NLP之基于Bi-LSTM和注意力机制的文本情感分类
Bi-LSTM(Attention)
文章目录
- Bi-LSTM(Attention)
-
- 1.理论
-
- 1.1 文本分类和预测(翻译)
- 1.2 注意力模型
-
- 1.2.1 Attention模型
- 1.2.2 Bi-LSTM(Attention)模型结构
- 2.实验
-
- 2.1 实验步骤
- 2.2 算法模型
1.理论
1.1 文本分类和预测(翻译)
文本分类的输入处理和预测(翻译)不同:
- 预测(翻译)通常用eye()把每个输入向量转换为one-hot向量,
- 但文本分类模型通常用Embedding初始化一个嵌入矩阵用来训练,不需要one-hot向量
1.2 注意力模型
1.2.1 Attention模型
注意力机制(Attention Mechanism)的本质是对于给定目标,通过生成一个权重系数对输入进行加权求和,来识别输入中哪些特征对于目标是重要的,哪些特征是不重要的;
为了实现注意力机制,我们将输入的原始数据看作
注意力机制在深度学习各个领域都有很多的应用.不过需要注意的是,注意力并不是一个统一的模型,它只是一个机制,在不同的应用领域有不同的实现方法。
- 注意力权重系数W的公式如下: W = s o f t m a x ( Q K T ) W=softmax(QK^T) W=softmax(QKT)
- 注意力权重系数W与Value做点积操作(加权求和)得到融合了注意力的输出:
A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) = W ⋅ V = s o f t m a x ( Q K T ) ⋅ V Attention(Q,K,V)=W⋅V=softmax(QK^T)⋅V Attention(Q,K,V)=W⋅V=softmax(QKT)⋅V
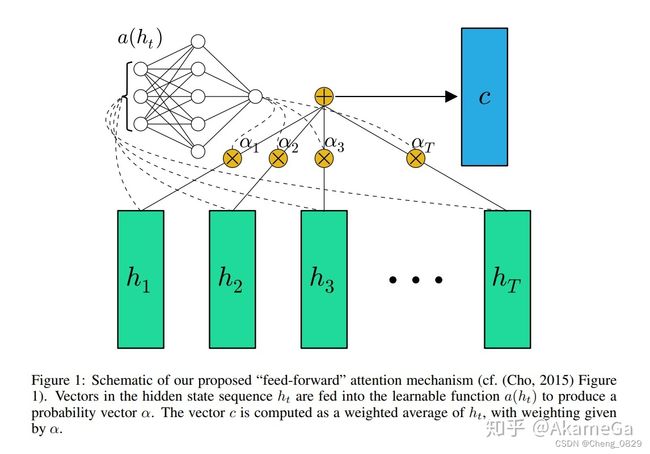
注意力模型的详细结构如下图所示:
在本实验中,Query是指final_hidden_state,Key和Value都是指lstm_output,注意力权重W是指attn_weights
- 两个输入值用bmm()进行加权求和得到注意力权重attn_weights(由于final_hidden_state是一维的,所以不需要像seq2seq2中一样遍历时间步)
- 然后注意力权重attn_weights和lstm_output再进行用bmm()进行加权求和,得到context,即融合了注意力的输出(不同任务处理方式不同,Bi-LSTM文本分类不需要和Seq2Seq任务一样把context再和decoder_output进行combine和fc)
1.2.2 Bi-LSTM(Attention)模型结构
2.实验
2.1 实验步骤
- 数据预处理,得到字典、样本数等基本数据
- 构建Bi-LSTM(Attention)模型,分别设置模型的输入
- 训练
- 代入数据
- 得到模型输出值,取其中最大值的索引,找到字典中对应的字母,即为模型预测的下一个字母.
