Python实现XGBoost+长短记忆神经网络(LSTM)+随机森林(RF)分析布鲁克林篮网队胜利因素并预测下一场比赛结果
最近看NBA被篮网队所吸引,有进攻有防守而且观赏性很强,所以特此使用算法来分析一下篮网队赢球的关键因素有哪些,同时也简单预测下一场比赛结果,仅供参考。

数据来源:布鲁克林篮网队20-21赛季数据
http://slamdunk.sports.sina.com.cn/team/stats?tid=583ec9d6-fb46-11e1-82cb-f4ce4684ea4c
1.数据预处理
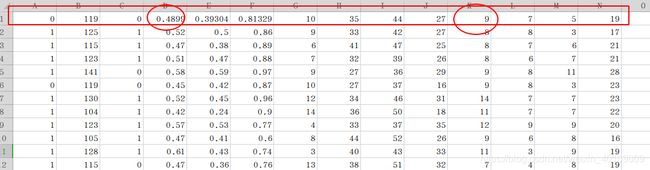
下载好的数据:
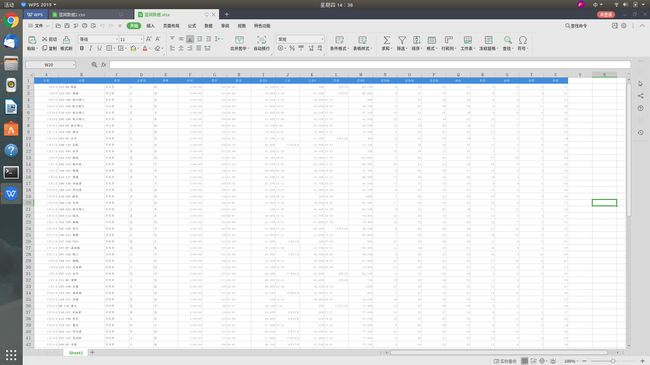
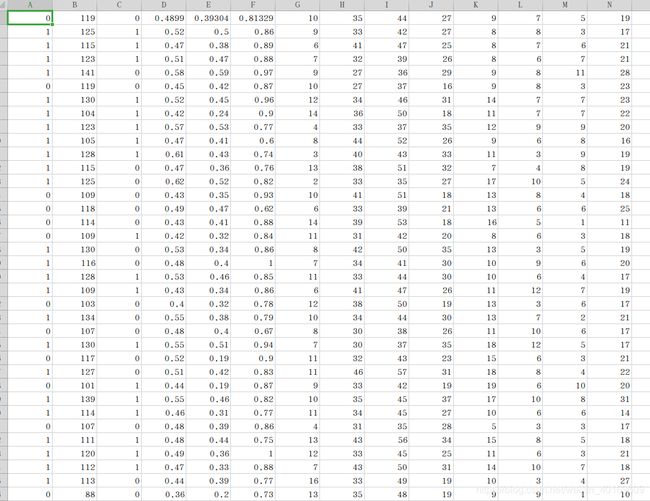
共包含:日期 比赛 类型 主客场 赛果 时间 得分 投篮 投篮% 三分 三分% 罚球 罚球% 前场板 后场板 总篮板 助攻 失误 抢断 盖帽 犯规 26列数据。
使用Excel公式将文本转化为数值:
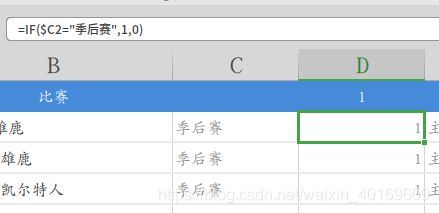
其中季后赛=1、常规赛=0、主场=1、客场=0、胜场=1、负场=0等,将全部数据转化为数值类型,删除一些不关心的数据,检索空格,一定要删除空格!一定要删除空格!一定要删除空格!否则一会读CSV时后有你受的。
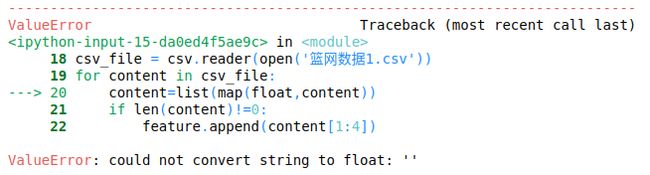
(改了半个小时才找到问题…,检索空格替换都不行,最后发现在后面有个“,”…删除就好了。)
最后将Excel转化成CSV文件,将胜负提到第一列。
CSV文件:
2.导包
用到了这么多包numpy、xgboost、matplotlib、csv、keras、pandas、metrics等
# plot feature importance using built-in function
from numpy import loadtxt
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from xgboost import plot_importance
from matplotlib import pyplot
import numpy as np
import csv
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.layers import LSTM
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from pandas import DataFrame
from pandas import Series
from pandas import concat
from pandas import read_csv
from pandas import datetime
3.导数据
#特征
feature=[]
#目标
target=[]
csv_file = csv.reader(open('篮网数据2.csv'))
for content in csv_file:
content=list(map(float,content))
if len(content)!=0:
feature.append(content[1:14])
target.append(content[0:1])
targets=[]
for i in target:
targets.append(i[0])
targets.reverse()
feature.reverse()
feature=np.array(feature)
targets=np.array(targets)
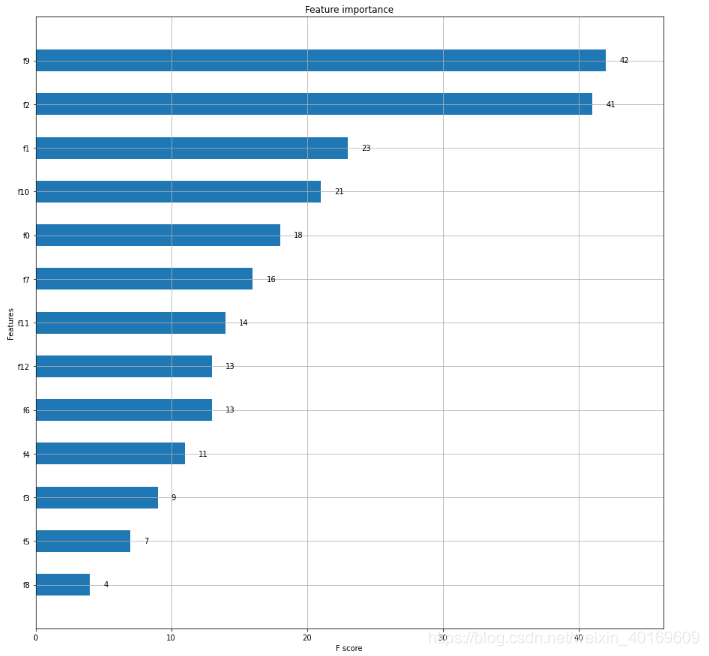
4.使用XGBoost分析影响胜负的关键因素
# fit model no training data
model = XGBClassifier()
model.fit(feature, targets)
# plot feature importance
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,15))
plot_importance(model,
height=0.5,
ax=ax,
max_num_features=64)
feature_AllName=['Total','HomeAndAway','FieldGoalPercentage','3-pointShootingPercentage',
'FreeThrowPercentage','TheFrontRebounds','TheBackRebounds','TotalRebounds',
