pytorch实现多分类
pytorch实现时频图多分类
- 1.数据集导入
- 2.网络层模块定义
- 3.开始训练并输出训练集准确率及损失
- 4.测试验证集准确率及损失
- 5.将最后训练好的模型保存下来
- 6.测试模型准确度
- 如何将整个训练过程放在GPU上
-
- 确定终端GPU可用
- 确定训练过程是在GPU上进行
-
- 1.通过任务管理器
- 2. 在命令行中输入nvidia-smi -l n
1.数据集导入
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.utils.data
import torchvision.datasets as datasets
import time
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # Q
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCHS = 20
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(224),
# transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(),
# transforms.RandomCrop(50),
# transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
# transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, contrast=0.5, hue=0.5),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Grayscale(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))
])
dataset_train = datasets.ImageFolder(r'~', transform)
# print(dataset_train.imgs)
# 对应文件夹的label
# print(dataset_train.class_to_idx)
dataset_test = datasets.ImageFolder(r'~', transform)
# 对应文件夹的label
# print(dataset_test.class_to_idx)
# 导入数据
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset_train, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset_test, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True,drop_last=True)
此处路径填入总文件夹路径即可(总文件夹之下的子文件夹应以分类类别包装)
2.网络层模块定义
class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
channel_expansion = 4 # {扩展后的最终输出通道数} / {扩展前的输出通道数(blk_mid_channels)}
def __init__(self, blk_in_channels, blk_mid_channels, stride=1): # REs1:16,4 Res2 16 8
super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=blk_in_channels, # blk_in_channels:block 中第一个 conv 层的输入通道数
out_channels=blk_mid_channels, # blk_mid_channels:block 中第一个 conv 层的输出通道数
kernel_size=1,
padding=0,
stride=1) # stride 恒为 1
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(blk_mid_channels)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=blk_mid_channels, # block 中第二个 conv 层的输入通道数
out_channels=int(blk_mid_channels*self.channel_expansion/2), # block 中第二个 conv 层的输出通道数
kernel_size=3,
padding=1,
stride=stride) # stride 可以任意指定
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(int(blk_mid_channels*self.channel_expansion/2))
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=int(blk_mid_channels*self.channel_expansion/2), # block 中第三个 conv 层的输入通道数
out_channels=blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion, # 扩展后的最终输出通道数
kernel_size=1,
padding=0,
stride=1) # stride 恒为 1
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion)
# 实现 shortcut connection:
# 假如 block 的输入 x 和 conv3/bn3 的输出形状相同:直接相加
# 假如 block 的输入 x 和 conv3/bn3 的输出形状不同:在 shortcut connection 上增加一次对 x 的 conv/bn 变换
if stride != 1 or blk_in_channels != blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion: # 形状不同
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=blk_in_channels,
out_channels=blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion, # 变换空间维度
kernel_size=1,
padding=0,
stride=stride), # 变换空间维度
nn.BatchNorm2d(blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion)
)
else: # 形状相同
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
def forward(self, t):
################### Please finish the following code ###################
# conv1
out = self.conv1(t)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = F.relu(out)
# conv2
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = F.relu(out)
# conv3 & shortcut
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out = out + self.shortcut(t)
out = F.relu(out)
########################################################################
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.residual_layers = 1 # 每个 "residual layer" 含多个 blocks,对应上面列表中的一行 (即 conv2_x, conv3_x, conv4_x 或 conv5_x)
self.blk1_in_channels = 8 # 输入卷积层
self.blk_mid_channels = [2] # 两个残差块的第一卷积层对应的通道
self.blk_channels = [self.blk1_in_channels] + self.blk_mid_channels # [8,2]
self.blk_stride = [1] # 每个 residual layer 的 stride
self.blk_channel_expansion = block.channel_expansion
# 第一个卷积层(独立于 residual layers 之外)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=self.blk_channels[0], kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.blk1_in_channels)
self.map1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# residual layers (打包在 self.layers 中)
self.layers = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(self.residual_layers): # 残差块进行循环
blk_in_channels = self.blk_channels[i] if i == 0 else self.blk_channels[i] * block.channel_expansion
blk_mid_channels = self.blk_channels[i + 1]
self.layers.add_module(f"residule_layer{i}", # 残差块1:in16 out4 残差块2 in;16 out:8
self._make_layer(block=block, # block 种类:BasicBlock 或 BottleneckBlock
blk_in_channels=blk_in_channels,
blk_mid_channels=blk_mid_channels,
num_blocks=num_blocks[i], # 该 residual layer 有多少个 blocks ,即一个残差块中有多少个残差独立单元
stride=self.blk_stride[i])
)
# 最后的全连接层
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features=self.blk_channels[self.residual_layers] * block.channel_expansion,
out_features=num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, block, blk_in_channels, blk_mid_channels, num_blocks, stride):
block_list = []
stride_list = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1) # 每个 block 的 stride
for block_idx in range(num_blocks):
if block_idx != 0: # 对于 residual layer 中非第一个 block: 调整其 blk_in_channels
blk_in_channels = blk_mid_channels * block.channel_expansion
block_list.append(
block(blk_in_channels=blk_in_channels,
blk_mid_channels=blk_mid_channels,
stride=stride_list[block_idx])
)
return nn.Sequential(*block_list) # 返回一个 residual layer
def forward(self, t):
