OpenCV-跟我一起学数字图像处理之拉普拉斯算子
Laplace算子和Sobel算子一样,属于空间锐化滤波操作。起本质与前面的Spatial Filter操作大同小异,下面就通过Laplace算子来介绍一下空间锐化滤波,并对OpenCV中提供的Laplacian函数进行一些说明。
离散函数导数
离散函数的导数退化成了差分,一维一阶差分公式和二阶差分公式分别为,

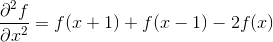
Laplace算子的差分形式
分别对Laplace算子x,y两个方向的二阶导数进行差分就得到了离散函数的Laplace算子。
在一个二维函数f(x,y)中,x,y两个方向的二阶差分分别为,


所以Laplace算子的差分形式为,

写成filter mask的形式如下,
注意该mask的特点,mask在上下左右四个90度的方向上结果相同,也就是说在90度方向上无方向性。为了让该mask在45度的方向上也具有该性质,对该filter mask进行扩展定义为,
注:
有时我们也会见到不同于上述结果的Laplace算子的filter mask,
| -1 |
-1 |
-1 |
| -1 |
8 |
-1 |
| -1 |
-1 |
-1 |
其原因是在定义二阶导数的时候采用了相反的定义,这个无关紧要,但是要注意,当用Laplace算子滤波后的图像与原图叠加时,混合操作是加还是减因上述的定义而异。
图像的Laplace操作
如同本文开始时说的那样,将Laplace算子写成filter mask后,其操作大同小异于其他的空间滤波操作。将filter mask在原图上逐行移动,然后mask中数值与其重合的像素相乘后求和,赋给与mask中心重合的像素,对图像的第一,和最后的行和列无法做上述操作的像素赋值零,就得到了拉普拉斯操作结果。
拉普拉斯操作结果与原图的混合
因为Laplace算子是二阶导数操作,其在强调图像素中灰度不连续的部分的同时也不在强调灰度值连续的部分。这样会产生一个具有很明显的灰度边界,但是没有足够特征的黑色背景。背景特征可以通过原图像与Laplace算子操作后的图像混合恢复。用公式,

其中的参数c的取值和上面的两种mask定义有关,当mask中心的数值取正时c=-1,相反c=1;
OpenCV中Laplacian函数可以实现对图像的Laplace操作,具体用法如下,
Laplacian( src_gray, dst, ddepth, kernel_size, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT );
参数意义为,
- src_gray,输入图像
- dst,Laplace操作结果
- ddepth,输出图像深度,因为输入图像一般为CV_8U,为了避免数据溢出,输出图像深度应该设置为CV_16S
- kernel_size,filter mask的规模,我们的mask时3x3的,所以这里应该设置为3
- scale,delta,BORDER_DEFAULT,默认设置就好
基于OpenCV的Laplace算子仿真代码段如下,
//load the Original Image and get some informations
Mat src = imread("012.jpg",0);
namedWindow("OriginalImage");
imshow("OriginalImage",src);
CV_Assert(src.depth() == CV_8U);
//OpenCV solution - Laplacian
Mat dst,abs_dst_laplace;
Laplacian(src,dst,CV_16S,3);
convertScaleAbs(dst,abs_dst_laplace);
//show the result
namedWindow(“result_laplacian”);
imshow(“result_laplacian”,abs_dst_laplace);
其中convertScaleAbs函数功能是将CV_16S型的输出图像转变成CV_8U型的图像。
仿真结果:
原图:

