跟着官方文档学DGL框架第十一天——训练图神经网络之整图分类(Graph Classification)
参考链接
- https://docs.dgl.ai/en/latest/guide/training-graph.html#guide-training-graph-classification
- https://docs.dgl.ai/en/latest/generated/dgl.readout_nodes.html#dgl.readout_nodes
- https://docs.dgl.ai/en/latest/generated/dgl.readout_edges.html#dgl.readout_edges
概述
整图分类 v.s. 节点分类
整图分类的分类对象是整个图,而节点分类则针对一个图中的单个结点。用“跟着官方文档学DGL框架第一天”中的“Zachary空手道俱乐部”为例,当时的节点分类任务是,判断里面成员属于由教练(节点0)领导的社区还是由会长(节点33)领导的社区;如果是整图分类的话,则是将整个俱乐部视为一个整体,分类“Zachary空手道俱乐部”、“健身俱乐部”、“学术俱乐部”等不同类型的人群社区。
整图分类的流程
- 批次化图;
- 在图上进行消息传递,以更新节点或边的特征;
- 将一张图里的节点或边特征聚合成整张图的图表示;
- 根据任务设计分类层
同构图上的整图分类
处理数据
加载数据
使用DGL的内置数据集“MUTAG”。
dataset = dgl.data.GINDataset('MUTAG', False)
如果无法成功下载,则访问“https://github.com/weihua916/powerful-gnns”,下载里面的“dataset.zip”,解压后将文件夹重命名为“GINDataset”,再将其放在本机对应的文件夹下“xx/.dgl/”。
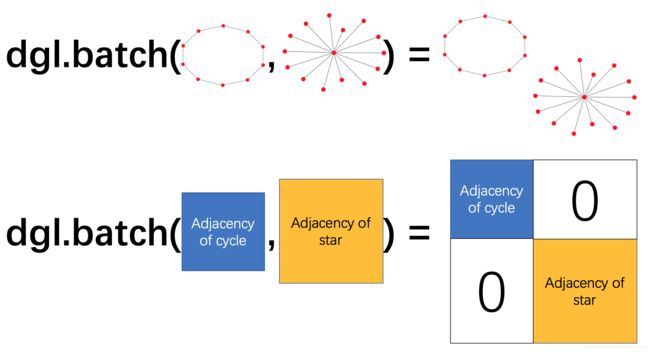
批次化图(batch)
如果每次训练只使用一张图,将十分低效。类比深度学习中小批次训练方式,我们将多张图组成一个批次进行训练,提高效率。一个图批次可以被看作是一张大图,图中的每个连通子图对应一张原始小图。
def collate(samples):
graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
batched_labels = torch.tensor(labels)
return batched_graph, batched_labels
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=1024,
collate_fn=collate,
drop_last=False,
shuffle=True)
构建分类模型
class Classifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, hidden_dim, n_classes):
super(Classifier, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = dglnn.GraphConv(in_dim, hidden_dim)
self.conv2 = dglnn.GraphConv(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.classify = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, n_classes)
def forward(self, g, h):
h = F.relu(self.conv1(g, h))
h = F.relu(self.conv2(g, h))
with g.local_scope():
g.ndata['h'] = h
hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
return self.classify(hg)
更新节点表示
这里使用了两层GraphSAGE。
h = F.relu(self.conv1(g, h))
h = F.relu(self.conv2(g, h))
获取整图表示
这里将图上所有节点的表示取平均,作为整图表示。
with g.local_scope():
g.ndata['h'] = h
hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
分类器
使用了一层全连接层作为分类器。
self.classify = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, n_classes)
开始训练
使用交叉熵作为损失函数。
model = Classifier(7, 20, 5)
opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
for epoch in range(20):
for batched_graph, labels in dataloader:
feats = batched_graph.ndata['attr'].float()
logits = model(batched_graph, feats)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, labels)
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
print(loss.item())
异构图上的整图分类
与同构图上的整图分类最大的区别在于,需要先对每种关系对应的二部图得到图表示,然后再聚合这些二部图的表示,形成整个异构图的图表示。
处理数据
加载数据
没有找到内置的异构图分类数据集,还是使用“跟着官方文档学DGL框架第八天”中人工构建的异构图数据集,包含两种类型的结点和六种类型的边。这里随机给每个图打个标签。
def create_graph():
n_users = 1000
n_items = 500
n_follows = 3000
n_clicks = 5000
n_dislikes = 500
n_hetero_features = 10
follow_src = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_follows)
follow_dst = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_follows)
click_src = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_clicks)
