CS131-PA1 全景拼接Panorama Stitching
全景拼接(Panoramic stitching)是机器视觉应用比较早也比较成功的方向,目前有大量的应用,比如google的街道全景图,手机的全景图像拼接,各种拼接软件(Photosynth and AutoStitch)等等.
本文方法是通过计算不同图像sift特征,并计算出图像之间的仿射关系,从而拼接出全景图像
其基本思路是:
• 利用Difference-of-Gaussians (DoG)差分高斯金字塔检测计算出sift特征点的位置和scale空间(此部分原始代码已给出)
• 计算上面的key points对应的sift特征算子
• 比较两幅图像的sift特征算子,并找到匹配的特征算子
• 给定已经匹配好的特征算子列表,利用最小二乘法去计算其仿射变化矩阵,匹配两幅图像的位置关系
• 利用随机抽样一致性算法 RANSAC 去噪,给出仿射变换矩阵的更鲁棒性估计
• 给定仿射变换矩阵和图像,将图像拼接起来(此部分原始代码已给出)
• 实验测试
1.计算key points对应的sift特征算子
参考CS143的project2
代码:略
2.比较两幅图像的sift特征算子,并找到匹配的特征算子
如何判断两个特征是匹配的呢?最简单的办法就是计算其间的距离,若距离够小(这里取最小距离和第二小距离的比值小于某个阀值),则说明此两个特征是匹配的。这里距离是使用Euclidean distance 欧式距离
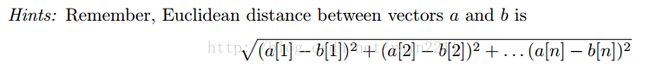 (来自http://vision.stanford.edu/teaching/cs131_fall1516/assignments/PA1.zip/PA1_2015.pdf)
(来自http://vision.stanford.edu/teaching/cs131_fall1516/assignments/PA1.zip/PA1_2015.pdf)
代码如下:
function match = SIFTSimpleMatcher(descriptor1, descriptor2, thresh)
% SIFTSimpleMatcher
% Match one set of SIFT descriptors (descriptor1) to another set of
% descriptors (decriptor2). Each descriptor from descriptor1 can at
% most be matched to one member of descriptor2, but descriptors from
% descriptor2 can be matched more than once.
%
% Matches are determined as follows:
% For each descriptor vector in descriptor1, find the Euclidean distance
% between it and each descriptor vector in descriptor2. If the smallest
% distance is less than thresh*(the next smallest distance), we say that
% the two vectors are a match, and we add the row [d1 index, d2 index] to
% the "match" array.
%
% INPUT:
% descriptor1: N1 * 128 matrix, each row is a SIFT descriptor.
% descriptor2: N2 * 128 matrix, each row is a SIFT descriptor.
% thresh: a given threshold of ratio. Typically 0.7
%
% OUTPUT:
% Match: N * 2 matrix, each row is a match.
% For example, Match(k, :) = [i, j] means i-th descriptor in
% descriptor1 is matched to j-th descriptor in descriptor2.
