QoS mechanisms——policing(管制)
流量管制与整形概述
 在流量管制和整形之前,必须先对报文进行分类;
在流量管制和整形之前,必须先对报文进行分类;
流量整形队列中多余的数据包,以保持所需的流量速率。
流量管制丢弃或标记超额流量,保持在一个流量速率限制。
管制和整形不是拥塞管理机制,即使没有产生拥塞,也能生效。
为什么需要管制?
限制访问资源的高速接入
限制访问某些应用程序或业务类的流量速率
对2层与3层超过的流量做标记
为什么需要整形?
预防和管理在ATM和帧中继网络中,非对称带宽的流量路径;
在帧中继或ATM网络中,规范发送流量速率
主要应用于低速链路中
传输管制举例
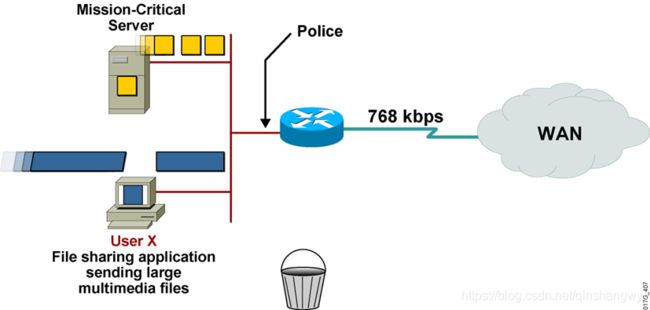
限制文件共享服务流量的速率为56Kbps
对关键业务流量不做限制
传输整形举例
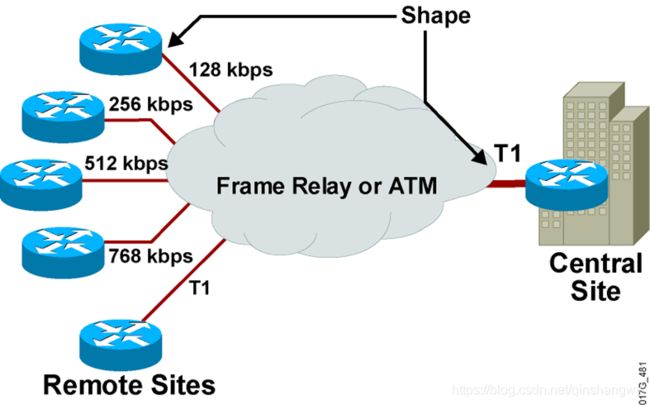 central site对remote site 速率不匹配
central site对remote site 速率不匹配
remote site对central site 流量超额
以上两种情况都会导致缓冲和延迟或丢弃数据包
管制与整形
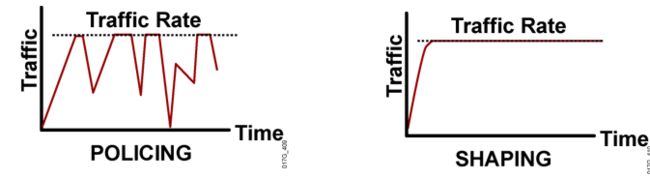 管制:
管制:
应用于输入方向和输出方向
丢弃超出限制的数据包
被丢弃的TCP数据包将导致重传
支持数据包标记和重标记
减少对缓冲区的使用(整形要求有额外的整形队列系统)
整形:
只能应用于输出方向
超过的流量将被放到缓冲区,直到缓冲区满为止
超出的数据包放入缓冲区可以减少TCP重传
不支持数据包标记与重标记
整形支持帧中继的拥塞指示
令牌桶
在实施QOS策略时,可以将用户的数据限制在特定的带宽,当用户的流量超过额定带宽时,超过的带宽将采取其它方式来处理。要衡量流量是否超过额定的带宽,网络设备并不是采用单纯的数字加减法来决定的。
比如带宽为100K,而用户发来的流量为110K,网络设备并不是靠110K减去100K等于10K,就认为用户超过流量10K。
当网络设备衡量流量是否超过额定带宽时,需要查看令牌桶,而令牌桶中会放置一定数量的令牌,一个令牌允许接口发送或接收1bit数据(有时是1 Byte数据),当接口通过1bit数据后,同时也要从桶中移除一个令牌。当桶里没有令牌的时候,任何流量都被视为超过额定带宽,只有当桶中有令牌时,数据才可以通过接口 。
单一的令牌桶
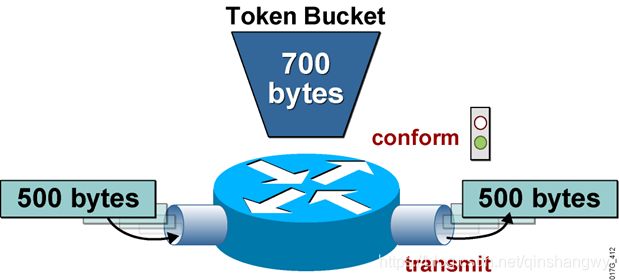 如果有足够的令牌桶可用(conform action),从桐中取出令牌相当于分组大小,该分组被转发,如果没有足够的令牌可用(exceed action),丢弃(或标记)数据包。
如果有足够的令牌桶可用(conform action),从桐中取出令牌相当于分组大小,该分组被转发,如果没有足够的令牌可用(exceed action),丢弃(或标记)数据包。
基于单令牌桶的管制
单速率(匀速率)单桶:流量出现两种结果,符合CIR和超出CIR
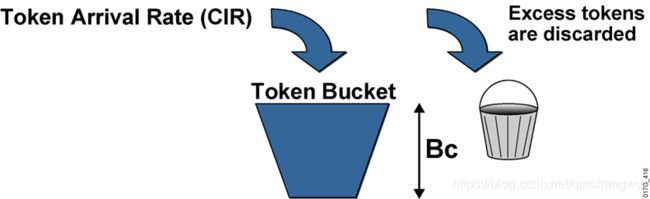 Bc:burst size,令牌桶的大小
Bc:burst size,令牌桶的大小
Tc:time interval 加令牌的时间,多久加一次令牌
CIR每秒种往桶里加令牌的速率,这个速率决定了用户流量
CIR=Bc/Tc
R1(config)#policy-map policy1
R1(config-pmap)#class c1
R1(config-pmap-c)#police ?
