OpenCV(四)——图像特征与目标检测
课程一览:
![]()
目录
1.图像特征的理解
2.形状特征描述
2.1 HOG原理
2.2 Harris
2.3 SIFT
3.纹理特征
4.模板匹配
5.人脸检测
1.图像特征的理解
图像特征是图像中独特的,易于跟踪和比较的特定模板或特定结构。
- 图像特征提取与匹配是计算机视觉中的一个关键问题,在目标检测、物体识别、三维重建、图像配准、图像理解等具体应用中发挥着重要作用。
- 图像特征主要有图像的颜色特征、纹理特征、形状特征和空间关系特征。
(1)颜色特征
- 颜色特征是一种全局特征,描述了图像或图像区域所对应的景物的表面性质
- 颜色特征描述方法
- 颜色直方图
- 颜色空间
- 颜色分布
(2)纹理特征
- 纹理特征也是一种全局特征,它也描述了图像或图像区域所对应景物的表面性质。但由于纹理只是一种物体表面的特性,并不能完全反映出物体的本质属性,所以仅仅利用纹理特征是无法获得高层次图像内容的。
(3)形状特征
- 形状特征有两类表示方法,一类是轮廓特征,另一类是区域特征。图像的轮廓特征主要针对物体的外边界,而图像的区域特征则描述了是图像中的局部形状特征。
(4)空间关系特征
- 空间关系特征,是指图像中分割出来的多个目标之间的相互的空间位置或相对方向关系
- 这些关系也可分为连接/邻接关系,交叠/重叠关系和包含/独立关系等。
2.形状特征描述
2.1 HOG原理
HOG特征提取
- 方向梯度直方图(HOG)特征是一种在计算机视觉和图像处理中用来进行物体检测的特征描述子。(主要用来提取形状特征)
- 它通过计算和统计图像局部区域的梯度直方图来构成特征。
- Hog特征结合SVM分类器已经被广泛应用于图像识别中,尤其在行人检测中获得了极大的成功。(用HOG提取特征,用SVM进行分类)
- 主要思想:在一幅图像中,目标的形状能够被梯度或边缘的方向密度分布很好的描述。
HOG实现过程
- 灰度化(将图像看做一个x,y,z(灰度)的三维图像)
- 采用Gamma校正法对输入图像进行颜色空间的标准化(归一化)
- 计算图像每个像素的梯度(包括大小和方向)
- 将图像划分成小cells
- 统计每个cell的梯度直方图(不同梯度的个数),得到cell的描述子
- 将每几个cell组成一个block,得到block的描述子
- 将图像image内的所有block的HOG特征descriptor串联起来就可以得到HOG特征,该特征向量就是用来目标检测或分类的特征
#=================================HOG 特征===============================#
# flag = 0
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
# 判断矩形i是否完全包含在矩形o中
def is_inside(o, i):
ox, oy, ow, oh = o
ix, iy, iw, ih = i
return ox > ix and oy > iy and ox + ow < ix + iw and oy + oh < iy + ih
# 对人体绘制颜色框
def draw_person(image, person):
x, y, w, h = person
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 255), 2)
img = cv2.imread("people.jpg")
hog = cv2.HOGDescriptor() # 启动检测器对象
hog.setSVMDetector(cv2.HOGDescriptor_getDefaultPeopleDetector()) # 指定检测器类型为人体
found, w = hog.detectMultiScale(img,0.1,(2,2)) # 加载并检测图像
print(found)
print(w)
# 丢弃某些完全被其它矩形包含在内的矩形
found_filtered = []
for ri, r in enumerate(found):
for qi, q in enumerate(found):
if ri != qi and is_inside(r, q):
break
else:
found_filtered.append(r)
print(found_filtered)
# 对不包含在内的有效矩形进行颜色框定
for person in found_filtered:
draw_person(img, person)
cv2.imshow("people detection", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()2.2 Harris
(1)Harris角点检测
- 角点:在现实世界中,角点对应于物体的拐角,道路的十字路口、丁字路口等。从图像分析的角度来定义角点可以有以下两种定义:
- 角点可以是两个边缘的交点
- 角点是邻域内具有两个主方向的特征点
- 角点计算方法:
- 前者通过图像边缘计算,计算量大,图像局部变化会对结果产生较大的影响
- 后者基于图像灰度的方法通过计算点的曲率及梯度来检测角点
- 角点所具有的特征:
- 轮廓之间的交点
- 对于同一场景,即使视角发生变化,通常具备稳定性质的特征
- 该点附近区域的像素点无论在梯度方向上还是其梯度幅值上有着较大变化
- 性能较好的角点:
- 检测出图像中“真实”的角点
- 准确的定位性能
- 很高的重复检测率
- 噪声的鲁棒性
- 较高的计算效率
(2)Harris实现过程
- 计算图像在X和Y方向的梯度
- 计算图像两个方向梯度的乘积
- 使用高斯函数对三者进行高斯加权,生成矩阵M的A,B,C
- 计算每个像素的Harris响应值R,并对小于某一阈值t的R置为零
- 在3×3或5×5的邻域内进行非最大值抑制,局部最大值点即为图像中的角点
(3)Harris代码应用
Open中的函数cv2.cornerHarris()可以用来进行角点检测。
参数如下:
- img:数据类型为float32的输入图像
- blockSize:角点检测中要考虑的领域大小
- ksize:Sobel求导中使用的窗口大小
- k:Harris角点检测方程中的自由参数,取值参数为[0.04,0.06]
#=================================Harris 角点===============================#
# flag = 0
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
img = cv2.imread('harris2.png')
