls)用于val。
训练需要support set原图+mask,query set原图,使用query集计算loss更新参数。
support set和query set的cls一样,但是取的不同的图
query_name = self.new_exist_class_list[index][0]
sample_class = self.new_exist_class_list[index][1] # random sample a class in this img
# return class's mask_list
support_img_list = self.binary_pair_list[sample_class] # all img that contain the sample_class
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
loss = loss_calc_v1(pred, query_mask, 0)
一、Dataset、Dataloader数据处理
PIL读入之后对象中w, h = img.size,转为numpy数组后变为:h,w,c(通道是RGB),转为Tensor后变为:c,h,w,最后如果要使用cv2保存图像需要转为:h,w,c
cv2.imread()读入之后经过如下代码也会变为h,w,c
image = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image = np.float32(image)
1.1 数据集文件夹:
1.2 Dataset和Dataloader:首先自定义Dataset类重写__getitem__方法:
index对应单张图片序号,batch_size不同也可能取到不同的类: 1 w a y − 1 s h o t \color{red}{1 way-1shot} 1way−1shot
# loading data
# trainset
dataset = Dataset_train(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD,prob=options.prob)
trainloader = data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# ipdb.set_trace()
# valset
# this only a quick val dataset where all images are 321*321.
valset = Dataset_val(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD)
valloader = data.DataLoader(valset, batch_size=options.bs_val, shuffle=False, num_workers=4,
drop_last=False)
1.21 Dataset得到query图片名和support图片名
index对应单张图片序号
每个split文件夹的图片及类别数量如下:
| 文件夹 | 图片+类别 数量 |
|---|---|
| split0_train.txt | 2286 |
| split1_train.txt | 3425 |
| split2_train.txt | 5883 |
| split3_train.txt | 2086 |
由于我是设置fold 0作为测试集:
parser.add_argument('-fold', type=int, help='fold', default=0)
所以new_exist_class_list [ 0 ] \color{red}{[0]} [0]得到的是除split0_train.txt文件之外的三个文件夹列表 训 练 集 \color{red}{训练集} 训练集new_exist_class_list中训练集某张图片名称,**new_exist_class_list [ 1 ] \color{red}{[1]} [1]得到这张训练图片所属类别:
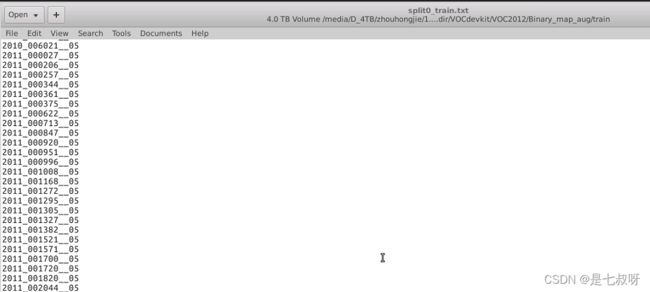
**binary_pair_list[sample_class]**从1.txt文件中得到此类别的所有图片名称的列表。
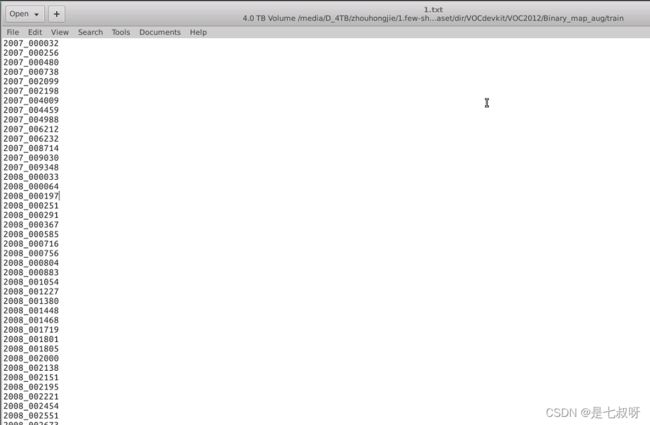
判断list中与query_name不同,来得到支撑集图片名称:
while True:
support_name = support_img_list[random.randint(0, len(support_img_list) - 1)] # [0, l-1]
if support_name != query_name:
break
Binary_map_aug文件夹中读取到了support和query的图片名称在这里插入代码片
CaNet/CaNet-master/dataset/dir/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Binary_map_aug/train/
1.22 Dataset加载图片
由于pytorch的顺序是 ( b a t c h , c , h , w ) \color{red}{(batch,c,h,w)} (batch,c,h,w),所以需要进行PIL类型到numpy类型转换,tensorflow,numpy的顺序是(batch,h,w,c):
PIL可以完美配合plt,但是如果使用PIL和imread显示的话要将RGB转换为BGR。
support_rgb = self.normalize(
self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_rgb(
self.flip(flip_flag,
# PIL format
Image.open(os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', support_name + '.jpg'))
))))
- c v 2. i m r e a d ( ) \color{red}{cv2.imread()} cv2.imread()得到的img数据类型是np.array()类型。 B G R ( 默 认 ) \color{red}{BGR(默认)} BGR(默认)
- 通过Image.open(path)读入的图片为Image对象,不是普通的数组。 w , h = i m g . s i z e \color{red}{w, h = img.size} w,h=img.size、 R G B ( 默 认 ) \color{red}{RGB(默认)} RGB(默认)
将 P I L \color{red}{PIL} PIL类型转化成numpy类型之后: H ∗ W ∗ C \color{red}{H*W*C} H∗W∗C - p l t \color{red}{plt} plt。matplotlib.pyplot.imshow()和matplotlib.pyplot.show()正好可以对应PIL对象读入的RGB,示例如下:
# 2. cover show
def show_mask_in_img2(imgfile, maskfile, trueMaskfile):
image1 = Image.open(imgfile)
image2 = Image.open(maskfile)
