【ECCV 2020】UDA with Noise Resistible Mutual-Training for Person Re-identification (NRMT)
NRMT:噪声可抵抗的Mutual-Training
- 1. 背景知识
-
- Pseudo-label based self-training
-
- Problem #1
- 2. 内容概要
-
- 本文工作
- 实验效果
- 相关工作
- 数据集
- 3. 方法提要
-
- Noise Resistible Mutual-Training (NRMT) method
- 方法框架
- 算法描述
- 实验结果
- 4. 方法详解
- 参考文献
1. 背景知识
Pseudo-label based self-training
Pseudo-label based self-training is one of the representative techniques to address UDA.
Problem #1
How- ever, label noise caused by unsupervised clustering is always a trouble to self-training methods. //然而,无监督聚类引起的标签噪声一直是自训练方法的一大难题。
2. 内容概要
本文工作
- We present a novel noise resistible mutual-training method for unsupervised domain adaptation in person re-ID, which exploits dual network interaction to depress noises in pseudo- labels of unsupervised iterative training on the target data. //提出了一种新的无监督域自适应的抗噪声互训练方法,利用双网络交互抑制目标数据无监督迭代训练中伪标签中的噪声。 解决Problem #1
- We introduce a collaborative clustering to ease the fitting to noisy instances by the memoriza- tion effects of deep networks. //我们引入了一种协作聚类方法,通过深度网络的记忆效应来简化对噪声实例的拟合。
- We propose a mutual instance selection based on the peer-confidence and relationship disagreement of networks on triplets of instances to select reliable and informative instances in a mini-batch. //提出了一种基于网络对三组实例的信任和关系不一致的互实例选择方法,在小批量中选择可靠且信息丰富的实例。
实验效果
the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art UDA methods for person re-ID.
相关工作
- Unsupervised Domain Adaptation.
- UDA for Person re-ID.
- Deep Learning with Noisy Labels.
数据集
- Market-1501 [52],
- ukeMTMC-reID [26,54]
- MSMT17 [39]
3. 方法提要
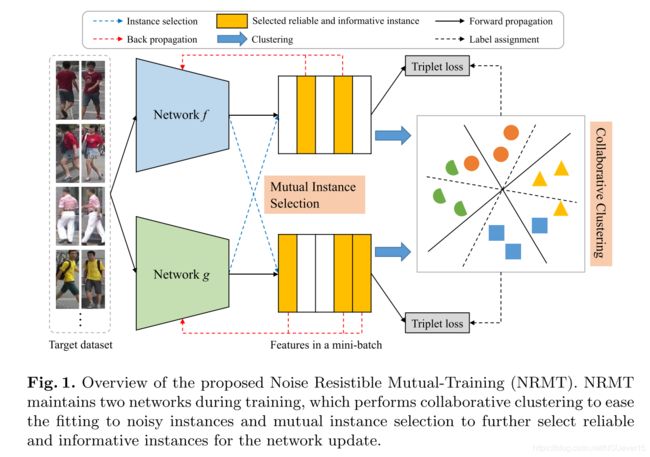
Noise Resistible Mutual-Training (NRMT) method
To depress noises in pseudo-labels, this paper proposes a Noise Resistible Mutual-Training (NRMT) method, which maintains two networks during training to perform collaborative clus- tering and mutual instance selection //为了抑制伪标签中的噪声,本文提出了一种抗噪声相互训练(NRMT)方法,该方法在训练过程中保持两个网络,以进行协作聚类和相互实例选择
- collaborative clus- tering eases the fitting to noisy instances by allowing the two networks to use pseudo-labels provided by each other as an additional supervi- sion. //协作聚类允许两个网络使用彼此提供的伪标签作为额外的监督,从而简化了对噪声实例的拟合。
- mutual instance selection further selects reliable and informative instances for training according to the peer-confidence and relationship disagreement of the networks. //互实例选择进一步根据网络的同伴信任和关系分歧,选择可靠且信息丰富的实例进行训练。
方法框架
算法描述
实验结果
4. 方法详解
。。。
参考文献
- Arpit, D., et al.: A closer look at memorization in deep networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) (2017)
- Blum, A., Mitchell, T.: Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory (1998)
- Bousmalis, K., Trigeorgis, G., Silberman, N., Krishnan, D., Erhan, D.: Domain separation networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) (2016)
- Campello, R.J.G.B., Moulavi, D., Sander, J.: Density-based clustering based on hierarchical density estimates. In: Pei, J., Tseng, V.S., Cao, L., Motoda, H., Xu, G. (eds.) PAKDD 2013. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 7819, pp. 160–172. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37456-2 14
- Chen, Y., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Instance-guided context rendering for cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
- Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2009)
- Deng, W., Zheng, L., Ye, Q., Kang, G., Yang, Y., Jiao, J.: Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re- identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018)
- Fan, H., Zheng, L., Yan, C., Yang, Y.: Unsupervised person re-identification: clus- tering and fine-tuning. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOM- CCAP) 14(4), 1–18 (2018)
- Felzenszwalb, P., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: A discriminatively trained, multi- scale, deformable part model (2008)
- Feng, Q., Kang, G., Fan, H., Yang, Y.: Attract or distract: exploit the margin of open set. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
- Fu, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, Y., Shi, H., Huang, T.S.: Self-similarity group- ing: a simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re- identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
- Ganin, Y., et al.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. (JMLR) 17(1), 2096–2130 (2016)
- Ge, Y., Chen, D., Li, H.: Mutual mean-teaching: pseudo label refinery for unsuper- vised domain adaptation on person re-identification. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) (2020)
- Han, B., et al.: Co-teaching: robust training of deep neural networks with extremely noisy labels. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) (2018)
- He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2016)
- Hermans, A., Beyer, L., Leibe, B.: In defense of the triplet loss for person re- identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07737 (2017)
- Li, Y.J., Yang, F.E., Liu, Y.C., Yeh, Y.Y., Du, X., Frank Wang, Y.C.: Adaptation and re-identification network: an unsupervised deep transfer learning approach to person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW) (2018)
- Liao, S., Hu, Y., Zhu, X., Li, S.Z.: Person re-identification by local maximal occur- rence representation and metric learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2015)
- Liu, Z., Wang, J., Gong, S., Lu, H., Tao, D.: Deep reinforcement active learning for human-in-the-loop person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Inter- national Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
- Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) (2015)
- Lv, J., Chen, W., Li, Q., Yang, C.: Unsupervised cross-dataset person re- identification by transfer learning of spatial-temporal patterns. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
- Malach, E., Shalev-Shwartz, S.: Decoupling “when to update” from “how to update”. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) (2017)
- Panareda Busto, P., Gall, J.: Open set domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2017)
