【ECCV 2020】Joint Visual and Temporal Consistency for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Person Re-ID
JVTC
- 1 背景知识
-
- 1.1Person Re-Identification (ReID)
- 1.2 supervised person ReID
-
- Problem #2
- Problem #3
- 1.3 unsupervised learning
- 1.4 unsupervised person ReID
- 1.5 Unsupervised domain adaptive person Re-IDentification
-
- Problem #1
- 2 内容概要
-
- 2.1 本文工作
- 2.2 实验效果
- 2.3 相关工作
-
- Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA)
- Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Person ReID
- 2.4 数据集
- 3 方法提要
-
- 3.1 方法框架
- 3.2 实验结果
- 4 方法详解
- 参考文献
下方↓公众号后台回复“JVTC”,即可获得论文电子资源。
![]()
1 背景知识
1.1Person Re-Identification (ReID)
Person Re-Identification (ReID) aims to identify a probe person in a camera net- work by matching his/her images or video sequences and has many promising applications like smart surveillance and criminal investigation. Recent
1.2 supervised person ReID
Problem #2
supervised person ReID methods rely on a large amount of labeled data which is expensive to annotate.
Problem #3
Deep models trained on the source domain suffer substantial performance drop when transferred to a different target domain.
1.3 unsupervised learning
To tackle Problem #2 and Problem #3, unsupervised learning [5,29,39] could take advantage of abundant unlabeled data for training. unsupervised learning relieves the requirement for expensive data annotation, hence shows better potential to push person ReID towards real applications.
1.4 unsupervised person ReID
unsupervised person ReID are defined as a transfer learning task, which leverages labeled data on other domains.
方法分类
- using Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to transfer the image style from labeled source domain to unlabeled target domain while preserving identity labels for training [31,39,41]
- pre-training a deep model on source domain, then clustering unlabeled data in target domain to estimate pseudo labels for training [5,34] (本文属于此类)
1.5 Unsupervised domain adaptive person Re-IDentification
Problem #1
Unsupervised domain adaptive person Re-IDentification (ReID) is challenging because of the large domain gap between source and target domains, as well as the lackage of labeled data on the tar- get domain.
2 内容概要
2.1 本文工作
- The SAC model efficiently performs feature optimization in each local train- ing batch by assigning images with different labels. //SAC模型通过为图像分配不同的标签,在每批局部训练中有效地进行特征优化
- The MTC method performs feature optimization in the global training set by predicting labels with visual similarity and temporal consistency. //MTC方法通过视觉相似性和时间一致性预测标签,在全局训练集中进行特征优化
- Our temporal consistency does not require any extra annotations or manual alignments, and could be utilized in both model training and ReID similarity computation. //我们的时间一致性不需要任何额外的注释或手动对齐,可以用于模型训练和ReID相似性计算。
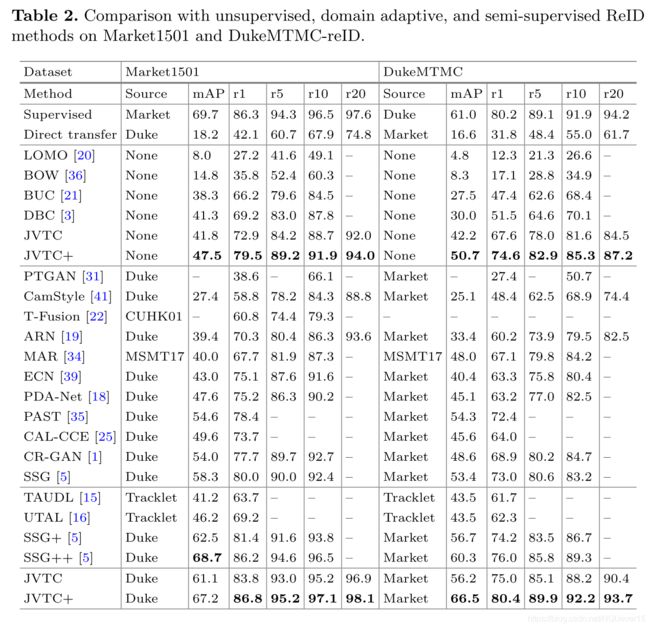
2.2 实验效果
the superiority of proposed method in both unsu- pervised and unsupervised domain adaptive ReID tasks.
2.3 相关工作
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA)
The aim of UDA is to align the domain distribution between source and target domains. A common solution of UDA is to define and minimize the domain discrepancy between source and target domain.
Different from domain adaption in person ReID, traditional UDA mostly assumes that the source domain and target domain share same classes. However, in person ReID, different domain commonly deals with different persons, thus have different classes.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Person ReID
2.4 数据集
- Market1501
- DukeMTMC-ReID
- MSMT17
3 方法提要
This paper tackles Problem #1 through jointly enforcing visual and temporal consistency in the combination of a local one-hot classification and a global multi-class classification.
- The local one-hot classification assigns images in a training batch with different person IDs, then adopts a Self-Adaptive Classification (SAC) model to classify them. //局部单热点分类在具有不同人id的训练批中分配图像,然后采用一个自适应分类(SAC)模型进行分类。
- The global multi-class classification is achieved by predicting labels on the entire unlabeled training set with the Memory-based Temporal- guided Cluster (MTC). //全局多类分类是通过使用基于记忆的时态引导聚类(MTC)预测整个无标记训练集上的标签来实现的。
- MTC predicts multi-class labels by considering both visual similarity and temporal consistency to ensure the quality of label prediction. //MTC通过同时考虑视觉相似性和时间一致性来预测多类标签,以保证标签预测的质量。
- two images are assigned with the same label if they
- a) share large visual similarity
- b) share enough temporal consistency.