image3 = Image.open(trueMaskfile)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(image1)
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(image2)
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(image1)
plt.imshow(image2, alpha=0.5)
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(image3)
plt.show()
Ps:plt.imshow与cv2.imshow显示颜色问题
在用plt.imshow和cv2.imshow显示同一幅图时可能会出现颜色差别很大的现象。这是因为:
opencv的接口使用BGR,而matplotlib.pyplot 则是RGB模式
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('lena_std.tif')
b,g,r = cv2.split(img)
img2 = cv2.merge([r,g,b])
plt.subplot(121);plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(122);plt.imshow(img2)
plt.show()
cv2.imshow('bgr image',img)
cv2.imshow('rgb image',img2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
程序运行结果如下:
Matplotlib显示结果
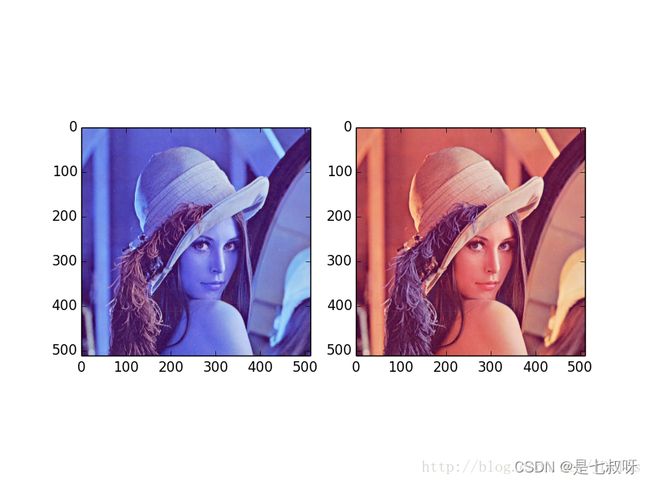
OpenCV显示结果

参考:Extracting a region from an image using slicing in Python, OpenCV
Image.open加载图片的代码示例如下:
# Load Image
img_fn = os.path.join(self.input_path, filenames)
img = Image.open(img_fn) # RGB(默认)
# img.show()
# resize/crop if needed:[128*128*3]
if self.input_size != 0:
height = width = self.input_size
img = img.resize((height, width), Image.BILINEAR)
# 将PIL类型转化成numpy类型
img = np.array(img).uint8() # H*W*C
Ps:transforms.Resize()的简单用法
而一般输入深度网络的特征图长宽是相等的,就不能采取等比例缩放的方式了,需要同时指定长宽:
transforms.Resize([h, w])
例如transforms.Resize([224, 224])就能将输入图片转化成224×224的输入特征图。
这样虽然会改变图片的长宽比,但是本身并没有发生裁切,仍可以通过resize方法返回原来的形状:
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
img = Image.open('1.jpg')
w, h = img.size
resize = transforms.Resize([224,244])
img = resize(img)
img.save('2.jpg')
resize2 = transforms.Resize([h, w])
img = resize2(img)
img.save('3.jpg')
需要注意的一点是PILImage对象size属性返回的是w, h,而resize的参数顺序是h, w。
注:对于Image.open()函数默认彩色图像读取通道的顺序为RGB,而cv2.imread()读取通道的顺序为BGR。
当 图 像 格 式 为 R G B A 时 \color{red}{当图像格式为RGBA时} 当图像格式为RGBA时,Image.open(‘—.jpg’)读取的格式为RGBA(其中A表示图像的alpha通道,即RGBA共四个通道),而cv2.imread(’—.jpg’)读取的格式是BGR,只有三个通道。
通过使用cv2.split(img)可得到cv2.imread()读取的图片img的BGR通道值。即使图片是RGBA四通道,cv2.imread()方法仍然读取的是BGR三通道。
resize的尺寸(根据random()函数来看是取不到1.5的):
# uniform(1 , 6)
# output: 3.001161523486847
scaled_size = int(random.uniform(1, 1.5)*input_size)
Ps:Python 中的 random.uniform( ) 函数
- x – 随机数的最小值,包含该值。
- y – 随机数的最大值,不包含该值。
- 返回一个浮点数
实例
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
import random
print("uniform(1 , 6) 的随机返回值为 : ", random.uniform(1 , 6))
print("uniform(10, 16) 的随机返回值为 : ", random.uniform(10, 16))
# 输出:
# uniform(1 , 6) 的随机返回值为 : 3.001161523486847
# uniform(10, 16) 的随机返回值为 : 13.70906147017741
flip水平翻转random()概率
output: 0 <= n < 1.0
flip_flag = random.random()
Ps:CaNet-master中代码,当random出的值>0.5的时候才会进行水平翻转:
def flip(self, flag, img):
if flag > 0.5:
return F.hflip(img)
else:
return img
最后调用ToTensor函数从 H ∗ W ∗ C \color{red}{H*W*C} H∗W∗C转为 C ∗ H ∗ W \color{red}{C*H*W} C∗H∗W:
self.ToTensor = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
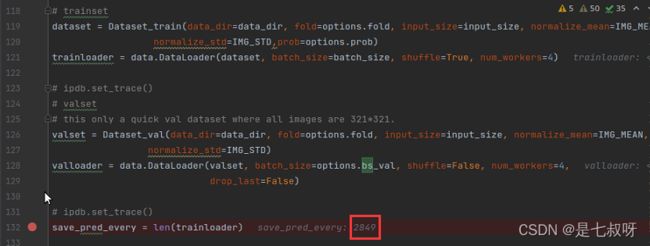
save_pred_every = len(trainloader)
下面的save_pred_every = len(trainloader)其实是11394/4=2848.5之后没有抛弃得到的2849个batch_size
1.23 DataLoader定义batch_size装载图片 C ∗ H ∗ W \color{red}{C*H*W} C∗H∗W为 B ∗ C ∗ H ∗ W \color{red}{B*C*H*W} B∗C∗H∗W
dataset = Dataset_train(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD,prob=options.prob)
trainloader = data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# ipdb.set_trace()