if ~exist('thresh', 'var'),
thresh = 0.7;
end
match = [];
for i = 1:size(descriptor1,1)
dist3=[];
for j = 1:size(descriptor2,1)
dist1 = descriptor1(i,:)-descriptor2(j,:);%每个维度求差
dist2 = sum(dist1.^2)^(1/2);%欧拉公式求距离
dist3 = [dist3,dist2];%所有距离值拼凑起来
end
[mindist,min_index] = min(dist3);%求最小距离
second_dis = min(dist3(find(dist3>mindist)));%求第二小距离
if mindist/second_dis < thresh %如果小于阀值
match_point = [i,min_index]; %匹配点对
match = [match;match_point]; %保存返回
end
end
end
3.计算仿射变换矩阵
有了匹配特征点对,下一步要做的是要计算出点对之间的仿射关系。通俗点说,比如要拼接两幅图A和B,就是要知道A图特征点对应B图的特征点的位置关系和角度关系。
以提供给最后步骤做拼接
(来自http://vision.stanford.edu/teaching/cs131_fall1516/assignments/PA1.zip/PA1_2015.pdf)
相关代码:
function H = ComputeAffineMatrix( Pt1, Pt2 )
%ComputeAffineMatrix
% Computes the transformation matrix that transforms a point from
% coordinate frame 1 to coordinate frame 2
%Input:
% Pt1: N * 2 matrix, each row is a point in image 1
% (N must be at least 3)
% Pt2: N * 2 matrix, each row is the point in image 2 that
% matches the same point in image 1 (N should be more than 3)
%Output:
% H: 3 * 3 affine transformation matrix,
% such that H*pt1(i,:) = pt2(i,:)
N = size(Pt1,1);
if size(Pt1, 1) ~= size(Pt2, 1),
error('Dimensions unmatched.');
elseif N<3
error('At least 3 points are required.');
end
% Convert the input points to homogeneous coordintes.
P1 = [Pt1';ones(1,N)];
P2 = [Pt2';ones(1,N)];
% Now, we must solve for the unknown H that satisfies H*P1=P2
% But MATLAB needs a system in the form Ax=b, and A\b solves for x.
% In other words, the unknown matrix must be on the right.
% But we can use the properties of matrix transpose to get something
% in that form. Just take the transpose of both sides of our equation
% above, to yield P1'*H'=P2'. Then MATLAB can solve for H', and we can
% transpose the result to produce H.
%me 标准最小二乘法只能处理Ax=b, and A\b solves for
%x.的情况,由于这里是H*P1=P2,所以要转换一下,转换推导可见PA1
H = [];
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% %
% YOUR CODE HERE: %
% Use MATLAB's "A\b" syntax to solve for H_transpose as discussed %
% above, then convert it to the final H %
% %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
H = P1'\P2';
H= H';
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% END OF YOUR CODE %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Sometimes numerical issues cause least-squares to produce a bottom
% row which is not exactly [0 0 1], which confuses some of the later
% code. So we'll ensure the bottom row is exactly [0 0 1].
H(3,:) = [0 0 1];
end
4.RANSAC去噪
为了得到更好的拼接效果,我们使用RANSAC算法来进行降噪处理
function H = RANSACFit(p1, p2, match, maxIter, seedSetSize, maxInlierError, goodFitThresh )
%RANSACFit Use RANSAC to find a robust affine transformation
%强大的(鲁棒性高)的仿射变换
% Input:
% p1: N1 * 2 matrix, each row is a point
% p2: N2 * 2 matrix, each row is a point
% match: M * 2 matrix, each row represents a match [index of p1, index of p2]
% maxIter: the number of iterations RANSAC will run
% 迭代次数
% seedNum: The number of randomly-chosen seed points that we'll use to fit
% our initial circle
% maxInlierError: A match not in the seed set is considered an inlier if
% its error is less than maxInlierError. Error is
% measured as sum of Euclidean distance between transformed
% point1 and point2. You need to implement the
% ComputeCost function.
%
% goodFitThresh: The threshold for deciding whether or not a model is
% good; for a model to be good, at least goodFitThresh
% non-seed points must be declared inliers.
