理解 tf.keras.layers.Attention
欢迎关注微信公众号:python科技园
官方链接:https://tensorflow.google.cn/versions/r2.1/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Attention
语法:
tf.keras.layers.Attention(
use_scale=False, **kwargs
)Inputs are query tensor of shape [batch_size, Tq, dim], value tensor of shape [batch_size, Tv, dim] and key tensor of shape [batch_size, Tv, dim]. The calculation follows the steps:
- Calculate scores with shape
[batch_size, Tq, Tv]as aquery-keydot product:scores = tf.matmul(query, key, transpose_b=True). - Use scores to calculate a distribution with shape
[batch_size, Tq, Tv]:distribution = tf.nn.softmax(scores). - Use
distributionto create a linear combination ofvaluewith shapebatch_size, Tq, dim]:return tf.matmul(distribution, value).
参数:
use_scale: IfTrue, will create a scalar variable to scale the attention scores.causal: Boolean. Set toTruefor decoder self-attention. Adds a mask such that positionicannot attend to positionsj > i. This prevents the flow of information from the future towards the past.
Call 参数:
inputs: List of the following tensors:- query: Query
Tensorof shape[batch_size, Tq, dim]. - value: Value
Tensorof shape[batch_size, Tv, dim]. - key: Optional key
Tensorof shape[batch_size, Tv, dim]. If not given, will usevaluefor bothkeyandvalue, which is the most common case.
- query: Query
mask: List of the following tensors:- query_mask: A boolean mask
Tensorof shape[batch_size, Tq]. If given, the output will be zero at the positions wheremask==False. - value_mask: A boolean mask
Tensorof shape[batch_size, Tv]. If given, will apply the mask such that values at positions wheremask==Falsedo not contribute to the result.
- query_mask: A boolean mask
输出 shape:
Attention outputs of shape [batch_size, Tq, dim].
The meaning of query, value and key depend on the application. In the case of text similarity, for example, query is the sequence embeddings of the first piece of text and value is the sequence embeddings of the second piece of text. key is usually the same tensor as value.
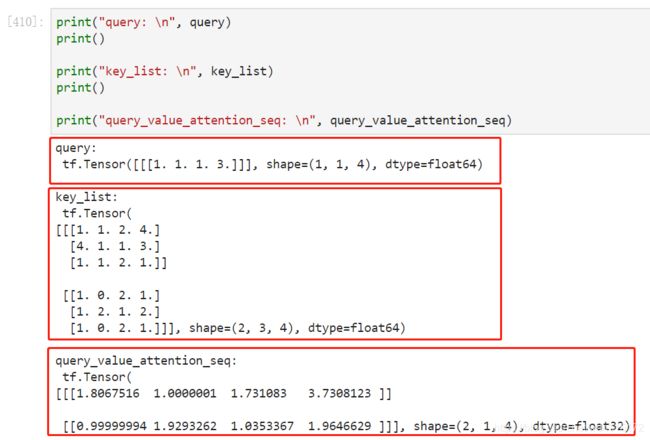
示例 1:
import tensorflow as tf
query = tf.convert_to_tensor(np.asarray([[[1., 1., 1., 3.]]]))
key_list = tf.convert_to_tensor(np.asarray([[[1., 1., 2., 4.], [4., 1., 1., 3.], [1., 1., 2., 1.]],
[[1., 0., 2., 1.], [1., 2., 1., 2.], [1., 0., 2., 1.]]]))
query_value_attention_seq = tf.keras.layers.Attention()([query, key_list])
结果 1:
采用 语法 中提到的计算方式计算,看看结果:
scores = tf.matmul(query, key, transpose_b=True)
distribution = tf.nn.softmax(scores)
print(tf.matmul(distribution, value))示例 2:
import tensorflow as tf
scores = tf.matmul(query, key_list, transpose_b=True)
distribution = tf.nn.softmax(scores)
result = tf.matmul(distribution, key_list)结果 2:
其中:distribution 的结果即为每个输入向量的权重值。
[0.731, 0.269, 9.02e-5] 分别代表 [[1., 1., 2., 4.], [4., 1., 1., 3.], [1., 1., 2., 1.]] 的权重值。
可见 结果 1 和 结果 2 的返回值一致。