- Peng, P., et al.: Unsupervised cross-dataset transfer learning for person re- identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2016)
- Qi, L., Wang, L., Huo, J., Zhou, L., Shi, Y., Gao, Y.: A novel unsupervised camera- aware domain adaptation framework for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
- Ristani, E., Solera, F., Zou, R., Cucchiara, R., Tomasi, C.: Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: Hua, G., J´egou,H.(eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9914, pp. 17–35. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/ 10.1007/978-3-319-48881-3 2
- Saito, K., Yamamoto, S., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T.: Open set domain adaptation by backpropagation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11209, pp. 156–171. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi. org/10.1007/978-3-030-01228-1 10
- Shu, R., Bui, H.H., Narui, H., Ermon, S.: A dirt-t approach to unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Represen- tations (ICLR) (2018)
- Song, C., Huang, Y., Ouyang, W., Wang, L.: Mask-guided contrastive attention model for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018)
- Song, J., Yang, Y., Song, Y.Z., Xiang, T., Hospedales, T.M.: Generalizable per- son re-identification by domain-invariant mapping network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
- Song, L., et al.: Unsupervised domain adaptive re-identification: theory and prac- tice. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.11334 (2018)
- Suh, Y., Wang, J., Tang, S., Mei, T., Lee, K.M.: Part-aligned bilinear represen- tations for person re-identification. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11218, pp. 418–437. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9 25
- Sun, B., Feng, J., Saenko, K.: Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In: Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2016)
- Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Deng, W., Wang, S.: SVDNet for pedestrian retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2017)
- Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, S.: Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Fer- rari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11208, pp. 501–518. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030- 01225-0 30
- Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Darrell, T., Saenko, K.: Simultaneous deep transfer across domains and tasks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Com- puter Vision (ICCV) (2015)
- Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pat- tern Recognition (CVPR) (2017)
- Wang, J., Zhu, X., Gong, S., Li, W.: Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018)
- Wei, L., Zhang, S., Gao, W., Tian, Q.: Person transfer Gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018)
- Wu, A., Zheng, W.S., Lai, J.H.: Unsupervised person re-identification by camera- aware similarity consistency learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
- Xie, G.S., et al.: Attentive region embedding network for zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
- Xie, G.S., et al.: Region graph embedding network for zero-shot learning. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12349, pp. 562–580. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030- 58548-8 33
- Yang, F., et al.: Asymmetric co-teaching for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) (2020)
- Yang, Q., Yu, H.X., Wu, A., Zheng, W.S.: Patch-based discriminative feature learn- ing for unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Confer- ence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
- Yu, H.X., Wu, A., Zheng, W.S.: Unsupervised person re-identification by deep asymmetric metric embedding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (TPAMI) 42, 956–973 (2018)
- Yu, H.X., Zheng, W.S., Wu, A., Guo, X., Gong, S., Lai, J.H.: Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Confer- ence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
- Yu, X., Han, B., Yao, J., Niu, G., Tsang, I., Sugiyama, M.: How does disagree- ment help generalization against label corruption? In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) (2019)
- Zhang, K., Luo, W., Ma, L., Liu, W., Li, H.: Learning joint gait representation via quintuplet loss minimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
- Zhang, X., Cao, J., Shen, C., You, M.: Self-training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019)
- Zhao, H., et al.: Spindle net: person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017)
- Zhao, L., Li, X., Zhuang, Y., Wang, J.: Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2017)
- Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Scalable person re- identification: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2015)
- Zheng, Z., Yang, X., Yu, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Kautz, J.: Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
- Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2017)
- Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Kang, G., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Random erasing data augmenta- tion. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.04896 (2017)
- Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Generalizing a Person retrieval model hetero- and homogeneously. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11217, pp. 176–192. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi. org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8 11
- Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Luo, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Invariance matters: exemplar mem- ory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Con- ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
- Zhou, S., Wang, J., Wang, J., Gong, Y., Zheng, N.: Point to set similarity based deep feature learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017)