% 判断好坏的阀值
% Output:
% H: a robust estimation of affine transformation from p1 to p2
%
%
N = size(match, 1);
if N<3
error('not enough matches to produce a transformation matrix')
end
if ~exist('maxIter', 'var'),
maxIter = 200;
end
if ~exist('seedSetSize', 'var'),
seedSetSize = ceil(0.2 * N);
end
seedSetSize = max(seedSetSize,3);
if ~exist('maxInlierError', 'var'),
maxInlierError = 30;
end
if ~exist('goodFitThresh', 'var'),
goodFitThresh = floor(0.7 * N);
end
H = eye(3);
% below is an obfuscated version of RANSAC. You don't need to
% edit any of this code, just the ComputeError() function below
iota = Inf;
kappa = 0;
lambda = iota;
alpha = seedSetSize;
for i = 1 : maxIter,
[beta, gamma] = part(match, alpha); %将样本匹配点随机拆分为7和62-7=55的数量矩阵
eta = ComputeAffineMatrix(p1(beta(:, 1), :), p2(beta(:, 2), :));%计算映射矩阵
delta = ComputeError(eta, p1, p2, gamma);%计算所有转换后的匹配点的距离
epsilon = (delta <= maxInlierError); %距离小于maxInlierError 的匹配点为1 ,其他为0
if sum(epsilon(:)) + alpha >= goodFitThresh, %如果在界内的匹配点数量超过阀值
zeta = [beta; gamma(epsilon, :)]; %把7个匹配点和界内的匹配点重新集合
eta = ComputeAffineMatrix(p1(zeta(:, 1), :), p2(zeta(:, 2), :));%重新计算仿射矩阵
theta = sum(ComputeError(eta, p1, p2, zeta));%重新计算距离,并求和
if theta < iota, %最小的距离总值
H = eta;
kappa = lambda;
iota = theta;
end
end
end
if sum(sum((H - eye(3)).^2)) == 0,
disp('No RANSAC fit was found.')
end
end
function dists = ComputeError(H, pt1, pt2, match)
% Compute the error using transformation matrix H to
% transform the point in pt1 to its matching point in pt2.
%
% Input:
% H: 3 x 3 transformation matrix where H * [x; y; 1] transforms the point
% (x, y) from the coordinate system of pt1 to the coordinate system of
% pt2.
% pt1: N1 x 2 matrix where each ROW is a data point [x_i, y_i]
% pt2: N2 x 2 matrix where each ROW is a data point [x_i, y_i]
% match: M x 2 matrix, each row represents a match [index of pt1, index of pt2]
%
% Output:
% dists: An M x 1 vector where dists(i) is the error of fitting the i-th
% match to the given transformation matrix.
% Error is measured as the Euclidean distance between (transformed pt1)
% and pt2 in homogeneous coordinates.
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% %
% YOUR CODE HERE. %
% Convert the points to a usable format, perform the %
% transformation on pt1 points, and find their distance to their %
% MATCHING pt2 points. %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% hint: If you have an array of indices, MATLAB can directly use it to
% index into another array. For example, pt1(match(:, 1),:) returns a
% matrix whose first row is pt1(match(1,1),:), second row is
% pt1(match(2,1),:), etc. (You may use 'for' loops if this is too
% confusing, but understanding it will make your code simple and fast.)
dists = zeros(size(match,1),1);
%循环每一行,hx=y 先做映射变化
%计算距离
pt1 = [pt1(match(:,1),:),ones(size(match,1),1)];
pt2 = [pt2(match(:,2),:),ones(size(match,1),1)];
%pt2_affine = H*pt1;
for i = 1:size(match,1)
pt2_affine = H*pt1(i,:)'; %H * [x1; y1; 1] = [x2;y2;1] 注意是;多行符号
pt2_affine = pt2_affine'; %转置为1行,方便计算
dist = ((pt2(i,1)-pt2_affine(1,1))^2+(pt2(i,2)-pt2_affine(1,2))^2)^1/2;%((x2-x1)^2+(y2-y1)^2)^1/2 欧式距离公式
dists(i) = dist;
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% %
% END YOUR CODE %
% %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
if size(dists,1) ~= size(match,1) || size(dists,2) ~= 1
error('wrong format');
end
end
function [D1, D2] = part(D, splitSize)
idx = randperm(size(D, 1));
D1 = D(idx(1:splitSize), :);
D2 = D(idx(splitSize+1:end), :);
end
2.实验测试
两幅图拼接效果:
多幅图拼接效果:
原始代码及paper下载: http://vision.stanford.edu/teaching/cs131_fall1516/assignments/PA1.zip