################### Please finish the following code ###################
# conv1
# ...
# print("shape:", t.shape) # shape: torch.Size([32, 1, 224, 224])
out = self.conv1(t)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = F.relu(out)
# print("shape:", out.shape)
out = self.map1(out)
# "residual layers"(打包在 self.layers 中)
# print("shape:", out.shape) #shape: torch.Size([32, 16, 224, 224])
out = self.layers(out)
# print("shape:",out.shape) #shape: torch.Size([32, 16, 112, 112]) batchsize channel height weight
# average pooling
out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 112) # shape of "out" before pooling (ResNet18): (batch_size, 256, 4, 4)#
# print("shape:", out.shape)
# linear layer
# out = out.reshape(XXX, XXX)
# out = self.linear(out)
out = out.reshape(BATCH_SIZE, 8) # 此处第二个参数应为通道数
out = self.linear(out)
########################################################################
return out
def ResNet50():
return ResNet(block=BottleneckBlock, num_blocks=[1], num_classes=6)
具体残差模块的分析与编写可参考这里
3.开始训练并输出训练集准确率及损失
network = ResNet50()
network = network.to(device) # 将模型转移到 GPU 上
modellr = 0.001
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 损失函数:交叉熵损失
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(network.parameters(), lr=modellr) # 优化器
def get_num_correct(preds, labels): # 计算正确分类的次数
return preds.argmax(dim=1).eq(labels).sum().item()
def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch): # 手动调整学习率
modellrnew = modellr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 5))
print("lr:", modellrnew)
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = modellrnew
min_loss = 100000
batch_num=0
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
t = time.perf_counter()
total_loss = 0
total_train_correct = 0
# 每个epoch之前手动调整学习率
adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
for batch in train_loader: # 抓取一个 batch
# 读取样本数据
images, labels = batch
images = images.to(device) # 数据转移到 GPU 上
labels = labels.to(device) # 标签转移到 GPU 上
# 完成正向传播,计算损失
preds = network(images)
loss = loss_func(preds, labels)
# 偏导归零
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
total_train_correct += get_num_correct(preds, labels)
print("epoch: ", epoch,
"correct times:", total_train_correct,
"training accuracy:", "%.3f" % (total_train_correct / len(dataset_train) * 100), "%",
"total_loss:", "%.3f" % total_loss)
print(f'time:{time.perf_counter() - t:.8f}s')
在训练了5轮以上之后,val_acc几乎可以稳定在1.0,60~70s可以完成一个epoch
4.测试验证集准确率及损失
num_correct = 0
val_loss = 0
network.eval() # 也可以不写,规范的话就写,用来表明是测试步骤
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in test_loader:
# 这里的每一次循环 都是一个minibatch
imgs, targets = batch
imgs = imgs.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
batch_num+=1
# print("images's shape", imgs.shape)
# print(batch_num)
output = network(imgs)
loss_in = loss_func(output, targets)
val_loss += loss_in
num_correct += get_num_correct(output, targets)
val_accuracy = num_correct / 1664
print("validation accuracy:",val_accuracy ,
"val_loss:",val_loss)
5.将最后训练好的模型保存下来
torch.save(network.cpu(), 'best_complete.pth') #
此处即便是在每个epoch下面都加上保存最好的模型,具体方法这里,还是需要将整个代码完整跑完(即不建议在精度已经最高时就手动停止代码,如果这样,会在加载调用该模型时重新开始训练)
并且此处建议把模型保存在cpu上,待到用时再将其添加至GPU.