# valset
# this only a quick val dataset where all images are 321*321.
valset = Dataset_val(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD)
valloader = data.DataLoader(valset, batch_size=options.bs_val, shuffle=False, num_workers=4,
drop_last=False)
1.24 margin_h = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)是取闭区间[0,scaled_size - input_size]中的一个int数。
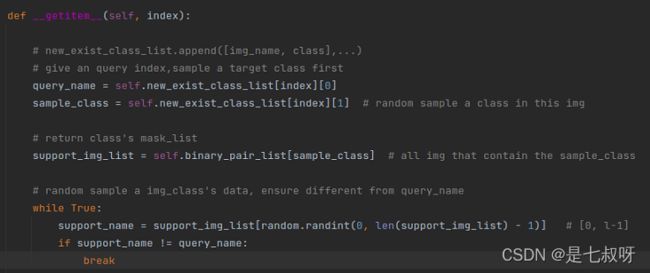
附:CaNet-master Dataset类__getitem__方法完整代码:
def __getitem__(self, index):
# new_exist_class_list.append([img_name, class],...)
# give an query index,sample a target class first
query_name = self.new_exist_class_list[index][0]
sample_class = self.new_exist_class_list[index][1] # random sample a class in this img
# return class's mask_list
support_img_list = self.binary_pair_list[sample_class] # all img that contain the sample_class
# random sample a img_class's data, ensure different from query_name
while True:
support_name = support_img_list[random.randint(0, len(support_img_list) - 1)] # [0, l-1]
if support_name != query_name:
break
# input_size=[321, 321]
input_size = self.input_size[0]
# random scale and crop for support
# uniform(1 , 6)
# output: 3.001161523486847
scaled_size = int(random.uniform(1, 1.5)*input_size)
# interpolation (int, optional): Desired interpolation enum defined by `filters`_.
# Default is ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``.
# If input is Tensor, only ``PIL.Image.NEAREST``, ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``and ``PIL.Image.BICUBIC`` are supported.
scale_transform_mask = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.NEAREST)
scale_transform_rgb = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.BILINEAR)
# output: 0 <= n < 1.0
flip_flag = random.random()
support_rgb = self.normalize(
self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_rgb(
self.flip(flip_flag,
# PIL format
Image.open(os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', support_name + '.jpg'))
))))
support_mask = self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_mask(
self.flip(flip_flag,
Image.open(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'Binary_map_aug', 'train', str(sample_class),
support_name + '.png')))))
margin_h = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
margin_w = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
# 3 * h * w, size_h_w
support_rgb = support_rgb[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
support_mask = support_mask[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
# random scale and crop for query
scaled_size = input_size
scale_transform_mask = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.NEAREST)
scale_transform_rgb = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.BILINEAR)
# query imgs don't flip
flip_flag = 0
query_rgb = self.normalize(
self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_rgb(
self.flip(flip_flag,
Image.open(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', query_name + '.jpg'))))))
query_mask = self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_mask(
self.flip(flip_flag,
Image.open(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'Binary_map_aug', 'train', str(sample_class),
query_name + '.png')))))
margin_h = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
margin_w = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
# ipdb.set_trace()
query_rgb = query_rgb[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
query_mask = query_mask[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
if self.history_mask_list[index] is None:
history_mask = torch.zeros(2,41,41).fill_(0.0)
else:
if random.random() > self.prob:
history_mask = self.history_mask_list[index]
else:
history_mask = torch.zeros(2, 41, 41).fill_(0.0)
return query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index
def flip(self, flag, img):
if flag > 0.5:
return F.hflip(img)
else:
return img
def __len__(self):
return len(self.new_exist_class_list)
二、网络训练
针对每一个epoch都有如下:
for epoch in range(0, num_epoch):
begin_time = time.time()
tqdm_gen = tqdm.tqdm(trainloader)
for i_iter, batch in enumerate(tqdm_gen):
query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index = batch
query_rgb = (query_rgb).cuda(0)
support_rgb = (support_rgb).cuda(0)
support_mask = (support_mask).cuda(0)
query_mask = (query_mask).cuda(0).long() # change formation for crossentropy use
