神经网络八股扩展(tensorflow)_4
六步法的扩展:
Import
train,test(自制数据集,数据增强)
Sequential/Class
model.compile
model.fit(断点续训)
model.summary(参数提取,acc/loss可视化,前向推理应用)
自制数据集导入:
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import os
train_path = './mnist_image_label/mnist_train_jpg_60000/'
train_txt = './mnist_image_label/mnist_train_jpg_60000.txt'
x_train_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_x_train.npy'
y_train_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_y_train.npy'
test_path = './mnist_image_label/mnist_test_jpg_10000/'
test_txt = './mnist_image_label/mnist_test_jpg_10000.txt'
x_test_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_x_test.npy'
y_test_savepath = './mnist_image_label/mnist_y_test.npy'
def generateds(path, txt):
f = open(txt, 'r') # 以只读形式打开txt文件
contents = f.readlines() # 读取文件中所有行
f.close() # 关闭txt文件
x, y_ = [], [] # 建立空列表
for content in contents: # 逐行取出
value = content.split() # 以空格分开,图片路径为value[0] , 标签为value[1] , 存入列表
img_path = path + value[0] # 拼出图片路径和文件名
img = Image.open(img_path) # 读入图片
img = np.array(img.convert('L')) # 图片变为28位宽灰度值的np.array格式
img = img / 255. # 数据归一化 (实现预处理)
x.append(img) # 归一化后的数据,贴到列表x
y_.append(value[1]) # 标签贴到列表y_
print('loading : ' + content) # 打印状态提示
x = np.array(x) # 变为np.array格式
y_ = np.array(y_) # 变为np.array格式
y_ = y_.astype(np.int64) # 变为64位整型
return x, y_ # 返回输入特征x,返回标签y_
if os.path.exists(x_train_savepath) and os.path.exists(y_train_savepath) and os.path.exists(
x_test_savepath) and os.path.exists(y_test_savepath):
print('-------------Load Datasets-----------------')
x_train_save = np.load(x_train_savepath)
y_train = np.load(y_train_savepath)
x_test_save = np.load(x_test_savepath)
y_test = np.load(y_test_savepath)
x_train = np.reshape(x_train_save, (len(x_train_save), 28, 28))
x_test = np.reshape(x_test_save, (len(x_test_save), 28, 28))
else:
print('-------------Generate Datasets-----------------')
x_train, y_train = generateds(train_path, train_txt)
x_test, y_test = generateds(test_path, test_txt)
print('-------------Save Datasets-----------------')
x_train_save = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), -1))
x_test_save = np.reshape(x_test, (len(x_test), -1))
np.save(x_train_savepath, x_train_save)
np.save(y_train_savepath, y_train)
np.save(x_test_savepath, x_test_save)
np.save(y_test_savepath, y_test)
数据增强:
扩展数据集,对图像的增强就是对图像的简单形变,用来应变因拍照角度不同引起的图片变形
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
image_gen_train = tf.kears.preprocessing.image.ImageDataGeneration(
rescale = 输入量×的超参数 # 改变输入大小
rotation_range = 图像随机旋转角度的范围
width_shift_range = 随机宽度偏移量
height_shift_range = 随机高度偏移量
水平翻转:horizontal_flip = 是否随机水平旋转
随机缩放:zoom_range = 随机缩放的范围[1-n,1+n])
image_gen_train.fit(x_train)
其中x_train是四维数据,所以对x_train进行reshape
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0],28,28,1) # 把(60000,28,28)转换成(60000,28,28,1),1是单通道,是灰度值
model.fit(x_train,y_train,bacth_size=32...)换为
model.fit(image_gen_train.flow(x_train,y_train,bacth_size=32),...)
数据增强在小数据量下可以增强模型泛化性
断点续训可以存取模型
读取模型:load_weights(路径文件名)
model_save_path = './checkpoint/mnist.ckpt' # 存放的路径和文件名,命名为ckpt文件
if os.path.exists(model_save_path + '.index'): # 生成ckpt文件的时候会同步生成index索引表,所以判断索引表是否存在就可以判断是否已保存过模型参数
model.load_weights(model_save_path) # 如果有模型参数,可以直接读取
保存模型参数:
tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath=文件存储路径,
save_weights_only=True/False, # 是否只保留模型参数
save_best_only=True/False, # 是否只保留最优结果
)
history=model.fit(callbacks=[cp_callback]) # 训练的时候加入callbacks选项,记录到history中
如
cp_callback = tf.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True)
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=5, validation_data=(x_test,y_test),
validation_freq=1, callbacks=[cp_callback])
参数提取
model.trainable_variables 返回模型可训练参数
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
print(model.trainable_variables) 打印出可训练参数
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf) # 设置打印参数时是无省略号的
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
# 断点续训:18~26
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/mnist.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True)
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=5, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1,
callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
print(model.trainable_variables) # 打印可训练参数
# 把可训练参数存入txt文件中:30~35
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w')
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
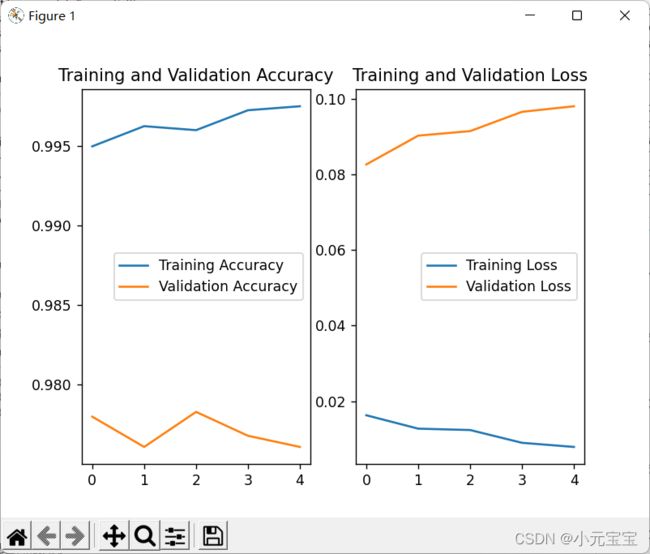
acc/loss可视化
history=model.fit(…)时history记录了
训练集loss:loss
测试集loss:val_loss
训练集准确率:sparse_categorical_accuracy
测试集准确率:val_sparse_categorical_accuracy
所以可用history.history[‘…’]提取出来
# 显示训练集和验证集的acc和loss曲线
acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(val_acc, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
训练模型之后的预测:
predict(输入特征,batch_size=整数)
给出输入特征,输出预测结果
实现预测的三步:
1.复现模型:model=tf.keras.models.Sequential([…])
2.加载参数:model.load_weights(model_save_path)
3.预测结果:result=model.predict(x_predict)
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
model_save_path = './checkpoint/mnist.ckpt'
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')])
model.load_weights(model_save_path)
preNum = int(input("input the number of test pictures:"))
for i in range(preNum):
image_path = input("the path of test picture:")
img = Image.open(image_path)
img = img.resize((28, 28), Image.ANTIALIAS)
img_arr = np.array(img.convert('L'))
for i in range(28):
for j in range(28):
if img_arr[i][j] < 200:
img_arr[i][j] = 255
else:
img_arr[i][j] = 0
img_arr = img_arr / 255.0
x_predict = img_arr[tf.newaxis, ...]
result = model.predict(x_predict)
pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1)
print('\n')
tf.print(pred)