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = np.float32(gray)
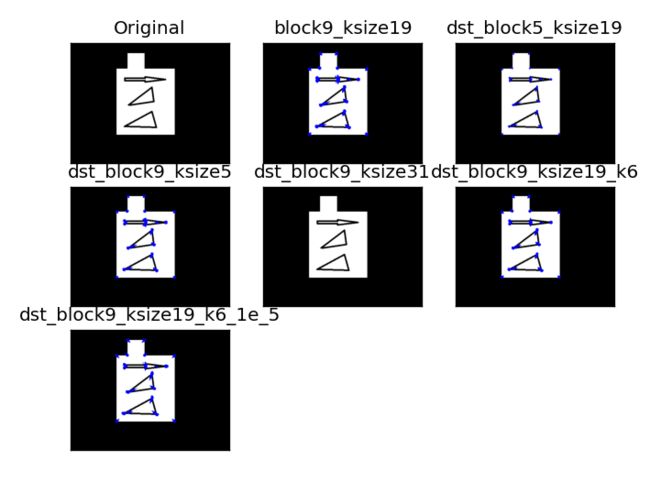
dst_block9_ksize19 = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 9, 19, 0.04)
img1 = np.copy(img)
img1[dst_block9_ksize19 > 0.01 * dst_block9_ksize19.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
dst_block5_ksize19 = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 5, 19, 0.04)
img2 = np.copy(img)
img2[dst_block5_ksize19 > 0.01 * dst_block5_ksize19.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
dst_block9_ksize5 = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 9, 5, 0.04)
img3 = np.copy(img)
img3[dst_block9_ksize5 > 0.01 * dst_block9_ksize5.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
dst_block9_ksize31 = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 9, 31, 0.04)
img4 = np.copy(img)
img4[dst_block9_ksize31 > 0.01 * dst_block9_ksize31.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
dst_block9_ksize19_k6 = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 9, 19, 0.06)
img5 = np.copy(img)
img5[dst_block9_ksize19_k6 > 0.01 * dst_block9_ksize19_k6.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
dst_block9_ksize19_k6_1e_5 = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 9, 19, 0.06)
img6 = np.copy(img)
img6[dst_block9_ksize19_k6_1e_5 > 0.00001 * dst_block9_ksize19_k6_1e_5.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
titles = ["Original", "block9_ksize19", "dst_block5_ksize19", "dst_block9_ksize5", "dst_block9_ksize31",
"dst_block9_ksize19_k6", "dst_block9_ksize19_k6_1e_5"]
imgs = [img, img1, img2, img3, img4, img5, img6]
for i in range(len(titles)):
plt.subplot(3, 3, i + 1), plt.imshow(imgs[i]), plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
# cv2.imshow('src',img)
# cv2.imshow('dst',img5)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()2.3 SIFT
(1)SIFT算法
- SIFT,即尺度不变特征变换算法,是用于图像处理领域的一种算法。SIFT具有尺度不变性,可在图像中检测出关键点,是一种局部特征描述子。
- 其应用范围包含物体辨识、机器人地图感知与导航、影响缝合、3D模型建立、手势辨识、影响追踪和动作比对。
(2)SIFT特性
- 独特性:也就是特征点可分变性高,类似指纹,适合在海量数据汇总匹配
- 多量性:提供的特征多
- 高速性:就是速度快
- 可扩展:能与其他特征向量联合使用
(3)SIFT特点
- 旋转、缩放、平移不变性
- 解决图像仿射变换,投影变换的关键的匹配
- 光照影响小
- 目标遮挡影响较小
- 噪声景物影响小
(4)SIFT算法步骤
- 尺度空间极值检测点检测
- 关键点定位:去除一些不好的特征点,保存下来的特征点能够满足稳定性等条件
- 关键点方向参数:获取关键点所在尺度空间的邻域,然后计算该区域的梯度和方向,根据计算得到的结果创建方向直方图,直方图的峰值为主方向的参数
- 关键点描述符:每个关键点用一组向量(位置、尺度、方向)将这个关键点描述出来,使其不随着光照、视角等等影响而改变
- 关键点匹配:分别对模板图和实时图建立关键点描述符集合,通过对比关键点描述符来判断两个关键点是否相同
#=================================SIFT===============================#
# flag = 0
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
img = cv2.imread('harris2.png')
gray= cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kp = sift.detect(gray,None)#找到关键点
img=cv2.drawKeypoints(gray,kp,img)#绘制关键点
cv2.imshow('sp',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()3.纹理特征
(1)LBP介绍
- LBP(局部二值模式),是一种用来描述图像局部纹理特征的算子;它具有旋转不变性和灰度不变性等显著的优点
(2)LBP原理