6.测试模型准确度
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.utils.data
import torchvision.datasets as datasets
import time
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # Q
BATCH_SIZE = 32
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(224),
# transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(),
# transforms.RandomCrop(50),
# transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
# transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, contrast=0.5, hue=0.5),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Grayscale(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))
])
data_test = datasets.ImageFolder(r'C:\Users\Yan WANG\Desktop\JC_CNN\pydata\test', transform)
test_load = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(data_test, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE) # 此处batch有所缺失,故添加测试集至1696
print("data done")
class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
channel_expansion = 4 # {扩展后的最终输出通道数} / {扩展前的输出通道数(blk_mid_channels)}
def __init__(self, blk_in_channels, blk_mid_channels, stride=1): # REs1:16,4 Res2 16 8
super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=blk_in_channels, # blk_in_channels:block 中第一个 conv 层的输入通道数
out_channels=blk_mid_channels, # blk_mid_channels:block 中第一个 conv 层的输出通道数
kernel_size=1,
padding=0,
stride=1) # stride 恒为 1
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(blk_mid_channels)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=blk_mid_channels, # block 中第二个 conv 层的输入通道数
out_channels=int(blk_mid_channels*self.channel_expansion/2), # block 中第二个 conv 层的输出通道数
kernel_size=3,
padding=1,
stride=stride) # stride 可以任意指定
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(int(blk_mid_channels*self.channel_expansion/2))
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=int(blk_mid_channels*self.channel_expansion/2), # block 中第三个 conv 层的输入通道数
out_channels=blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion, # 扩展后的最终输出通道数
kernel_size=1,
padding=0,
stride=1) # stride 恒为 1
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion)
# 实现 shortcut connection:
# 假如 block 的输入 x 和 conv3/bn3 的输出形状相同:直接相加
# 假如 block 的输入 x 和 conv3/bn3 的输出形状不同:在 shortcut connection 上增加一次对 x 的 conv/bn 变换
if stride != 1 or blk_in_channels != blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion: # 形状不同
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=blk_in_channels,
out_channels=blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion, # 变换空间维度
kernel_size=1,
padding=0,
stride=stride), # 变换空间维度
nn.BatchNorm2d(blk_mid_channels * self.channel_expansion)
)
else: # 形状相同
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
def forward(self, t):
################### Please finish the following code ###################
# conv1
out = self.conv1(t)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = F.relu(out)
# conv2
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = F.relu(out)
# conv3 & shortcut
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out = out + self.shortcut(t)
out = F.relu(out)
########################################################################
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.residual_layers = 1 # 每个 "residual layer" 含多个 blocks,对应上面列表中的一行 (即 conv2_x, conv3_x, conv4_x 或 conv5_x)
self.blk1_in_channels = 8 # 输入卷积层
self.blk_mid_channels = [2] # 两个残差块的第一卷积层对应的通道
self.blk_channels = [self.blk1_in_channels] + self.blk_mid_channels # [8,2]
self.blk_stride = [1] # 每个 residual layer 的 stride
self.blk_channel_expansion = block.channel_expansion
# 第一个卷积层(独立于 residual layers 之外)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=self.blk_channels[0], kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.blk1_in_channels)
self.map1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# residual layers (打包在 self.layers 中)
self.layers = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(self.residual_layers): # 残差块进行循环
blk_in_channels = self.blk_channels[i] if i == 0 else self.blk_channels[i] * block.channel_expansion
blk_mid_channels = self.blk_channels[i + 1]
self.layers.add_module(f"residule_layer{i}", # 残差块1:in16 out4 残差块2 in;16 out:8
self._make_layer(block=block, # block 种类:BasicBlock 或 BottleneckBlock
blk_in_channels=blk_in_channels,
blk_mid_channels=blk_mid_channels,
num_blocks=num_blocks[i], # 该 residual layer 有多少个 blocks ,即一个残差块中有多少个残差独立单元
stride=self.blk_stride[i])
)
# 最后的全连接层
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features=self.blk_channels[self.residual_layers] * block.channel_expansion,
out_features=num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, block, blk_in_channels, blk_mid_channels, num_blocks, stride):
block_list = []
stride_list = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1) # 每个 block 的 stride
for block_idx in range(num_blocks):
if block_idx != 0: # 对于 residual layer 中非第一个 block: 调整其 blk_in_channels
blk_in_channels = blk_mid_channels * block.channel_expansion
block_list.append(
block(blk_in_channels=blk_in_channels,
blk_mid_channels=blk_mid_channels,
stride=stride_list[block_idx])
)
return nn.Sequential(*block_list) # 返回一个 residual layer
def forward(self, t):