Laplace操作结果:
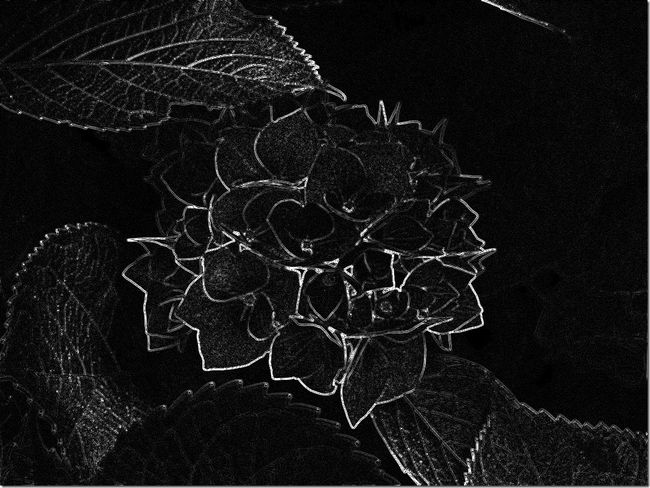

Laplace算子滤波仿真
根据数学原理中介绍的算法,编写相应代码,进行相关仿真。其中对Laplace操作结果进行了图像拉伸显示,因为Laplace操作结果的像素值范围可能落在了[0,255]之外,而计算机在显示的时候将赋值全部置为0,大于255的像素全部显示成255。
代码段如下,
//get some informations of original image
int nr = src.rows;
int nc = src.cols;
int n = nr*nc;
int arr[9] = {0};
//scan the whole pixels of original image
//and do Laplacian Operation
int* table_lap = new int[n];
int* table_orig = new int[n];
int l;
for (int i=0;i {
table_lap[i] = 0;
table_orig[i] = 0;
}
for (int i=1;i {
const uchar* previous = src.ptr(i-1);
const uchar* current = src.ptr(i);
const uchar* next = src.ptr(i+1);
for (int j=1;j {
for (int k=0;k<3;k++)
{
arr[k] = previous[j+k-1];
arr[k+3] = current[j+k-1];
arr[k+6] = next[j+k-1];
}
l = nc*i+j; //calculate the location in the table of current pixel
Lmaskoperation(table_lap,arr,l);
table_orig[l] = arr[4];
}
}
//pixels scale
uchar* La_scaled = new uchar[n];
table_scale(table_lap,La_scaled,n);
//padding values
Mat LaResult_own;
LaResult_own.create(src.size(),src.type());
uchar* p = NULL;
for (int i=0;i {
p = LaResult_own.ptr(i);
for (int j=0;j {
l = nc*i+j;
p[j] = La_scaled[l];
}
}
//show results
namedWindow(“LaResult_own”);
imshow(“LaResult_own”,LaResult_own);
其中Lmaskoperation是我写的mask为Laplace mask的mask operation操作函数,函数段如下,
//**********************//
//Laplacian mask operation
//**********************//
void Lmaskoperation(int* table,int* arr,int l)
{
int tmp[9] = {-1,-1,-1,-1,8,-1,-1,-1,-1};
for (int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
table[l] = table[l] + tmp[i]*arr[i];
}
}
tabel_scale函数就是我写的图像拉伸函数,将Laplace操作结果拉伸到[0,255],具体函数段如下,
//*****************************//
//scale the pixels to [0 255]
//*****************************//
void table_scale(int* table,uchar* result,int n)
{
int min = table[0];
int max = table[0];
for (int i=0;itable[i])
{
min = table[i];
}
if(max
仿真结果,拉伸后Laplace算子的操作结果

以灰色为主色调的显示结果就是Laplace算子操作拉伸后显示的一大特点。
Laplace滤波图像与原图像的混合
我使用的mask中心值为正,所以混合操作需要原图减去Laplace滤波图像,代码段如下,
//blending with the original image using Eq g(x,y)=f(x,y)+c*Lap(x,y)
int* table_blend = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i255)
{
table_blend[i] = 255;
}
}
//padding values to blending result
Mat Blresult;
Blresult.create(src.size(),src.type());
for (int i=0;i {
p = Blresult.ptr(i);
for(int j=0;j {
l = nc*i+j;
p[j] = table_blend[l];
}
}
//show blending result
namedWindow(“blending result_laplacian”);
imshow(“blending result_laplacian”,Blresult);
仿真结果:

最后给出冈萨雷斯在介绍Laplacian时所给素材的仿真结果

![]()
![]()