- LBP算子定义在一个3×3的窗口内,以窗口中心像素为阈值,与相邻的8个像素的灰度值比较,若周围的像素值大于中心像素值,则该位置被标记为1;否则标记为0。如此可以得到一个8位二进制数(通常还要转换为10进制,即LBP码,共256种),将这个值作为窗口中心像素点的LBP值,以此来反应这个3×3区域的纹理信息.
- 数学公式:
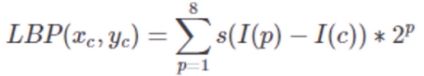
- 其中,p表示3×3窗口中除中心像素点外的第p个像素点
- l(c)表示中心像素点的灰度值,l(p)表示邻域内第p个像素点的灰度值
- s(x)公式如下:
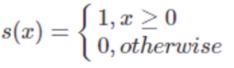
- LBP记录的是中心像素点与邻域像素点之间的差值
- 当光照变化引起像素灰度值同增同减时,LBP变化并不明显
- LBP对与光照变化不敏感,LBP检测的仅仅是图像的纹理信息
#=================================LBP===============================#
# flag = 0
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
def LBP(src):
'''
:param src:灰度图像
:return:
'''
height = src.shape[0]
width = src.shape[1]
dst = src.copy()
lbp_value = np.zeros((1, 8), dtype=np.uint8)
# print(lbp_value)
neighbours = np.zeros((1, 8), dtype=np.uint8)
# print(neighbours)
for x in range(1, width - 1):
for y in range(1, height - 1):
neighbours[0, 0] = src[y - 1, x - 1]
neighbours[0, 1] = src[y - 1, x]
neighbours[0, 2] = src[y - 1, x + 1]
neighbours[0, 3] = src[y, x - 1]
neighbours[0, 4] = src[y, x + 1]
neighbours[0, 5] = src[y + 1, x - 1]
neighbours[0, 6] = src[y + 1, x]
neighbours[0, 7] = src[y + 1, x + 1]
center = src[y, x]
for i in range(8):
if neighbours[0, i] > center:
lbp_value[0, i] = 1
else:
lbp_value[0, i] = 0
lbp = lbp_value[0, 0] * 1 + lbp_value[0, 1] * 2 + lbp_value[0, 2] * 4 + lbp_value[0, 3] * 8 \
+ lbp_value[0, 4] * 16 + lbp_value[0, 5] * 32 + lbp_value[0, 6] * 64 + lbp_value[0, 7] * 128
# print(lbp)
dst[y, x] = lbp
return dst
img = cv2.imread('people.jpg', 0)
print(img.shape)
cv2.imshow('src', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
new_img = LBP(img)
cv2.imshow('dst', new_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()4.模板匹配
(1)模板匹配介绍
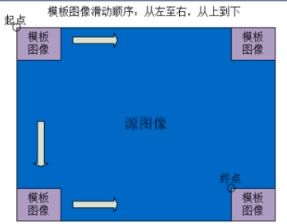
- 模板匹配是一种最原始、最基本的模式识别方法,研究某一特定目标的图像位于图像的什么地方,进而对图像进行定位。
- 在待检测图像上,从左到右,从上向下计算模板图像与重叠子图像的匹配度,匹配程度越大,两者相同的可能性越大。
(2)函数:result = cv2.matchTemplate(image,templ,method)
- image参数表示待搜索图像
- templ参数表示模板图像,必须不大于原图像并具有相同的数据类型
- method参数表示计算匹配程度的方法
(3)匹配方法
- TM_SQDIFF_NORMED是标准平方差匹配,通过计算两图之间平方差来进行匹配,最好匹配为0,匹配越差,匹配值越大。
- TM_CCORR_NORMED是标准相关性匹配,采用模板和图像间的乘法操作,数越大表示匹配程度较高,0表示最坏的匹配效果,这种方法除了亮度线性变化对相似度计算的影响。
- TM_CCOEFF_NORMED是标准相关性系数匹配,两图减去了各自的平均值之外,还要各自除以各自的方差。将模板对其均值的相对值对其均值的相关值进行匹配,1表示完美匹配,-1表示糟糕的匹配,0表示没有任何相关性(随机序列)。
函数:minVal,maxVal,minLoc,maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc()
- minVal参数表示返回的最小值
- maxVal参数表示返回的最大值
- minLoc参数表示返回的最小位置
- maxLoc参数表示返回的最大位置
# =================================模板检测===============================#
# flag = 0
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
def template_demo(tpl, target):
methods = [cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED, cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED] # 3种模板匹配方法
th, tw = tpl.shape[:2]
for md in methods:
# print(md)
result = cv2.matchTemplate(target, tpl, md)
# print(result.shape)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
print(min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc)