click_dst = np.random.randint(0, n_items, n_clicks)
dislike_src = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_dislikes)
dislike_dst = np.random.randint(0, n_items, n_dislikes)
hetero_graph = dgl.heterograph({
('user', 'follow', 'user'): (follow_src, follow_dst),
('user', 'followed-by', 'user'): (follow_dst, follow_src),
('user', 'click', 'item'): (click_src, click_dst),
('item', 'clicked-by', 'user'): (click_dst, click_src),
('user', 'dislike', 'item'): (dislike_src, dislike_dst),
('item', 'disliked-by', 'user'): (dislike_dst, dislike_src)})
hetero_graph.nodes['user'].data['feat'] = torch.randn(n_users, n_hetero_features)
hetero_graph.nodes['item'].data['feat'] = torch.randn(n_items, n_hetero_features)
label = np.random.randint(0, 5, 1)
return hetero_graph, torch.LongTensor(label)、
dataset = [create_graph() for i in range(1000)]
批次化图
与同构图无异。
def collate(samples):
# graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
graphs, labels = zip(*samples)
batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
batched_labels = torch.tensor(labels)
return batched_graph, batched_labels
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=1024,
collate_fn=collate,
drop_last=False,
shuffle=True)
构建分类模型
class HeteroClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, hidden_dim, n_classes, rel_names):
super().__init__()
self.rgcn = RGCN(in_dim, hidden_dim, hidden_dim, rel_names)
self.classify = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, n_classes)
def forward(self, g):
h = g.ndata['feat']
h = self.rgcn(g, h)
with g.local_scope():
g.ndata['h'] = h
hg = 0
for ntype in g.ntypes:
hg = hg + dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h', ntype=ntype)
return self.classify(hg)
更新节点表示
使用“RGCN()”得到节点的表示。
h = g.ndata['feat']
h = self.rgcn(g, h)
获取整图表示
通过“dgl.mean_nodes(g, ‘h’, ntype=ntype)”得到每种类型对应的二部图的图表示,然后求和得到整个异构图的图表示。
with g.local_scope():
g.ndata['h'] = h
hg = 0
for ntype in g.ntypes:
hg = hg + dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h', ntype=ntype)
分类器
使用了一层全连接层作为分类器。
self.classify = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, n_classes)
开始训练
使用交叉熵作为损失函数。
etypes = dataset[0][0].etypes
model = HeteroClassifier(10, 20, 5, etypes)
opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
for epoch in range(20):
for batched_graph, labels in dataloader:
logits = model(batched_graph)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, labels.squeeze(-1))
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
print(loss.item())
附
图读出(Graph Readout)
聚合并汇总单个图节点和边的信息。这类操作叫做“读出”。常见的聚合方法包括:对所有节点或边特征求和、取平均值、逐元素求最大值或最小值。
dgl.readout_nodes
dgl.readout_nodes(graph, feat, weight=None, *, op='sum', ntype=None)
- feat:字符串,为想汇总读出的节点特征名称;
- weight:字符串,为节点权重特征的名称,如果汇总时要考虑权重,则将节点乘以自身的权重特征值,再汇总;如:
g1 = dgl.graph(([0, 1], [1, 0])) # Graph 1
g1.ndata['h'] = th.tensor([1., 2.])
g2 = dgl.graph(([0, 1], [1, 2])) # Graph 2
g2.ndata['h'] = th.tensor([1., 2., 3.])