- 把模型输出值和真实值相比,求得误差损失函数,运用Adam动量法梯度下降
- 测试
- 可视化注意力权重矩阵
2.2 算法模型
"""
Task: 基于Bi-LSTM和注意力机制的文本情感分类
Author: ChengJunkai @github.com/Cheng0829
Email: [email protected]
Date: 2022/09/14
Reference: Tae Hwan Jung(Jeff Jung) @graykode
"""
import numpy as np
import torch, time, os, sys
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''1.数据预处理'''
def pre_process(sentences):
word_sequence = " ".join(sentences).split()
word_list = []
'''
如果用list(set(word_sequence))来去重,得到的将是一个随机顺序的列表(因为set无序),
这样得到的字典不同,保存的上一次训练的模型很有可能在这一次不能用
(比如上一次的模型预测碰见i:0,love:1,就输出you:2,但这次模型you在字典3号位置,也就无法输出正确结果)
'''
for word in word_sequence:
if word not in word_list:
word_list.append(word)
word_dict = {w:i for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}
word_dict["''"] = len(word_dict)
word_list = word_list.append("''")
vocab_size = len(word_dict) # 词库大小16
max_size = 0
for sen in sentences:
if len(sen.split()) > max_size:
max_size = len(sen.split()) # 最大长度3
for i in range(len(sentences)):
if len(sentences[i].split()) < max_size:
sentences[i] = sentences[i] + " ''" * (max_size - len(sentences[i].split()))
return sentences, word_list, word_dict, vocab_size, max_size
def make_batch(sentences):
# 对于每个句子,返回包含句子内每个单词序号的列表
inputs = [np.array([word_dict[n] for n in sen.split()]) for sen in sentences] # [6,3]
targets = [out for out in labels]
inputs = torch.LongTensor(np.array(inputs)).to(device)
targets = torch.LongTensor(np.array(targets)).to(device)
'''情感分类构建嵌入矩阵,没有eye()'''
return inputs, targets
class BiLSTM_Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BiLSTM_Attention, self).__init__()
'''情感分类构建嵌入矩阵,没有eye()'''
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, n_hidden, bidirectional=True)
self.out = nn.Linear(2*n_hidden, num_classes)
def forward(self, X):
# input : [batch_size, n_step, embedding_dim] [6,3,2]
input = self.embedding(X)
# input : [n_step, batch_size, embedding_dim] [3,6,2]
# input : [输入序列长度(时间步长度),样本数,嵌入向量维度]
input = input.permute(1, 0, 2)
# hidden_state : [num_layers(=1)*num_directions(=2), batch_size, n_hidden]
# hidden_state : [层数*网络方向,样本数,隐藏层的维度(隐藏层神经元个数)]
hidden_state = torch.zeros(1*2, len(X), n_hidden).to(device)
# cell_state : [num_layers*num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size]
# cell_state : [层数*网络方向,样本数,隐藏层的维度(隐藏层神经元个数)]
cell_state = torch.zeros(1*2, len(X), n_hidden).to(device)
# final_hidden_state, final_cell_state : [num_layers(=1)*num_directions(=2), batch_size, n_hidden]
ltsm_output, (final_hidden_state, final_cell_state) = self.lstm(input, (hidden_state, cell_state))
# ltsm_output : [batch_size, n_step, n_hidden*num_directions(=2)]
ltsm_output = ltsm_output.permute(1, 0, 2)
attn_output, attention = self.attention_net(ltsm_output, final_hidden_state)
# model : [batch_size, num_classes], attention : [batch_size, n_step]
return self.out(attn_output), attention
'''两次bmm加权求和,相当于两次for循环'''
# lstm_output : [batch_size, n_step, n_hidden*num_directions(=2)] [6,3,16]
# final_hidden_state : [num_layers(=1)*num_directions(=2), batch_size, n_hidden] [2,6,8]
def attention_net(self, lstm_output, final_hidden_state):
# final_hidden_state : [batch_size, n_hidden*num_directions(=2), 1(=n_layer)] [6,16,1]
final_hidden_state = final_hidden_state.view(-1, 2*n_hidden, 1)
'''第一次bmm加权求和:: lstm_output和final_hidden_state生成注意力权重attn_weights'''
# [6,3,16]*[6,16,1] -> [6,3,1] -> attn_weights : [batch_size, n_step] [6,3]
attn_weights = torch.bmm(lstm_output, final_hidden_state).squeeze(2) # 第3维度降维