'Assists','Error','Steals','Blocks','foul']
,
feature_name=[feature_AllName[9],feature_AllName[2],feature_AllName[12],feature_AllName[0]
,feature_AllName[1],feature_AllName[10],feature_AllName[7],feature_AllName[6]
,feature_AllName[4],feature_AllName[3],feature_AllName[5],feature_AllName[11]
,feature_AllName[8]]
feature_name.reverse()
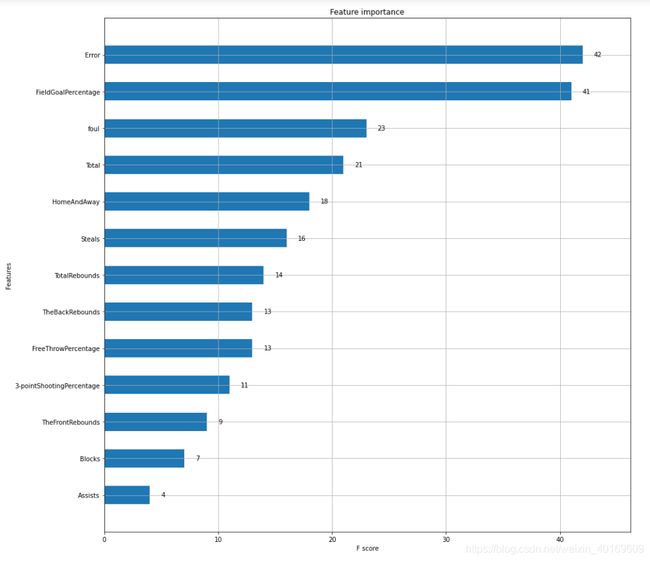
没想到啊,对篮网队来说,影响胜负的最关键因素是失误、其次是投篮命中率、接下来是犯规、总分、主客场、抢断…助攻是最不关键的因素。
5.使用LSTM对失误、投篮命中率进行单步预测
使用LSTM预测篮网下一场比赛的失误数、投篮命中率。其他因素没有二者关键,直接取平均值了…
重新取出失误数和投篮命中率:
ERROR=[]
FieldGoalPercentage=[]
csv_file = csv.reader(open('篮网数据2.csv'))
for content in csv_file:
content=list(map(float,content))
if len(content)!=0:
ERROR.append(content[10:11])
FieldGoalPercentage.append(content[3:4])
Foul.append(content[13:14])
Total.append(content[1:2])
HomeAndAway.append(content[2:3])
ERROR1=[]
for j in ERROR:
ERROR1.append(j[0])
FieldGoalPercentage1=[]
for j in FieldGoalPercentage:
FieldGoalPercentage1.append(j[0])
预测失误数:
结果等于:9(8.699947)
train, test =ERROR1[0:int(len(ERROR1)*0.7)],targets[int(len(ERROR1)*0.7):int(len(ERROR1))]
def timeseries_to_supervised(data, lag=1):
df = DataFrame(data)
columns = [df.shift(i) for i in range(1, lag+1)]
columns.append(df)
df = concat(columns, axis=1)
df.fillna(0, inplace=True)
return df
def fit_lstm(train, batch_size, nb_epoch, neurons):
X, y = train[:, 0:-1], train[:, -1]
X = X.reshape(X.shape[0], 1, X.shape[1])
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(neurons, batch_input_shape=(batch_size, X.shape[1], X.shape[2]), stateful=True))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error', optimizer='adam')
for i in range(nb_epoch):
model.fit(X, y, epochs=1, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=0, shuffle=False)
model.reset_states()
return model
# make a one-step forecast
def forecast_lstm(model, batch_size, X):
X = X.reshape(1, 1, len(X))
yhat = model.predict(X, batch_size=batch_size)
return yhat[0,0]
c2d=[]
for i in ERROR1:
c2d.append([i,i])
supervised= c2d # 转换数据集
c1d=[]
for j in supervised:
c1d.append(j[0])
supervised = timeseries_to_supervised(c1d, 1)
