使用 OpenCV 在 Python 中检测图像中的形状
OpenCV 是一个开源库,主要用于处理图像和视频以识别形状、对象、文本等。它主要与 python 一起使用。在本文中,我们将了解如何检测图像中的形状。为此,我们需要OpenCV 的cv2.findContours()函数,并且我们将使用cv2.drawContours()函数在图像上绘制边缘。轮廓是形状的轮廓或边界。
方法
- 导入模块
- 导入图片
- 将其转换为灰度图像
- 对图像应用阈值,然后找出轮廓。
- 在轮廓范围内运行一个循环并遍历它。
- 在这个循环中绘制形状的轮廓(使用 drawContours() )并找出形状的中心点。
- 根据检测到的形状有多少个轮廓点对检测到的形状进行分类,并将检测到的形状名称放在形状的中心点。
使用的功能
- cv2.findContours():基本上这个方法找出图像中所有形状的边界点。
语法: cv2.findContours(src, contour_retrieval, contours_approximation)
参数:
- src:输入图像 n 维(但在我们的示例中,我们将使用
最首选的 2 维图像。)- 轮廓检索:
- cv.RETR_EXTERNAL:只检索极端外轮廓
- cv.RETR_LIST:检索所有轮廓而不建立任何层次关系。
- cv.RETR_TREE:检索所有轮廓并重建嵌套轮廓的完整层次结构。
- 轮廓近似:
- cv.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:它将存储所有边界点。
- cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:它将存储端点的数量(例如,如果是矩形,它将存储4个)
返回值:轮廓点列表
- cv2.drawContours() :此方法绘制轮廓。如果您提供边界点,它也可以绘制形状。
语法: cv.DrawContours(src、contour、contourIndex、color、thickness)
参数:
- src: n维图像
- 轮廓:可以列出轮廓点。
- 轮廓指数:
- -1:绘制所有轮廓
- 要绘制单个轮廓,我们可以在此处传递索引值
- 颜色:颜色值
- 厚度:轮廓的大小
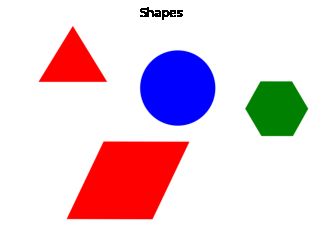
输入:
程序:
- Python3
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# reading image
img = cv2.imread('shapes.png')
# converting image into grayscale image
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# setting threshold of gray image
_, threshold = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# using a findContours() function
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(
threshold, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
i = 0
# list for storing names of shapes
for contour in contours:
# here we are ignoring first counter because
# findcontour function detects whole image as shape
if i == 0:
i = 1
continue
# cv2.approxPloyDP() function to approximate the shape
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(
contour, 0.01 * cv2.arcLength(contour, True), True)
# using drawContours() function
cv2.drawContours(img, [contour], 0, (0, 0, 255), 5)
# finding center point of shape
M = cv2.moments(contour)
if M['m00'] != 0.0:
x = int(M['m10']/M['m00'])
y = int(M['m01']/M['m00'])
# putting shape name at center of each shape
if len(approx) == 3:
cv2.putText(img, 'Triangle', (x, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 255, 255), 2)
elif len(approx) == 4:
cv2.putText(img, 'Quadrilateral', (x, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 255, 255), 2)
elif len(approx) == 5:
cv2.putText(img, 'Pentagon', (x, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 255, 255), 2)
elif len(approx) == 6:
cv2.putText(img, 'Hexagon', (x, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 255, 255), 2)
else:
cv2.putText(img, 'circle', (x, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 255, 255), 2)
# displaying the image after drawing contours
cv2.imshow('shapes', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
|
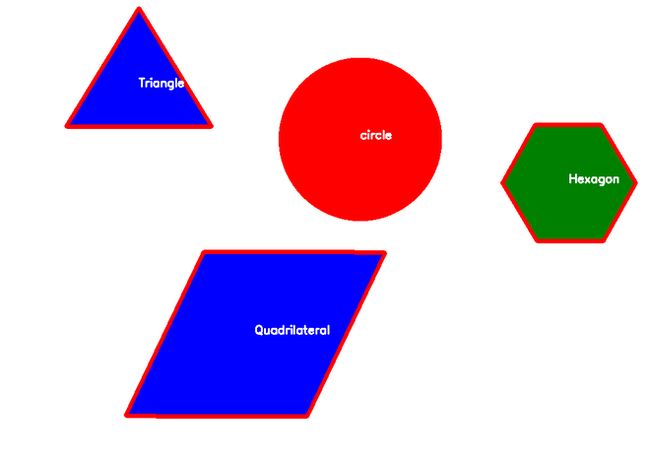
输出: