Numpy教程(一)
参考资料:清华计算机博士带你学-Python金融量化分析
目录
demo1-numpy与for循环对比
demo2-向量内(点)积求和(对应位置相乘)
demo3-ndarray常见属性
demo4-数组的创建
demo5-批量运算
demo6-索引与切片
demo7-布尔型索引
demo8-花式索引
demo9-取整
demo10-通用函数
demo11-Numpy统计方法
demo12-随机数生成
demo13-正态分布与均匀分布
demo1-numpy与for循环对比
import numpy as np
import random
#numpy是高性能计算和数据分析的基础包
#是pandas等其他工具的基础包
#ndarray 多维数组结构,高校且节省时间
#无需循环即可对整体进行操作
#线性代数、随机数、傅里叶变换等功
#demo1-numpy与for循环对比
#numpy
value = np.array([random.uniform(100,200) for i in range(5)])
print(value)
newValue = value * 5
print(newValue)
print("\n")
#常规for循环
print(value)
newValue = []
for each in value:
newValue.append(each*5)
print(newValue)
[114.7388318 164.09261949 111.88378219 123.49759661 141.26457631] [573.69415901 820.46309746 559.41891096 617.48798305 706.32288156] [114.7388318 164.09261949 111.88378219 123.49759661 141.26457631] [573.6941590053353, 820.4630974561366, 559.4189109581303, 617.4879830450645, 706.3228815622876]
demo2-向量内(点)积求和(对应位置相乘)
price = np.array([random.uniform(10,20) for i in range(50)])
count = np.array([random.randint(1,10) for i in range(50)])
print((price*count).sum())
3895.638762940498
demo3-ndarray常见属性
#demo3-ndarray常见属性
#T 转置
#size 大小
#ndim 维度
#shape 维度大小 tuple
#dtype 类型
print("*****一维*****")
value = np.array([random.uniform(100,200) for i in range(5)])
print(value.dtype) #uniform浮点数
print(value.size)
print(value.ndim)
print(value.shape)
print("*****二维*****")
value = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(value.dtype)
print(value.size)
print(value.ndim)
print(value.shape)
print("*****三维*****")
value = np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]])
print(value.dtype)
print(value.size)
print(value.ndim)
print(value.shape)
value = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print("转置前:")
print(value)
print("转置后:")
print(value.T)*****一维***** float64 5 1 (5,) *****二维***** int32 6 2 (2, 3) *****三维***** int32 12 3 (2, 2, 3) 转置前: [[1 2 3] [4 5 6]] 转置后: [[1 4] [2 5] [3 6]]
demo4-数组的创建
#demo4-数组的创建
print("*****array将列表转化为数组*****")
print(np.array(range(5)))
print(np.array([1,2,3,4]))
print(np.array([0]*10))
print("*****ones zeros empty*****")
#ones zeros empty:据指定形状和类型创建数组
print(np.zeros(10)) #默认是浮点数,因为可能有除法运算
print(np.zeros(10,dtype="int")) #默认是浮点数,因为可能有除法运算
print(np.ones(10))
print(np.empty(20)) #垃圾值/内存中之前存放的值,接触索引,并不会清空内存的值
print(np.ones((2,2))) #根据指定形状生成数组
print("*****arange*****")
#arange numpy版的range 支持浮点数
print(np.arange(10))
print(np.arange(1,11,2)) #第三个参数为步长
print(np.arange(1,11,0.5)) #步长可以为小数!!!
# print(range(1,11,0.5))#报错
print("*****linspace*****")
#linspace 类似range 但第三个数为数组长度
print(np.linspace(0,10,11)) #0-10分为11个数字
print(len(np.linspace(0,10,11))) #linspace第三个参数为数组长度
print("*****eye*****")
#单位矩阵
print(np.eye(2))
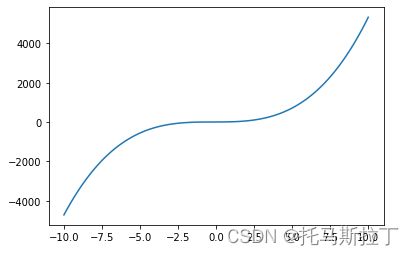
print("linspace画图")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-10,10,100)
y = 5*x**3 + 3*x**2 + 2*x + 5
plt.plot(x,y)*****array将列表转化为数组***** [0 1 2 3 4] [1 2 3 4] [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0] *****ones zeros empty***** [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0] [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] [[1. 1.] [1. 1.]] *****arange***** [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [1 3 5 7 9] [ 1. 1.5 2. 2.5 3. 3.5 4. 4.5 5. 5.5 6. 6.5 7. 7.5 8. 8.5 9. 9.5 10. 10.5] *****linspace***** [ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.] 11 *****eye***** [[1. 0.] [0. 1.]] linspace画图
demo5-批量运算
#demo5-批量运算
print("*****数组和标量运算*****")
test = np.arange(10)
print(test)
print(test+4)
print(test*2.5)
print(test/2)
print(test-10)
print("*****数组和数组运算*****")
test1 = np.arange(10)
test2 = np.arange(10,20)
print(test1,test2,len(test1),len(test2))
print(test1+test2) #对应位置做操作
print("*****比较关系符*****")
print(test1*****数组和标量运算***** [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [ 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13] [ 0. 2.5 5. 7.5 10. 12.5 15. 17.5 20. 22.5] [0. 0.5 1. 1.5 2. 2.5 3. 3.5 4. 4.5] [-10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1] *****数组和数组运算***** [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19] 10 10 [10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28] *****比较关系符***** [ True True True True True True True True True True] [ True False True True True True True True True True] *****reshape***** (15,) (3, 5)
demo6-索引与切片
#demo6-索引与切片
print("*****二维数组的两种索引*****")
test = np.arange(15).reshape((3,5))
print(test)
print(test[2][1])
print(test[2,1])
print(test[2,2])
print("*****list与array的切片差异*****")
testArray = np.arange(10)
testList = list(range(10))
print(testArray,testList)
print(testArray[4:],testList[4:])
sliceArray = testArray[:4] #浅拷贝/引用/数据量可能特别大,复制耗时占内存/默认是引用
sliceArrayCopy = testArray[:4].copy() #复制
sliceList = testList[:4] #复制-深拷贝
sliceArray[0] = 999
sliceList[0] = 666
sliceArrayCopy[-1] = 333
print(sliceArray,sliceList)
print(testArray,testList)
print(sliceArrayCopy,testArray)
print("*****二维数组的切片*****")
test = np.arange(15).reshape((3,5))
print(test)
#切0 1 5 6
print(test[:2,:2]) # 逗号{行,列} 对比:test[:2][:2]是错误切法,对比差异
#切7 8 12 13
print(test[1:,2:4])*****二维数组的两种索引***** [[ 0 1 2 3 4] [ 5 6 7 8 9] [10 11 12 13 14]] 11 11 12 *****list与array的切片差异***** [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [4 5 6 7 8 9] [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [999 1 2 3] [666, 1, 2, 3] [999 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [ 0 1 2 333] [999 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] *****二维数组的切片***** [[ 0 1 2 3 4] [ 5 6 7 8 9] [10 11 12 13 14]] [[0 1] [5 6]] [[ 7 8] [12 13]]
demo7-布尔型索引
#demo7-布尔型索引
print("*****选出数组中所有大于平均数的数*****")
#Q:选出数组中所有大于平均数的数
test = np.array([random.randint(0,20) for i in range(10)])
print(test,test.mean())
print(list(filter(lambda x:x>test.mean(),test))) #filter是惰性序列,需要使用List列表化
print(test[test>test.mean()])
print(test>test.mean()) #打印[False False True False True True True False True False]
print("*****布尔型索引原理*****")
boolIndex = [False,False,True,False,True,True,True,False,True,False]
print(test[boolIndex]) #打印出值为True对应位置的数组值
print("*****给定一个数组,选出数组中所有大于5的偶数*****")
#Q:给定一个数组,选出数组中所有大于5的偶数
test = np.array([random.randint(0,20) for i in range(10)])
print(test)
# print(test[test>5][test%2==0]) #第一次布尔型索引后长度已经变化
print(test[test%2==0][test[test%2==0]>5])
print(test[(test>5) & (test%2==0)]) #得加括号,因为位运算符优先级更高
print(test[(test>5) | (test%2==0)]) #大于5或者为偶数
print("*****逻辑与*****")
print(3 & 5) #011 101 001
print(bin(23))
print(bin(53))
#110101
#010111
#010101 -> 1+4+16
print(23 & 53)*****选出数组中所有大于平均数的数***** [ 8 5 11 4 9 12 17 6 19 3] 9.4 [11, 12, 17, 19] [11 12 17 19] [False False True False False True True False True False] *****布尔型索引原理***** [11 9 12 17 19] *****给定一个数组,选出数组中所有大于5的偶数***** [13 11 18 8 0 9 15 4 11 9] [18 8] [18 8] [13 11 18 8 0 9 15 4 11 9] *****逻辑与***** 1 0b10111 0b110101 21
demo8-花式索引
#demo8-花式索引
print("*****一维数组,选出其中第1,3,5,6,7个元素*****")
#Q:对于一个数组,选出其中第1,3,5,6,7个元素,组成新的二维数组
test = np.arange(20)
print(test)
print(test[[1,3,5,6,7]])
print("*****二维数组,花式索引*****")
test = np.arange(20).reshape(4,5)
print(test)
print(test[0,2:3]) #左边常规索引,右边切片
print(test[0,test[0]>2]) #左边常规索引,右边布尔型索引
print(test[0,test[0]>2]) #左边常规索引,右边布尔型索引
print("*****二维数组索引两边不能同时为花式索引*****")
#选6 8 16 18
test = np.arange(20).reshape(4,5)
print(test)
print(test[[1,3],[1,3]]) #错误!!!
print(test[[1,3],:][:,[1,3]]) #分开花式索引
*****一维数组,选出其中第1,3,5,6,7个元素***** [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19] [1 3 5 6 7] *****二维数组,花式索引***** [[ 0 1 2 3 4] [ 5 6 7 8 9] [10 11 12 13 14] [15 16 17 18 19]] [2] [3 4] [3 4] *****二维数组索引两边不能同时为花式索引***** [[ 0 1 2 3 4] [ 5 6 7 8 9] [10 11 12 13 14] [15 16 17 18 19]] [ 6 18] [[ 6 8] [16 18]]
demo9-取整
#demo9-取整
print("*****1.6取整*****")
test = 1.6
test = np.array(test)
print(int(test)) #向0取整
print(np.floor(test)) #向下取整
print(np.ceil(test)) #向上取整
print(np.round(test))
print("*****-1.6取整*****")
test = -1.6
test = np.array(test)
print(int(test)) #向0取整
print(np.floor(test)) #向下取整
print(np.ceil(test)) #向上取整
print(np.round(test))
print("*****列表取整*****")
x = np.arange(-5.5,5.5)
print(x)
print(np.ceil(x)) #向上
print(np.floor(x))#向下
print(np.trunc(x))#截断 向0取整
#round到两边距离相等时为偶数值!!!!
print("*****round到两边距离相等时为偶数值*****")
print(x)
print(np.round(x))
print(np.rint(x)) #rint与round一样
*****1.6取整***** 1 1.0 2.0 2.0 *****-1.6取整***** -1 -2.0 -1.0 -2.0 *****列表取整***** [-5.5 -4.5 -3.5 -2.5 -1.5 -0.5 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5] [-5. -4. -3. -2. -1. -0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.] [-6. -5. -4. -3. -2. -1. 0. 1. 2. 3. 4.] [-5. -4. -3. -2. -1. -0. 0. 1. 2. 3. 4.] *****round到两边距离相等时为偶数值***** [-5.5 -4.5 -3.5 -2.5 -1.5 -0.5 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5] [-6. -4. -4. -2. -2. -0. 0. 2. 2. 4. 4.] [-6. -4. -4. -2. -2. -0. 0. 2. 2. 4. 4.]