query_mask = query_mask[:, 0, :, :] # remove the second dim,change formation for crossentropy use
history_mask=(history_mask).cuda(0)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# pred = torch.Size([4, 2, 41, 41])
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
# index 1 sum = 1
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
# update history mask
for j in range (support_mask.shape[0]):
sub_index = index[j]
dataset.history_mask_list[sub_index] = pred_softmax[j]
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)# upsample
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
# query mask:[4, 321, 321]
# output: tensor(n)
loss = loss_calc_v1(pred, query_mask, 0)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# highest_iou is last epoch max iou
# tqdm_gen.set_description('e:%d loss = %.4f-:%.4f' % (
tqdm_gen.set_description('epoch:%d loss = %.4f-:%.4f' % (epoch, loss.item(), highest_iou))
# save training loss
tempory_loss += loss.item()
if i_iter % (save_pred_every - 1) == 0 and i_iter != 0: # every epoch: save
print("---------------save----------------")
loss_list.append(tempory_loss / save_pred_every)
plot_loss(checkpoint_dir, loss_list, save_pred_every)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'loss_history.txt'), np.array(loss_list))
tempory_loss = 0
其中pred的tensor尺寸: p r e d = t o r c h . S i z e ( [ 4 , 2 , 41 , 41 ] ) \color{red}{pred = torch.Size([4, 2, 41, 41])} pred=torch.Size([4,2,41,41])
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
2.1 torch.max(input, dim) 函数
- 返回值:减少一个维度,两个Tensor 索引的最大值,索引)
_, pred_label = torch.max(pred, 1)
随后pred_label维度从 [ 64 , 2 , 321 , 321 ] \color{red}{[64, 2, 321, 321]} [64,2,321,321]变为:
- pred_label: [ 64 , 321 , 321 ] \color{red}{[64, 321, 321]} [64,321,321]
- query_mask:[64, 321, 321]
在64这里是每张图的最大值下标:0/1
inter_list, union_list, _, num_predict_list = get_iou_v1(query_mask, pred_label)
下面通过一个实例可以更容易理解这个函数的用法。
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[1,5,62,54], [2,6,2,6], [2,65,2,6]])
print(a)
# 输出:
tensor([[ 1, 5, 62, 54],
[ 2, 6, 2, 6],
[ 2, 65, 2, 6]])
索引每行的最大值:(在计算准确率时第一个tensor values是不需要的,所以我们只需提取第二个tensor,并将tensor格式的数据转换成array格式。)
torch.max(a, 1)
# 输出:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([62, 6, 65]),
indices=tensor([2, 3, 1]))
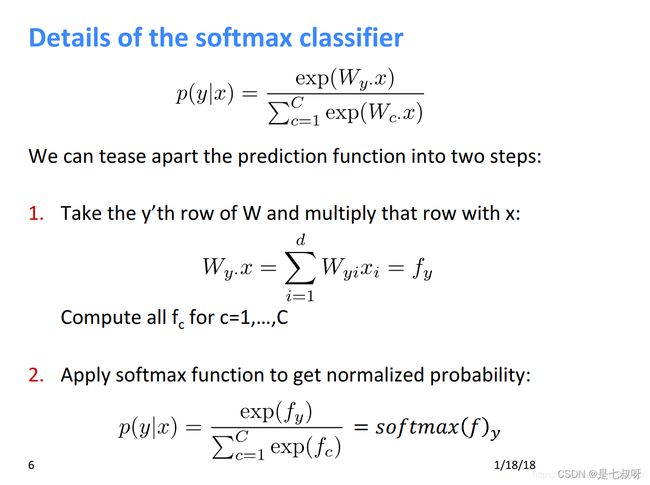
2.2 softmax(index 1 sum = 1)
之后经过softmax后(index 1 sum = 1),之后尺寸变为: p r e d s o f t m a x = T e n s o r : ( 4 , 2 , 41 , 41 ) \color{red}{pred_softmax=Tensor:(4,2,41,41)} predsoftmax=Tensor:(4,2,41,41)
其中,[4, 2, 41, 41]的softmax dim=1表示每一个像素点2class概率之和为1。(2分类:背景目标)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
softmax的维度为1的时候,是下标为1的这个维度所有元素之和为1:
>>> import torch
>>> import torch.nn.functional as F
>>> logits = torch.rand(2,2)
>>> pred = F.softmax(logits, dim=1)
>>> logits
tensor([[0.4140, 0.4571],
[0.9392, 0.6504]])
>>> pred
tensor([[0.4892, 0.5108],
[0.5717, 0.4283]])
>>>
2.3 nn.functional.interpolate
这个函数是用来上采样或下采样,可以给定size或者scale_factor来进行上下采样。同时支持3D、4D、5D的张量输入。
插值算法可选:最近邻、线性、双线性等等。
CaNet-master代码使用双线性插值上采样:
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)# upsample
2.4 计算损失:torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
- query mask:[4, 321, 321]
- output: tensor(n)
loss = loss_calc_v1(pred, query_mask, 0)
看代码是直接使用的交叉熵损失
Pytorch中CrossEntropyLoss()函数的主要是将softmax-log-NLLLoss合并到一块得到的结果。
1、Softmax后的数值都在0~1之间,所以ln之后值域是负无穷到0。
2、然后将Softmax之后的结果取log,将乘法改成加法减少计算量,同时保障函数的单调性 。其
其中x是网络的输出向量,class是真实标签。
代码:
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
# query mask:[4, 321, 321]
# output : tensor
def loss_calc_v1(pred, label, gpu):
label = label.long()
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=255).cuda(gpu)
return criterion(pred, label)
三、验证集val Evaluation
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
# update history mask
for j in range(support_mask.shape[0]):
sub_index = index[j]
valset.history_mask_list[sub_index] = pred_softmax[j]
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear',
align_corners=True) # upsample # upsample
_, pred_label = torch.max(pred, 1)
# pred_label:[64, 321, 321]
# query_mask:[64, 321, 321]
inter_list, union_list, _, num_predict_list = get_iou_v1(query_mask, pred_label)
for j in range(query_mask.shape[0]): # batch size
# fold 0 : 1-5 - 10
# fold 1 : 6-10 - 6
all_inter[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += inter_list[j]