train_scaled, test_scaled =supervised[0:int(len(supervised)*0.7)], supervised[int(len(supervised)*0.7):int(len(supervised))]
train_scaled=np.array(train_scaled)
test_scaled=np.array(test_scaled)
print("开始")
# fit the model
lstm_model = fit_lstm(train_scaled, 1, 30, 4)
# forecast the entire training dataset to build up state for forecasting
train_reshaped = train_scaled[:, 0].reshape(len(train_scaled), 1, 1)
lstm_model.predict(train_reshaped, batch_size=1)
# walk-forward validation on the test data
predictions = list()
for i in range(len(test_scaled)):
# make one-step forecast
X, y = test_scaled[i, 0:-1], test_scaled[i, -1]
yhat = forecast_lstm(lstm_model, 1,X)
# store forecast
predictions.append(yhat)
print("结束")
预测投篮命中率:
结果等于:0.48989984
train, test =FieldGoalPercentage1[0:int(len(FieldGoalPercentage1)*0.7)],targets[int(len(FieldGoalPercentage1)*0.7):int(len(FieldGoalPercentage1))]
def timeseries_to_supervised(data, lag=1):
df = DataFrame(data)
columns = [df.shift(i) for i in range(1, lag+1)]
columns.append(df)
df = concat(columns, axis=1)
df.fillna(0, inplace=True)
return df
def fit_lstm(train, batch_size, nb_epoch, neurons):
X, y = train[:, 0:-1], train[:, -1]
X = X.reshape(X.shape[0], 1, X.shape[1])
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(neurons, batch_input_shape=(batch_size, X.shape[1], X.shape[2]), stateful=True))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error', optimizer='adam')
for i in range(nb_epoch):
model.fit(X, y, epochs=1, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=0, shuffle=False)
model.reset_states()
return model
# make a one-step forecast
def forecast_lstm(model, batch_size, X):
X = X.reshape(1, 1, len(X))
yhat = model.predict(X, batch_size=batch_size)
return yhat[0,0]
c2d=[]
for i in FieldGoalPercentage1:
c2d.append([i,i])
supervised= c2d # 转换数据集
c1d=[]
for j in supervised:
c1d.append(j[0])
supervised = timeseries_to_supervised(c1d, 1)
train_scaled, test_scaled =supervised[0:int(len(supervised)*0.7)], supervised[int(len(supervised)*0.7):int(len(supervised))]
train_scaled=np.array(train_scaled)
test_scaled=np.array(test_scaled)
print("开始")
# fit the model
lstm_model = fit_lstm(train_scaled, 1, 30, 4)