demo10-通用函数
#demo10-通用函数
#通用函数:能同时对数组中所有元素进行运算的函数
#一元通用函数:abs sqrt exp log ceil floor rint trunc modf isnan isinf cos sin tan
#二元通用函数:add substract multiply divide power mod maximum minimum
print("*****abs sqrt modf....*****")
test = np.arange(-5.5,5.5)
print(test)
print(np.abs(test))
print(np.sqrt(test))
print(np.modf(test)) #整数与小数部分分开
print("*****nan与inf*****")
print(5/test) #inf 无穷大,比任何一个数都大
print(np.sqrt(test)) #nan not a number
#nan与Inf是特殊的浮点数
print(np.nan == np.nan)
print(np.nan is np.nan)
print("*****删除数组中的nan*****")#判断inf同理
test = np.arange(5)
test = test/test
print(test)
print(np.isnan(test)) #判断nan
print(test[~np.isnan(test)]) #位反
print("*****二元函数*****")
a = np.arange(3,8)
b = np.array([2,5,3,7,4])
print(a)
print(b)
print(np.maximum(a,b)) #比较取大
print(np.minimum(a,b))
print(np.mod(a,b)) #取模
print(np.power(a,b))*****abs sqrt modf....***** [-5.5 -4.5 -3.5 -2.5 -1.5 -0.5 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5] [5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5] [ nan nan nan nan nan nan 0.70710678 1.22474487 1.58113883 1.87082869 2.12132034] (array([-0.5, -0.5, -0.5, -0.5, -0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]), array([-5., -4., -3., -2., -1., -0., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.])) *****nan与inf***** [ -0.90909091 -1.11111111 -1.42857143 -2. -3.33333333 -10. 10. 3.33333333 2. 1.42857143 1.11111111] [ nan nan nan nan nan nan 0.70710678 1.22474487 1.58113883 1.87082869 2.12132034] False True *****删除数组中的nan***** [nan 1. 1. 1. 1.] [ True False False False False] [1. 1. 1. 1.] *****二元函数***** [3 4 5 6 7] [2 5 3 7 4] [3 5 5 7 7] [2 4 3 6 4] [1 4 2 6 3] [ 9 1024 125 279936 2401]
demo11-Numpy统计方法
#demo11-numpy统计方法
test = np.arange(15)
print(test.sum())
print(test.mean())
print(test.std())
print(test.var())
print("*"*20)
test = np.arange(0,10,0.2)
print(test)
print(test.mean())
print(test.std())
print(test.mean()-test.std(),test.mean()+test.std())
print(test.mean()-2*test.std(),test.mean()+2*test.std()) #2倍标准差 95.5%
print(test.max(),test.min())
print(test.argmax(),test.argmin())105 7.0 4.320493798938574 18.666666666666668 ******************** [0. 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1. 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2. 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3. 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4. 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5. 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6. 6.2 6.4 6.6 6.8 7. 7.2 7.4 7.6 7.8 8. 8.2 8.4 8.6 8.8 9. 9.2 9.4 9.6 9.8] 4.9 2.8861739379323628 2.0138260620676376 7.786173937932363 -0.8723478758647252 10.672347875864727 9.8 0.0 49 0
demo12-随机数生成
#demo12-numpy随机数生成
print("*****random*****")
import random
print(random.random()) #0-1之间的数字
print(random.randint(0,10)) #[a,b]
print(random.choice([1,2,3,4,5]))
print(random.choice("hello world"))
tempList = [2,3,5,6,3,432,5,6]
random.shuffle(tempList)
print(tempList)
print("*****np.random*****") #指定数组长度或形状
print(np.random.randint(0,10,10))
print(np.random.randint(0,10,(3,5)))
print(np.random.rand(10)) #生成10个0-1的浮点数
print(np.random.uniform(0,10,10)) #生成10个0-10的浮点数 #均匀分布
print(np.random.choice([1,2,3,5,6,43,4],10))#随机出10个
*****random***** 0.6089449206423057 7 3 o [3, 3, 6, 2, 6, 5, 432, 5] *****np.random***** [3 0 5 2 4 1 1 7 5 1] [[9 2 4 1 1] [1 4 6 3 8] [0 8 9 8 7]] [0.29993867 0.58133357 0.38837081 0.8073509 0.58386204 0.02121475 0.14208183 0.13526007 0.28158366 0.10912549] [4.61452949 4.05137104 9.72873352 3.17844699 8.05749104 8.10677542 2.78802965 6.65677334 1.19002791 5.73758801] [ 6 4 4 6 3 1 6 5 2 43]
demo13-正态分布与均匀分布
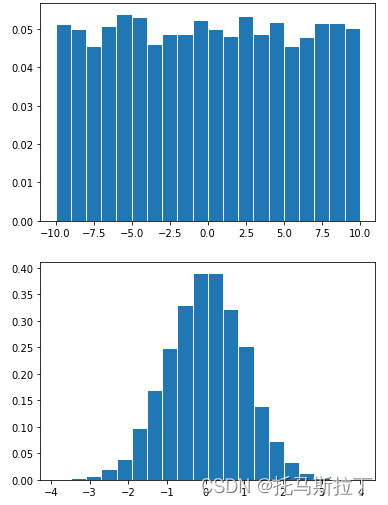
#demo13-正态分布与均匀分布
testUniformList = np.random.uniform(-10,10,10000)#均匀分布
testNormList = np.random.randn(10000) #标准正态分布
plt.hist(testUniformList,bins=20,density=True,edgecolor="white")
plt.show()
plt.hist(testNormList,bins=20,density=True,edgecolor="white")
plt.show()