all_union[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += union_list[j]
3.1 计算IOU
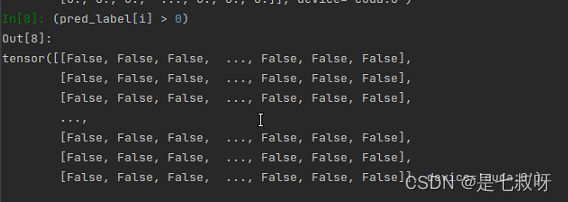
3.11 输出布尔值的Tensor:
(pred_label[i] > 0)
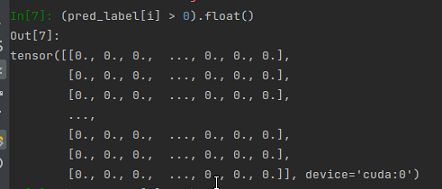
3.12 输出0/1值的Tensor:
(pred_label[i] > 0).float()
torch.sum((pred_label[i] > 0).float())
3.13 之后求内部所有值的和:
.item()方法返回张量元素的值。
其中sample_class经过打包之后变成:
query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index = batch
四、损失函数
4.1 val
4.11 在eval()阶段会使用with torch.no_grad()
而使用no_grad则设置让梯度Autograd设置为False(因为在训练中我们默认是True),这样保证了反向过程为纯粹的测试,而不变参数。
参考文档说这样避免每一个参数都要设置,解放了GPU底层的时间开销,在测试阶段统一梯度设置为False
4.12 验证的时候batch_size=64,枚举valloader:
for i_iter, batch in enumerate(valloader):
query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index = batch
query_rgb = (query_rgb).cuda(0)
support_rgb = (support_rgb).cuda(0)
support_mask = (support_mask).cuda(0)
query_mask = (query_mask).cuda(0).long() # change formation for crossentropy use
query_mask = query_mask[:, 0, :, :] # remove the second dim,change formation for crossentropy use
history_mask = (history_mask).cuda(0)
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
# update history mask
for j in range(support_mask.shape[0]):
sub_index = index[j]
valset.history_mask_list[sub_index] = pred_softmax[j]
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear',
align_corners=True) #upsample # upsample
_, pred_label = torch.max(pred, 1)
# pred_label:[64, 321, 321]
# query_mask:[64, 321, 321]
inter_list, union_list, _, num_predict_list = get_iou_v1(query_mask, pred_label)
for j in range(query_mask.shape[0]): # batch size
# fold 0 : 1-5 - 10
# fold 1 : 6-10 - 6
all_inter[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += inter_list[j]
all_union[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += union_list[j]
IOU = [0] * 5
for j in range(5):
IOU[j] = all_inter[j] / all_union[j]
mean_iou = np.mean(IOU)
print('IOU:%.4f' % (mean_iou))
if mean_iou > best_iou:
best_iou = mean_iou
else:
break
4.13 每个DataLoader打包好的64张图片,计算inter之和、union之和、mIOU
for j in range(query_mask.shape[0]): # batch size
# fold 0 : 1-5 - 10
# fold 1 : 6-10 - 6
all_inter[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += inter_list[j]
all_union[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += union_list[j]
由于每次测试使用5cls,所以枚举5次,索引0-4,计算 I O U \color{red}{IOU} IOU和 m I O U \color{red}{mIOU} mIOU:
for j in range(5):
IOU[j] = all_inter[j] / all_union[j]
mean_iou = np.mean(IOU)
保存best_iou
print('IOU:%.4f' % (mean_iou))
if mean_iou > best_iou:
best_iou = mean_iou
else:
break
4.14 通过plot_iou函数来画出IOU随着每个epoch的变化曲线,并保存最好的权重:
iou_list.append(best_iou)
plot_iou(checkpoint_dir, iou_list)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'iou_history.txt'), np.array(iou_list))
if best_iou > highest_iou:
highest_iou = best_iou
model = model.eval()
torch.save(model.cpu().state_dict(), osp.join(checkpoint_dir, 'model', 'best' '.pth'))
model = model.train()
best_epoch = epoch
print('A better model is saved')
在训练和测试函数中model.eval(),和model.train()的区别
一般情况下,我们训练过程如下:
1、拿到数据后进行训练,在训练过程中,使用
model.train():告诉我们的网络,这个阶段是用来训练的,可以更新参数。
2、训练完成后进行预测,在预测过程中,使用
model.eval() : 告诉我们的网络,这个阶段是用来测试的,于是模型的参数在该阶段不进行更新。
其中,里面的model = model.eval()、model = model.train()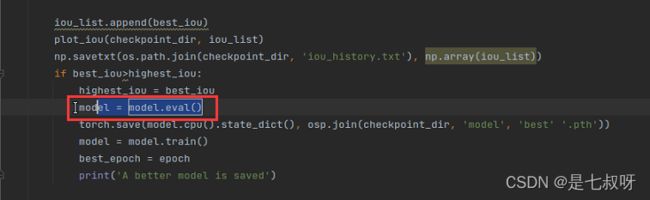
五、可视化
自己写了一个test.py函数。
5.1 加载best.pth
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pthfile, map_location='cpu'))
model.cuda()
5.2 输出预测的mask(321,321)
输出的pred_label维度[64, 321, 321],之后pred_label[i]维度为[321, 321],使用cv2.imwrite无最后一个维度,输出灰度图
- Image.open()之后对象通道数为: [ W , H ] \color{red}{[W, H]} [W,H],可以通过w, h = img.size()知道;(如果之后转numpy数组会变成 [ H , W , C ] \color{red}{[H, W, C]} [H,W,C])
- 之后转Tensor变为 [ C , H , W ] \color{red}{[C, H, W]} [C,H,W],像素值由0-255变为0-1
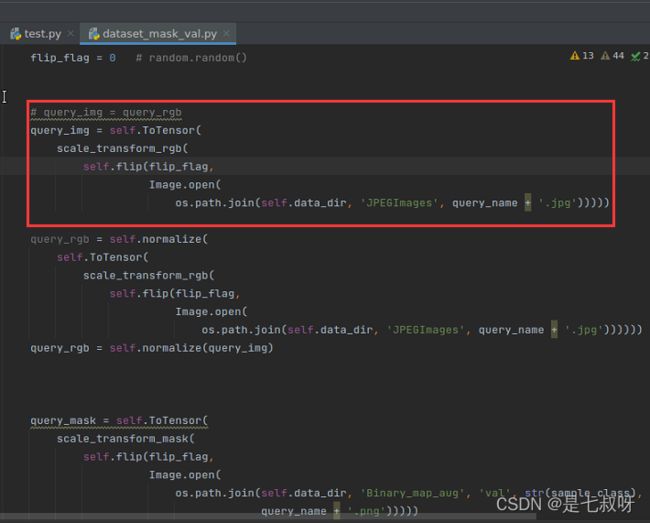
修改dataset_val将没有标准化的、resize过的Tensor query图像取出:
输出mask图: - 在每一个打包后的dataloader中(这里是64张图片),将pred_mask移动到cpu上(不移动会报错),(张量与数组运算报错(Use Tensor.cpu() to copy the tensor to host memory first;RuntimeError: Expected all tensors to be on the same device))
- 转numpy数组后维度变为 [ C , H , W ] \color{red}{[C, H, W]} [C,H,W]
- 最后通过修改dataset_val得到query_name[i],img*255之后,通过cv2.imwrite保存图片(实验室服务器cv2.show函数会出问题)
- 不用加img_rgb = np.uint8(img_rgb),因为cv2.imwrite函数会自动改变数据类型。
for i in range(pred_label.shape[0]):
pred_mask = pred_label[i]
img = pred_mask.cpu().numpy()
cv2.imwrite(pth_file + '{}_pre.jpg'.format(query_name[i]), 255 * img)
cv2.waitKey(100)
Ps:为什么0是黑色,255是白色?