<8000-2000000000> Bits per second /CIR
cir Committed information rate
rate Specify police rate
R1(config-pmap-c)#police 8000 ?
<1000-512000000> Burst bytes /Bc
bc Conform burst
conform-action action when rate is less than conform burst
pir Peak Information Rate
R1(config-pmap-c)#police 8000 1000 ?
<1000-512000000> Burst bytes
be Excess burst
conform-action action when rate is less than conform burst
pir Peak Information Rate
R1(config-pmap-c)#police 8000 1000 conform-action ?
drop drop packet
set-clp-transmit set atm clp and send it
set-discard-class-transmit set discard-class and send it
set-dscp-transmit set dscp and send it
set-frde-transmit set FR DE and send it
set-mpls-exp-imposition-transmit set exp at tag imposition and send it
set-mpls-exp-topmost-transmit set exp on topmost label and send it
set-prec-transmit rewrite packet precedence and send it
set-qos-transmit set qos-group and send it
transmit transmit packet
R1(config-pmap-c)#police 8000 1000 conform-action transmit ex
R1(config-pmap-c)#police 8000 1000 conform-action transmit exceed-action drop
单速率双桶
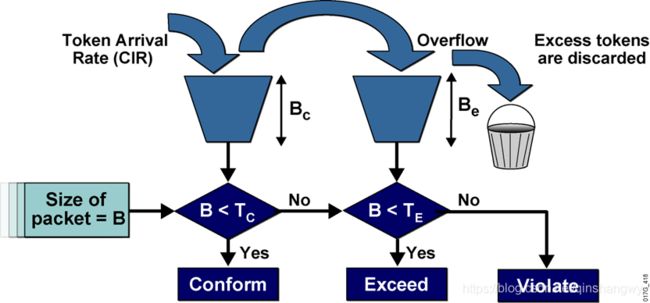 Be:超出的突发数量(多余的数量)
Be:超出的突发数量(多余的数量)
Tc:在Bc令牌桶的令牌
Te:在Be令牌桶的令牌
返回值是conform符合 exceed超出 ,violate违反
当往第一个桶里加了多余的令牌,会放入到第二个桶中。
与前者相比,只是允许了流量的突发,实际上超出了Te,一样是被丢弃的。
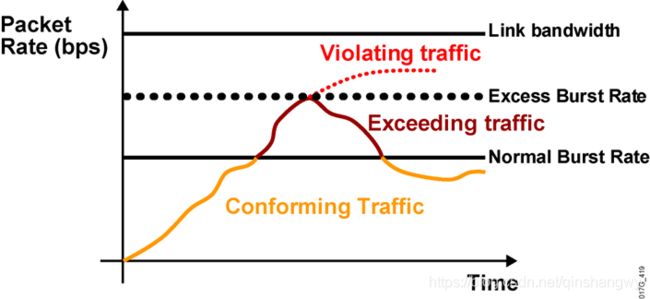 案例:
案例:
平均速率还是8000bit/s,正常桶(normal burst size)的大小为1000字节,超出桶(the excess burst)的大小是1000字节。
policy-map policy1
class c1
police 8000 1000 1000 conform-action transmit exceed-action set-qos-transmit 1 violate-action drop
双速率双桶
 Tc: Token in CIR bucket
Tc: Token in CIR bucket
Tp: Token in PIR bucket PIR>CIR, Be>Bc
根据两个不同的速率实施流量监管:
Committed Information Rate 承诺信息速率
Peak Information Rate 峰值信息速率
单速率配置,单桶与双桶的区别无非是动作一个是2个,一个是3个
 avg-rate: Traffic rate in bps (8,000 to 200,000,000)
avg-rate: Traffic rate in bps (8,000 to 200,000,000)
BC : normal burst sets the size in bytes
Default is 1500 bytes, or CIR / 32, whatever is higher
BE: Excess burst sets the size in bytes
Default is BC
action:
transmit (default conform action)
drop (default exceed and violate action)
set-prec-transmit ip-precedence
set-dscp-transmit dscp
set-qos-transmit qos-group
set-mpls-exp-transmit mpls-exp
set frde-transmit
set-clp-transmit
双速率配置
 指定CIR和PIR
指定CIR和PIR
CIR =提交信息率(bps)
PIR峰值信息率(bps)
bc和be关键字及其相关的参数(分别为整合-突发和峰值-突发)是可选的
policy-map policy
class c1
police cir 1600000 bc 400000 pir 2400000 be 400000
conform-action transmit
exceed-action transmit
violate-action drop
policy-map police1
class bulk-ftp
police cir percent 20 pir percent 40 conform-action set-dscp-transmit af11 exceed-action set-dscp-transmit 0 violate-action drop
!
interface Ethernet 0/0
service-policy input police1
!
interface Serial 0/0
service-policy input police1