# forecast the entire training dataset to build up state for forecasting
train_reshaped = train_scaled[:, 0].reshape(len(train_scaled), 1, 1)
lstm_model.predict(train_reshaped, batch_size=1)
# walk-forward validation on the test data
predictions = list()
for i in range(len(test_scaled)):
# make one-step forecast
X, y = test_scaled[i, 0:-1], test_scaled[i, -1]
yhat = forecast_lstm(lstm_model, 1,X)
# store forecast
predictions.append(yhat)
print("结束")
6.修改原始数据集
预设篮网下一场输了,投篮命中率维0.489、失误9个。其他数值去平均数四舍五入。
7.使用随机森林算法(RF)预测篮网队下一场比赛胜负
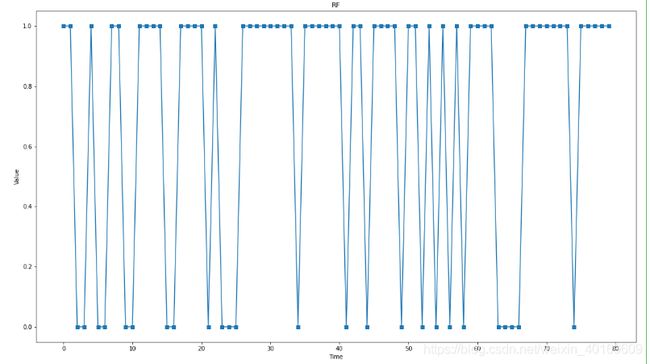
先显示出篮网队20-21赛季全部胜负场。
plt.plot(targets,marker='s')#测试数组
fig = plt.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(18.5, 10.5)
plt.title("RF") # 标题
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.show()
使用RF算法:
设置seed为5 防止每次预测效果不同。可以自行修改。
手动分割训练集和测试集,分割点为0.8。
from numpy.random import seed
seed(5)
feature_train=feature[0:int(len(feature)*0.80)]
target_train=targets[0:int(len(targets)*0.80)]
feature_test=feature[int(len(feature)*0.80):int(len(feature))]
target_test=targets[int(len(targets)*0.80):int(len(targets))]
# clf = RandomForestClassifier(criterion='entropy')
clf = RandomForestClassifier()
clf.fit(feature_train,target_train)
predict_results=clf.predict(feature_test)
plt.plot(target_test,marker='s')#测试数组
plt.plot(predict_results,marker='o')#测试数组
plt.legend(['True','RF'])
fig = plt.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(18.5, 10.5)
plt.title("RF") # 标题
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.show()
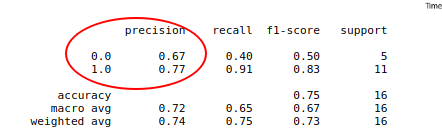
print(classification_report(target_test, predict_results))
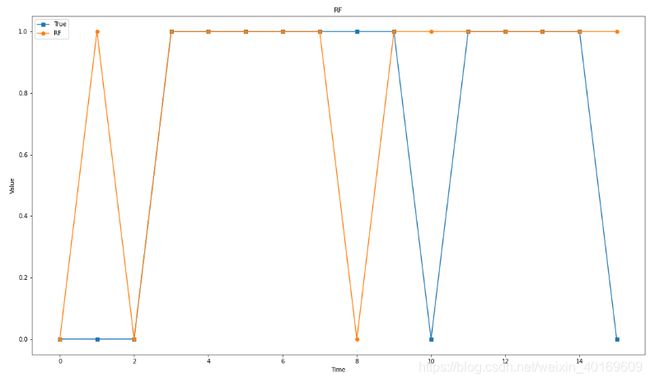
结果如下:
最后一场是随便设置的输球,但RF预测是赢球。
除去最后一场外,其他15场预测对了12场,准确率为80%。
进一步求精度:
print(classification_report(target_test, predict_results))
可知,预测赢球准确率为77%,预测输球准确率为67%,而RF预测下场赢球,故下一场赢球的可能性为77%!!
以上实验仅供学习参考,真实情况远比数据所描述的情况复杂的多,球员受伤、拉肚子、打架、心情不好、某某球员爆发、裁判原因等情况很多,所以结果仅供娱乐,但是我还是很看好篮网赢球的。
实验中LSTM可以对全部特征都进行预测,也可以可以调参,如果使用优化算法调优相信模型精度还会进一步提高,以此提高可信度。
实验中RF算法也可以调参提高精度,但由于本实验未考虑对手球队,所以对双方球队都进行胜负预测,再对比可能比单方预测的结果更可靠一些,比如预测雄鹿下一场赢球可能性90%,那即使篮网赢球可能性是77%,那么也是篮网输球可能性较大。
算法可供学习,结果仅供参考。