在单色图中, intensity 是 强度 gray scale 是灰度。而强度一般由 光源的能量和物体反射能量的比例的乘积 决定。 所以如果能量很低,颜色就很暗,极限就是能量为0,是黑色,而能量很大,就很亮,就是白色。
5.3 输出对应于mask的原图(所预测的等比例resize后的原图)
transpose、permute()和reshape的区别:
参考:numpy的reshape和transpose机制解释
参考:Pytorch中view, transpose, permute等方法的区别

- t r a n s p o s e 与 p e r m u t e 会 实 实 在 在 的 根 据 需 求 ( 要 交 换 的 d i m ) 把 相 应 的 T e n s o r 元 素 \color{red}{transpose与permute会实实在在的根据需求(要交换的dim)把相应的Tensor元素} transpose与permute会实实在在的根据需求(要交换的dim)把相应的Tensor元素的位置进行调整, 而view 会将Tensor所有维度拉平成一维 (即按行, 这 也 是 为 什 么 v i e w 操 作 要 求 T e n s o r 是 c o n t i g u o u s 的 原 因 \color{red}{这也是为什么view操作要求Tensor是contiguous的原因} 这也是为什么view操作要求Tensor是contiguous的原因),然后再根据传入的的维度(只要保证各维度的乘积=总元素个数即可)信息重构出一个Tensor。
- transpose改变了数组的维度(axis)排列顺序。比如对于二维数组,如果我们把两个维度的顺序互换,那就是我们很熟悉的矩阵转置。而transpose可以在更多维度的情况下生效。transpose的入参是输出数组的维度排列顺序,序号从0开始计数。
- reshape仅仅只是改变了数组的shape属性,比如把shape从( 4 , ) (4,)(4,)改成( 2 , 2 ) (2,2)(2,2)
如果我们从最后一个维度开始,依次向前循环打印数组的话,会发现无论怎么样reshape,数组打印的顺序不会发生任何变化。也就是说无论reshape多少次,数组打印顺序不变。
类似于python的浅拷贝,reshape之后,尽管变量发生了变化,但是变量内的数据体却未被碰过。下面列子中,改变reshape后的b的第一个值,发现所有相关的变量的第一个值都发生了变化,所以就可以知道,经reshape后,变量用于保存数据的那块内存没有被碰过。
transpose 与 reshape 的最大区别: reshape 修改的只是维度,填充顺序不变,transpose 修改的是轴,填充顺序改变
- img_rgb输出后维度(3, 321, 321),由于是Image.open打开的,所以第一个维度的3表示每张321*321图的RGB值
- transpose((1, 2, 0))之后,一张321*321的矩阵,每个点都有RGB3个值,是正常的
- !!!如果使用reshape,就会出现问题,示例图如下:
img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]
img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().reshape([321, 321, 3])[:, :, ::-1]
原图:(没有resize为321, 321)resize之后应该为(3, 321, 321)

当使用reshape的时候,是类似于这样的,会造成困扰,所以怀疑是reshape函数不行:

不修改C通道:(RGB的使用cv2默认是BGR,红色的原图R被输出成了蓝色的B)
- RGB—>
- BGR

使用transpose后,再通过 [ : , : , : : − 1 ] \color{red}[:, :, ::-1]{} [:,:,::−1]修改RGB为BGR,就完全正常了:(参考:pytorch实现HWC转CHW)
Ps: i m g 2 = i m g [ : , : , [ 2 , 1 , 0 ] ] \color{red}{img_2 = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]} img2=img[:,:,[2,1,0]]将最后一个维度C—>BGR(0,1,2)转为RGB(2,1,0)
img_2 = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
plt.imshow(img_2)
主要添加的代码:
# c h w
img_rgb = query_img[i]
img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]
# img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().reshape([321, 321, 3])[:, :, ::-1]
# img_rgb = np.uint8(img_rgb)
cv2.imwrite(pth_file + '{}.jpg'.format(query_name[i]), img_rgb * 255)
cv2.waitKey(100)
5.4 可视化完整代码
test.py
"""Evaluation Script"""
import os
import shutil
import cv2
import tqdm
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.optim
import torch.nn as nn
from PIL import Image
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
from torchvision.transforms import Compose
import ipdb
from torch.utils import data
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import os.path as osp
from utils import *
import time
import torch.nn.functional as F
import tqdm
import random
import argparse
from dataset_mask_train import Dataset as Dataset_train
from dataset_mask_val import Dataset as Dataset_val
import os
import torch
# from network import Res_Deeplab
from one_shot_network import Res_Deeplab
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-lr',
type=float,
help='learning rate',
default=0.00025)
parser.add_argument('-prob',
type=float,
help='dropout rate of history mask',
default=0.7)
parser.add_argument('-bs',
type=int,
help='batchsize',
default=4)
parser.add_argument('-bs_val',
type=int,
help='batchsize for val',
default=64)
parser.add_argument('-fold',
type=int,
help='fold',
# default=1)
default=0)
parser.add_argument('-gpu',
type=str,
help='gpu id to use',
# default='0,1')
default='0, 1')
parser.add_argument('-iter_time',
type=int,
default=5)
options = parser.parse_args()
# data_dir = '/your/dataset/dir/VOCdevkit/VOC2012'
data_dir = './dataset/dir/VOCdevkit/VOC2012'
#set gpus
gpu_list = [int(x) for x in options.gpu.split(',')]
os.environ['CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER'] = 'PCI_BUS_ID'
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = options.gpu
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
IMG_MEAN = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
IMG_STD = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
num_class = 2
num_epoch = 200
learning_rate = options.lr # 0.000025#0.00025
input_size = (321, 321)