- To further ensure the accuracy of clustering result, MTC utilizes image features stored in the memory bank. //为了进一步保证聚类结果的准确性,MTC利用存储在存储库中的图像特征
- Memory bank is updated with augmented features after each training iteration to improve feature robustness. //记忆库在每次训练迭代后通过增强特征进行更新,以提高特征的鲁棒性。
3.1 方法框架
3.2 实验结果
4 方法详解
参考文献
- Chen, Y., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Instance-guided context rendering for cross-domain person re-identification. In: ICCV (2019)
- Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR (2009)
- Ding, G., Khan, S., Yin, Q., Tang, Z.: Dispersion based clustering for unsupervised person re-identification. In: BMVC (2019)
- Ester, M., Kriegel, H.P., Sander, J., Xu, X.: Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise. In: KDD (1996)
- Fu, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, Y., Shi, H., Huang, T.S.: Self-similarity group- ing: a simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re- identification. In: ICCV (2019)
- Ganin, Y., Lempitsky, V.: Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.7495 (2014)
- Ghifary, M., Kleijn, W.B., Zhang, M., Balduzzi, D., Li, W.: Deep reconstruction- classification networks for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9908, pp. 597–613. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0 36
- Gray, D., Tao, H.: Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008. LNCS, vol. 5302, pp. 262–275. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10. 1007/978-3-540-88682-2 21
- Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K., Rasch, M., Sch¨olkopf, B., Smola, A.J.: A kernel method for the two-sample-problem. In: NeurIPS (2007)
- He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
- Li, J., Wang, J., Tian, Q., Gao, W., Zhang, S.: Global-local temporal representa- tions for video person re-identification. In: ICCV (2019)
- Li, J., Zhang, S., Huang, T.: Multi-scale 3D convolution network for video based person re-identification. In: AAAI (2019)
- Li, J., Zhang, S., Huang, T.: Multi-scale temporal cues learning for video person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 4461–4473 (2020)
- Li, J., Zhang, S., Tian, Q., Wang, M., Gao, W.: Pose-guided representation learning for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2019)
- Li, M., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Unsupervised person re-identification by deep learning tracklet association. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11208, pp. 772–788. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi. org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0 45
- Li, M., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Unsupervised tracklet person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42, 1770–1778 (2019)
- Li, W., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Harmonious attention network for person re- identification. In: CVPR (2018)
- Li, Y.J., Lin, C.S., Lin, Y.B., Wang, Y.C.F.: Cross-dataset person re- identification via unsupervised pose disentanglement and adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.09675 (2019)
- Li, Y.J., Yang, F.E., Liu, Y.C., Yeh, Y.Y., Du, X., Frank Wang, Y.C.: Adaptation and re-identification network: an unsupervised deep transfer learning approach to person re-identification. In: CVPR Workshops (2018)
- Liao, S., Hu, Y., Zhu, X., Li, S.Z.: Person re-identification by local maximal occur- rence representation and metric learning. In: CVPR (2015)
- Lin, Y., Dong, X., Zheng, L., Yan, Y., Yang, Y.: A bottom-up clustering approach to unsupervised person re-identification. In: AAAI (2019)
- Lv, J., Chen, W., Li, Q., Yang, C.: Unsupervised cross-dataset person re- identification by transfer learning of spatial-temporal patterns. In: CVPR (2018)
- Mao, S., Zhang, S., Yang, M.: Resolution-invariant person re-identification. In: IJCAI (2019)
- Pan, Y., Yao, T., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Ngo, C.W., Mei, T.: Transferrable prototypical networks for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: CVPR (2019)
- Qi, L., Wang, L., Huo, J., Zhou, L., Shi, Y., Gao, Y.: A novel unsupervised camera- aware domain adaptation framework for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.03425 (2019)
- Ristani, E., Solera, F., Zou, R., Cucchiara, R., Tomasi, C.: Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: Hua, G., J´egou,H.(eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9914, pp. 17–35. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/ 10.1007/978-3-319-48881-3 2
- Su, C., Li, J., Zhang, S., Xing, J., Gao, W., Tian, Q.: Pose-driven deep convolu- tional model for person re-identification. In: ICCV (2017)
- Sun, B., Feng, J., Saenko, K.: Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In: AAAI (2016)
- Wang, D., Zhang, S.: Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classi- fication. In: CVPR (2020)
- Wang, G., Lai, J., Huang, P., Xie, X.: Spatial-temporal person re-identification. In: AAAI (2019)
- Wei, L., Zhang, S., Gao, W., Tian, Q.: Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2018)
- Wei, L., Zhang, S., Yao, H., Gao, W., Tian, Q.: Glad: Global-local-alignment descriptor for pedestrian retrieval. In: ACM MM (2017)
- Wu, Z., Xiong, Y., Yu, S.X., Lin, D.: Unsupervised feature learning via non- parametric instance discrimination. In: CVPR (2018)
- Yu, H.X., Zheng, W.S., Wu, A., Guo, X., Gong, S., Lai, J.H.: Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning. In: CVPR (2019)
- Zhang, X., Cao, J., Shen, C., You, M.: Self-training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: ICCV (2019)
- Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Scalable person re- identification: a benchmark. In: ICCV (2015)
- Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: ICCV (2017)
- Zhong, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, S.: Robust partial matching for person search in the wild. In: CVPR (2020)
- Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Luo, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Invariance matters: exemplar mem- ory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: CVPR (2019)
- Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Zheng, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Camera style adaptation for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2018)
- Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Zheng, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y.: CamStyle: a novel data aug- mentation method for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(3), 1176–1190 (2018)
- Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: ICCV (2017)