################### Please finish the following code ###################
# conv1
# ...
# print("shape:", t.shape) # shape: torch.Size([32, 1, 224, 224])
out = self.conv1(t)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = F.relu(out)
# print("shape:", out.shape)
out = self.map1(out)
# "residual layers"(打包在 self.layers 中)
# print("shape:", out.shape) #shape: torch.Size([32, 16, 224, 224])
out = self.layers(out)
# print("shape:",out.shape) #shape: torch.Size([32, 16, 112, 112]) batchsize channel height weight
# average pooling
out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 112) # shape of "out" before pooling (ResNet18): (batch_size, 256, 4, 4)#
# print("shape:", out.shape)
# linear layer
# out = out.reshape(XXX, XXX)
# out = self.linear(out)
out = out.reshape(BATCH_SIZE, 8) # 此处第二个参数应为通道数
out = self.linear(out)
########################################################################
return out
network = torch.load(r"best_complete.pth")
network = network.to(device)
num_correct = 0
print("model load done")
def get_num_correct(preds, labels): # 计算正确分类的次数
return preds.argmax(dim=1).eq(labels).sum().item()
t = time.perf_counter()
print("start test")
for i, batch in enumerate(test_load):
images, labels = batch
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
preds = network(images)
num_correct += get_num_correct(preds, labels)
print(f'time:{time.perf_counter() - t:.8f}s')
test_accuracy = num_correct/1696
print("test accuracy:", test_accuracy*100,"%")
此处需要将模型中定义过的类名重新引入到测试文件中,该模型对测试集的分类准确率为100%
如何将整个训练过程放在GPU上
确定终端GPU可用
可输入如下代码进行测试
# setting device on GPU if available, else CPU
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print('Using device:', device)
print()
#Additional Info when using cuda
if device.type == 'cuda':
print(torch.cuda.get_device_name(0))
print('Memory Usage:')
print('Allocated:', round(torch.cuda.memory_allocated(0)/1024**3,1), 'GB')
print('Cached: ', round(torch.cuda.memory_reserved(0)/1024**3,1), 'GB')
若输出如下内容:(device型号根据自己GPU)
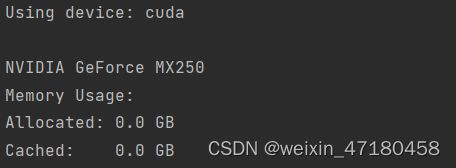
则证明GPU可用
确定训练过程是在GPU上进行
即便GPU可用,在pytorch框架中还是需要手动将模型和框架部署到GPU上
network = network.to(device) # 将模型转移到 GPU 上
images, labels = batch
images = images.to(device) # 数据转移到 GPU 上
labels = labels.to(device) # 标签转移到 GPU 上
在运行过程中可通过以下方式查看是否在使用GPU 以及GPU的利用率
1.通过任务管理器
Ctrl+Win+Delete打开任务管理器
进入到性能模块

2. 在命令行中输入nvidia-smi -l n
最后的n是自定义的每隔几秒刷新一次
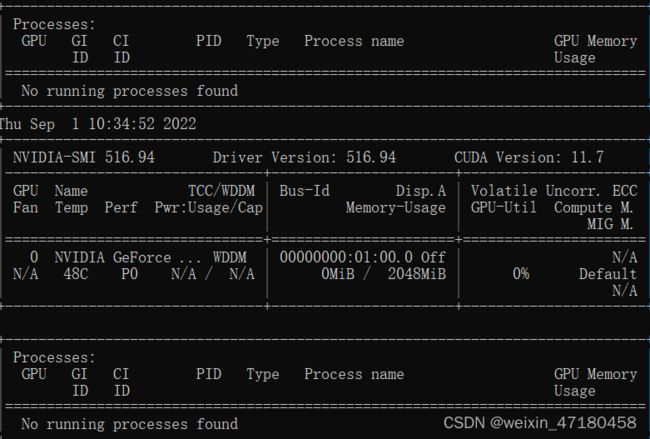
如果是在服务器上训练数据,需要将数据传送到服务器的本地资源上,如果只是通过网络连接共享数据,则会出现,GPU可用,模型和数据也都部署到了GPU上,但是会出现GPU利用率为零的情况。