batch_size = options.bs
weight_decay = 0.0005
momentum = 0.9
power = 0.9
cudnn.enabled = True
# Create network.
model = Res_Deeplab(num_classes=num_class)
# load resnet-50 pretrained parameter
model = load_resnet50_param(model, stop_layer='layer4')
model = nn.DataParallel(model, [0, 1])
# disable the gradients of not optimized layers
turn_off(model)
checkpoint_dir = 'checkpoint/fo=%d/'% options.fold
check_dir(checkpoint_dir)
# loading data
# trainset
dataset = Dataset_train(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD,prob=options.prob)
trainloader = data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# ipdb.set_trace()
# valset
# this only a quick val dataset where all images are 321*321.
valset = Dataset_val(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD)
valloader = data.DataLoader(valset, batch_size=options.bs_val, shuffle=False, num_workers=4,
drop_last=False)
# ipdb.set_trace()
save_pred_every = len(trainloader)
optimizer = optim.SGD([{'params': get_10x_lr_params(model), 'lr': 10 * learning_rate}],
lr=learning_rate, momentum=momentum, weight_decay=weight_decay)
loss_list = [] #track training loss
iou_list = [] #track validaiton iou
highest_iou = 0
pthfile = '/media/D_4TB/zhouhongjie/1.few-shot segmentation/3.CaNet/CaNet-master/checkpoint/fo=000/model/best.pth'
pth_file = '/media/D_4TB/zhouhongjie/1.few-shot segmentation/3.CaNet/CaNet-master/checkpoint/fo=0/pred_img/'
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pthfile, map_location='cpu'))
model.cuda()
tempory_loss = 0 # accumulated loss
# model = model.train()
best_epoch=0
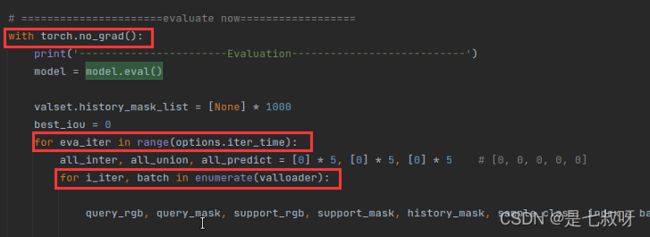
if __name__ == '__main__':
with torch.no_grad():
print('-----------------------Evaluation---------------------------')
model = model.eval()
valset.history_mask_list = [None] * 1000
best_iou = 0
for eva_iter in range(options.iter_time):
all_inter, all_union, all_predict = [0] * 5, [0] * 5, [0] * 5 # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for i_iter, batch in enumerate(valloader):
query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index, query_name, query_img = batch
query_rgb = (query_rgb).cuda(0)
support_rgb = (support_rgb).cuda(0)
support_mask = (support_mask).cuda(0)
query_mask = (query_mask).cuda(0).long() # change formation for crossentropy use
query_mask = query_mask[:, 0, :, :] # remove the second dim,change formation for crossentropy use
history_mask = (history_mask).cuda(0)
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
# update history mask
for j in range(support_mask.shape[0]):
sub_index = index[j]
valset.history_mask_list[sub_index] = pred_softmax[j]
# pred:[64, 2, 321, 321]
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear',
align_corners=True) # upsample # upsample
_, pred_label = torch.max(pred, 1)
for i in range(pred_label.shape[0]):
# # output query pred_mask
# # pred_label = np.array(pred_label)
# # [321, 321]
# pred_mask = pred_label[i]
# img = pred_mask.cpu().numpy()
# # cv2.imshow("result", img)
# cv2.imwrite(pth_file + '/masks/' + '{}_pre.jpg'.format(query_name[i]), 255 * img)
# cv2.waitKey(100)
#
# # c h w
# # output query img
# img_rgb = query_img[i]
# img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]
# # img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().reshape([321, 321, 3])[:, :, ::-1]
# # img_rgb = np.uint8(img_rgb)
# cv2.imwrite(pth_file + '/images/' + '{}.jpg'.format(query_name[i]), img_rgb * 255)
# cv2.waitKey(100)
# output query_mask
true_mask = query_mask[i]
true_mask = true_mask.cpu().numpy()
cv2.imwrite(pth_file + '/trueMasks/' + '{}_true.jpg'.format(query_name[i]), 255 * true_mask)
cv2.waitKey(100)
# pred_label:[64, 321, 321]
# query_mask:[64, 321, 321]
inter_list, union_list, _, num_predict_list = get_iou_v1(query_mask, pred_label)
for j in range(query_mask.shape[0]): # batch size
# fold 0 : 1-5 - 10
# fold 1 : 6-10 - 6
all_inter[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += inter_list[j]
all_union[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += union_list[j]
IOU = [0] * 5
for j in range(5):
IOU[j] = all_inter[j] / all_union[j]
mean_iou = np.mean(IOU)
print('IOU:%.4f' % (mean_iou))
if mean_iou > best_iou:
best_iou = mean_iou
else:
break