softmax_attn_weights = F.softmax(attn_weights, 1) # 按列求值 [6,3]
'''第二次bmm加权求和 : lstm_output和注意力权重attn_weights生成上下文向量context,即融合了注意力的模型输出'''
# [batch_size, n_hidden*num_directions, n_step] * [batch_size,n_step,1] \
# = [batch_size, n_hidden*num_directions, 1] : [6,16,3] * [6,3,1] -> [6,16,1] -> [6,16]
context = torch.bmm(lstm_output.transpose(1, 2), softmax_attn_weights.unsqueeze(2)).squeeze(2)
softmax_attn_weights = softmax_attn_weights.to('cpu') # numpy变量只能在cpu上
'''各个任务求出context之后的步骤不同,LSTM的上下文不需要和Seq2Seq中的一样和decoder_output连接'''
return context, softmax_attn_weights.data.numpy()
if __name__ == '__main__':
chars = 30 * '*'
embedding_dim = 3 # embedding size
n_hidden = 8 # number of hidden units in one cell
num_classes = 2 # 0 or 1
'''GPU比CPU慢的原因大致为:
数据传输会有很大的开销,而GPU处理数据传输要比CPU慢,
而GPU在矩阵计算上的优势在小规模神经网络中无法明显体现出来
'''
device = ['cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'][0]
# 3 words sentences (=sequence_length is 3)
sentences = ["i love you", "he loves me", "don't leave", \
"i hate you", "sorry for that", "this is awful"]
labels = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0] # 1 is good, 0 is not good.
'''1.数据预处理'''
sentences, word_list, word_dict, vocab_size, max_size = pre_process(sentences)
inputs, targets = make_batch(sentences)
'''2.构建模型'''
model = BiLSTM_Attention()
model.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
if os.path.exists('model_param.pt') == True:
# 加载模型参数到模型结构
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_param.pt', map_location=device))
'''3.训练'''
print('{}\nTrain\n{}'.format('*'*30, '*'*30))
loss_record = []
for epoch in range(10000):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output, attention = model(inputs)
output = output.to(device)
loss = criterion(output, targets)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(loss)
if loss >= 0.001: # 连续30轮loss小于0.01则提前结束训练
loss_record = []
else:
loss_record.append(loss.item())
if len(loss_record) == 30:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_param.pt')
break
if (epoch + 1) % 1000 == 0:
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'Loss = {:.6f}'.format(loss))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_param.pt')
'''4.测试'''
print('{}\nTest\n{}'.format('*'*30, '*'*30))
test_text = 'sorry i hate you'
# 返回包含每个单词序号的列表矩阵(为了有2个维度,还要加一个中括号升维)
tests = [np.array([word_dict[n] for n in test_text.split()])]
test_batch = torch.LongTensor(np.array(tests)).to(device)
predict, attn_test = model(test_batch)
predict = predict.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
print('The emotion of "%s" is '%test_text, end='')
if predict[0][0] == 0:
print('bad!')
else:
print('good!')
'''5.可视化注意力权重矩阵'''
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(0.5*len(sentences), 0.5*len(sentences[0]))) # [batch_size, n_step]
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
# attention : (6, 3)
ax.matshow(attention, cmap='viridis')
word_show = ['单词'] * len(sentences[0])
word_show = [word_show[i] + str(i+1) for i in range(len(sentences[0]))] # ['word_1', 'word_2', 'word_3']
ax.set_xticklabels([''] + word_show, fontdict={'fontsize': 14} , fontproperties='SimSun')
sentence_show = ['句子'] * len(sentences)
sentence_show = [sentence_show[i] + str(i+1) for i in range(len(sentence_show))] # ['sentence_1', 'sentence_2', 'sentence_3', 'sentence_4', 'sentence_5', 'sentence_6']
ax.set_yticklabels([''] + sentence_show, fontdict={'fontsize': 14}, fontproperties='SimSun')
plt.show()