if md == cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED:
tl = min_loc
else:
tl = max_loc
br = (tl[0] + tw, tl[1] + th) # br是矩形右下角的点的坐标
cv2.rectangle(target, tl, br, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.namedWindow("match-" + np.str(md), cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("match-" + np.str(md), target)
tpl = cv2.imread("sample2.jpg")
print(tpl.shape)
target = cv2.imread("target1.jpg")
print(target.shape)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv2.namedWindow('template image', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("template image", tpl)
cv2.namedWindow('target image', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("target image", target)
template_demo(tpl, target)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()5.人脸检测
- 一般而言,一个完整的人脸识别系统包含四个主要组成部分,即人脸检测、人脸对齐、人类特征提取以及人脸识别。
- 四部分流水线操作:
- 人脸检测在图像中找到人脸的位置
- 人脸配准在人脸上找到眼镜、鼻子、嘴巴等面部器官的位置
- 通过人脸特征提取将人脸图像信息抽象为字符串信息
- 人脸识别将目标人脸图像与既有人脸比对计算相似度,确认人脸对应的身份
# =================================人脸检测===============================#
# flag = 0
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
# 读入图像
img = cv2.imread("3.png")
# 加载人脸特征,该文件在 python安装目录\Lib\site-packages\cv2\data 下
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(r'haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
# 将读取的图像转为COLOR_BGR2GRAY,减少计算强度
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
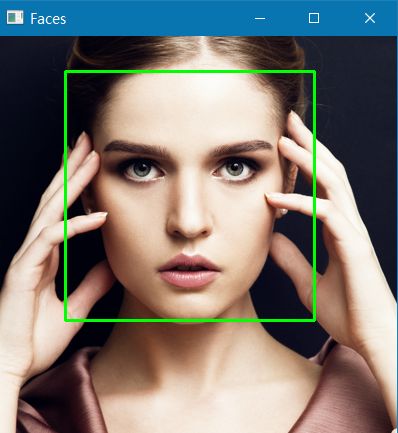
# 检测出的人脸个数
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor=1.15, minNeighbors=4, minSize=(5, 5))
print("Face : {0}".format(len(faces)))
print(faces)
# 用矩形圈出人脸的位置
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.namedWindow("Faces")
cv2.imshow("Faces", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()# ==================================人脸检测===============================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
predictor_model = 'shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat'
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(predictor_model)
# cv2读取图像
test_film_path = "3.png"
img = cv2.imread(test_film_path)
# 取灰度
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# 人脸数rects
rects = detector(img_gray, 0)
print(rects[0])
for i in range(len(rects)):
landmarks = np.matrix([[p.x, p.y] for p in predictor(img, rects[i]).parts()])
print(landmarks, type(landmarks))
for idx, point in enumerate(landmarks):
# 68点的坐标
pos = (point[0, 0], point[0, 1])
# print(idx+1, pos)
# 利用cv2.circle给每个特征点画一个圈,共68个
cv2.circle(img, pos, 3, color=(0, 255, 0))
# 利用cv2.putText输出1-68
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv2.putText(img, str(idx + 1), pos, font, 0.5, (0, 0, 25 5), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
# cv2.imwrite("result.png", img)
cv2.imshow("img", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()