# iou_list.append(best_iou)
# plot_iou(checkpoint_dir, iou_list)
# np.savetxt(os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'iou_history.txt'), np.array(iou_list))
# if best_iou > highest_iou:
# highest_iou = best_iou
# model = model.eval()
# torch.save(model.cpu().state_dict(), osp.join(checkpoint_dir, 'model', 'best' '.pth'))
# model = model.train()
# best_epoch = epoch
# print('A better model is saved')
#
# print('IOU for this epoch: %.4f' % (best_iou))
#
# model = model.train()
# model.cuda()
#
# epoch_time = time.time() - begin_time
# print('best epoch:%d ,iout:%.4f' % (best_epoch, highest_iou))
# print('This epoch taks:', epoch_time, 'second')
# print('still need hour:%.4f' % ((num_epoch - epoch) * epoch_time / 3600))
# 1. margin show
def show_mask_in_img(imgfile, maskfile):
img = cv2.imread(imgfile, 1)
mask = cv2.imread(maskfile, 0)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 1)
img = img[:, :, ::-1]
img[..., 2] = np.where(mask == 1, 255, img[..., 2])
plt.imshow(img, alpha=0.6)
plt.show()
# 2. cover show
def show_mask_in_img2(imgfile, maskfile, trueMaskfile, pred_img_save_name):
image1 = Image.open(imgfile)
image2 = Image.open(maskfile)
image3 = Image.open(trueMaskfile)
# img = Image.open(imgfile) # 打开图片
# mask = sio.loadmet(maskfile) # 打开掩膜
# array = np.array(img)
# # array维度 [W, H, C] -> [C, W, H]
# array = np.transpose(array, [2, 0, 1])
# array = array * mask # 点乘
# # array维度 [C, W, H] -> [W, H, C]
# array = np.transpose(array, [1, 2, 0])
# img = Image.fromarray(array, mode='RGB') # ????
# img.show()
image1 = image1.convert('RGBA')
image2 = image2.convert('RGBA') # RGBA save to jpg ERROR, but to png TRUE
image = Image.blend(image1, image2, 0.4)
# image.show()
image.save(pred_img_save_name)
# image1 = plt.imread(imgfile)
# image2 = plt.imread(maskfile)
# image3 = plt.imread(trueMaskfile)
#
# plt.figure()
#
# plt.subplot(221)
# plt.imshow(image1)
#
# # plt.title("pred_mask")
# plt.subplot(222)
# plt.imshow(image2)
#
# # plt.title("pred_mask_img")
# plt.subplot(223)
# plt.imshow(image1)
# plt.imshow(image2, alpha=0.5)
#
# # plt.title("true_mask_img")
# plt.subplot(224)
# plt.imshow(image1)
# plt.imshow(image3, alpha=0.5)
#
# plt.show()
# 3. cover show 4 imgs
def show_mask_in_img2(imgfile, maskfile, trueMaskfile, pred_img_save_name):
image1 = Image.open(imgfile)
image2 = Image.open(maskfile)
image3 = Image.open(trueMaskfile)
# img = Image.open(imgfile) # 打开图片
# mask = sio.loadmet(maskfile) # 打开掩膜
# array = np.array(img)
# # array维度 [W, H, C] -> [C, W, H]
# array = np.transpose(array, [2, 0, 1])
# array = array * mask # 点乘
# # array维度 [C, W, H] -> [W, H, C]
# array = np.transpose(array, [1, 2, 0])
# img = Image.fromarray(array, mode='RGB')
# img.show()
#
# image1 = image1.convert('RGBA')
# image2 = image2.convert('RGBA') # RGBA save to jpg ERROR, but to png TRUE
# image = Image.blend(image1, image2, 0.4)
# # image.show()
# image.save(pred_img_save_name)
# image1 = plt.imread(imgfile)
# image2 = plt.imread(maskfile)
# image3 = plt.imread(trueMaskfile)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(image1)
# plt.title("pred_mask")
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(image2)
# plt.title("pred_mask_img")
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(image1)
plt.imshow(image2, alpha=0.5)
# plt.title("true_mask_img")
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(image1)
plt.imshow(image3, alpha=0.5)
# plt.show()
plt.savefig(pred_img_save_name)
val_show.py
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# import test
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
from PIL import Image
from test import show_mask_in_img, show_mask_in_img2
path_file = '/media/D_4TB/zhouhongjie/1.few-shot segmentation/3.CaNet/CaNet-master/checkpoint/fo=0/pred_img/'
img_path = os.path.join(path_file, 'images')
mask_path = os.path.join(path_file, 'masks')
show_path = os.path.join(path_file, 'show')
trueMask_path = os.path.join(path_file, 'trueMasks')
pred_img_save_path = os.path.join(path_file, 'pred_img')
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in os.listdir(img_path):
img_name = os.path.join(img_path, i) # all path
img_number = i.split('.')[0]
mask_name = os.path.join(mask_path, img_number + '_pre.jpg')
trueMask_name = os.path.join(trueMask_path, img_number + '_true.jpg')
pred_img_save_name = os.path.join(pred_img_save_path, img_number + '_prePIL.png')
# show_mask_in_img(img_name, mask_name)
show_mask_in_img2(img_name, mask_name, trueMask_name, pred_img_save_name)
# image = mpimg.imread(img_name)
# image = np.require(image, dtype='f4', requirements=['O', 'W'])
# image.flags.writeable = True
# Image.fromarray(np.uint8(image))
# mask = mpimg.imread(mask_name)
# image = image[:, :, ::-1]
# image[:, :, :][mask[:, :] > 0] = 255
#
# show_name = os.path.join(show_path, img_number + '.png')
# cv2.imwrite(show_name, image)