bg.ndata['w'] = th.tensor([.1, .2, .1, .5, .2])
dgl.readout_nodes(bg, 'h', 'w')
# tensor([.5, 1.7])
- op:字符串,读出运算,可选‘sum’, ‘max’, ‘min’, ‘mean’;如:
dgl.readout_nodes(bg, 'h', op='max')
# tensor([2., 3.])
- ntype:字符串,节点类型,指定需要汇总的节点类型。
上述代码中使用的“dgl.mean_nodes(graph, feat)”应该等价于“dgl.readout_nodes(graph, feat, op=‘mean’)”。
dgl.readout_edges
dgl.readout_edges(graph, feat, weight=None, *, op='sum', etype=None)
只有etype与上dgl.readout_nodes中不同。
etype:用于指定边类型。可以是(str, str, str)或str两种形式,前者为源节点-边-目标节点三元组形式,后者为单独的边类型,在不引起混淆的情况下可以使用后者。
同构图上的整图分类完整代码
import dgl
import dgl.nn.pytorch as dglnn
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Classifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, hidden_dim, n_classes):
super(Classifier, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = dglnn.GraphConv(in_dim, hidden_dim)
self.conv2 = dglnn.GraphConv(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.classify = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, n_classes)
def forward(self, g, h):
h = F.relu(self.conv1(g, h))
h = F.relu(self.conv2(g, h))
with g.local_scope():
g.ndata['h'] = h
hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
return self.classify(hg)
dataset = dgl.data.GINDataset('MUTAG', False)
def collate(samples):
graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
batched_labels = torch.tensor(labels)
return batched_graph, batched_labels
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=1024,
collate_fn=collate,
drop_last=False,
shuffle=True)
model = Classifier(7, 20, 5)
opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
for epoch in range(20):
for batched_graph, labels in dataloader:
feats = batched_graph.ndata['attr'].float()
logits = model(batched_graph, feats)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, labels)
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
print(loss.item())
异构图上的整图分类完整代码
import dgl
import dgl.nn.pytorch as dglnn
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
def create_graph():
n_users = 1000
n_items = 500
n_follows = 3000
n_clicks = 5000
n_dislikes = 500
n_hetero_features = 10
follow_src = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_follows)
follow_dst = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_follows)
click_src = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_clicks)
click_dst = np.random.randint(0, n_items, n_clicks)
dislike_src = np.random.randint(0, n_users, n_dislikes)
dislike_dst = np.random.randint(0, n_items, n_dislikes)
hetero_graph = dgl.heterograph({
('user', 'follow', 'user'): (follow_src, follow_dst),
('user', 'followed-by', 'user'): (follow_dst, follow_src),
('user', 'click', 'item'): (click_src, click_dst),
('item', 'clicked-by', 'user'): (click_dst, click_src),
('user', 'dislike', 'item'): (dislike_src, dislike_dst),
('item', 'disliked-by', 'user'): (dislike_dst, dislike_src)})
hetero_graph.nodes['user'].data['feat'] = torch.randn(n_users, n_hetero_features)
hetero_graph.nodes['item'].data['feat'] = torch.randn(n_items, n_hetero_features)
label = np.random.randint(0, 5, 1)
return hetero_graph, torch.LongTensor(label)
class RGCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_feats, hid_feats, out_feats, rel_names):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = dglnn.HeteroGraphConv({
rel: dglnn.GraphConv(in_feats, hid_feats)
for rel in rel_names}, aggregate='sum')
self.conv2 = dglnn.HeteroGraphConv({
rel: dglnn.GraphConv(hid_feats, out_feats)
for rel in rel_names}, aggregate='sum')
def forward(self, graph, inputs):
h = self.conv1(graph, inputs)
h = {k: F.relu(v) for k, v in h.items()}
h = self.conv2(graph, h)
return h
class HeteroClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, hidden_dim, n_classes, rel_names):
super().__init__()
self.rgcn = RGCN(in_dim, hidden_dim, hidden_dim, rel_names)
self.classify = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, n_classes)
def forward(self, g):
h = g.ndata['feat']
h = self.rgcn(g, h)
with g.local_scope():
g.ndata['h'] = h
hg = 0
for ntype in g.ntypes:
hg = hg + dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h', ntype=ntype)
return self.classify(hg)
dataset = [create_graph() for i in range(1000)]
def collate(samples):
# graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
graphs, labels = zip(*samples)
batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
batched_labels = torch.tensor(labels)
return batched_graph, batched_labels
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=1024,
collate_fn=collate,
drop_last=False,
shuffle=True)
etypes = dataset[0][0].etypes
model = HeteroClassifier(10, 20, 5, etypes)
opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
for epoch in range(20):
for batched_graph, labels in dataloader:
logits = model(batched_graph)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, labels.squeeze(-1))
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
print(loss.item())