NLP深入学习——文本表示与相似度计算(text representation and Similarity calculation)
文章目录
-
- 返回主目录
- 文本表示(text representation)
- 文本表示方法(text representation method)
-
- 单词表示(word representation):
-
-
- One-hot representation
-
- 句子表示(sentence representation):
-
-
- ① Boolean-based representation
- ② Count-based representation
- ③ Tf-idf representation
-
- 文本相似度(text similarity)
-
-
-
- ① 欧氏距离(Euclidean distance)
- ② 余弦相似度(Cosine similarity)
-
-
- 总结(summary)
返回主目录
这是一个系列的文章,点击返回综合目录页
文本表示(text representation)
计算机不像人类,可以很好的理解文本(文字)的含义、意思。
但是计算机有很强大的计算能力,可以很快速地处理数值问题,所以,我们希望将文本转化成数值,来帮助计算机理解。
文本表示方法(text representation method)
单词表示(word representation):
One-hot representation
句子表示(sentence representation):
① Boolean-based representation
② Count-based representation
③ Tf-idf representation
t f − i d f ( w ) = t f ( d , w ) ∗ i d f ( w ) tf-idf(w) = tf(d,w)*idf(w) tf−idf(w)=tf(d,w)∗idf(w)
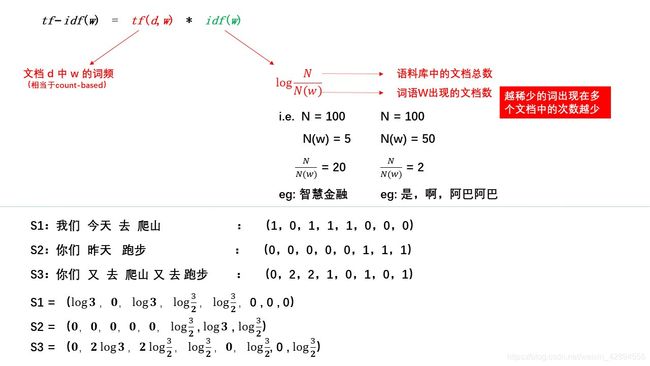
文本相似度(text similarity)
① 欧氏距离(Euclidean distance)
d = ∣ S 1 − S 2 ∣ d = |S_1-S_2| d=∣S1−S2∣
S 1 = ( x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ) ; S 2 = ( y 1 , y 2 , y 3 ) S_1 = (x_1,x_2,x_3) ; S_2 = (y_1,y_2,y_3) S1=(x1,x2,x3);S2=(y1,y2,y3)
d = ( x 1 − y 1 ) 2 + ( x 2 − y 2 ) 2 + ( x 3 − y 3 ) 2 d =\sqrt{(x_1-y_1)^2 + (x_2-y_2)^2 + (x_3-y_3)^2} d=(x1−y1)2+(x2−y2)2+(x3−y3)2
② 余弦相似度(Cosine similarity)
d = S 1 ⋅ S 2 ∣ S 1 ∣ ∗ ∣ S 2 ∣ d =\frac {S_1·S_2}{|S_1|*|S_2|} d=∣S1∣∗∣S2∣S1⋅S2
S 1 = ( x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ) ; S 2 = ( y 1 , y 2 , y 3 ) S_1 = (x_1,x_2,x_3) ; S_2 = (y_1,y_2,y_3) S1=(x1,x2,x3);S2=(y1,y2,y3)
d = x 1 y 1 + x 2 y 2 + x 3 y 3 x 1 2 + x 2 2 + x 3 2 ∗ y 1 2 + y 2 2 + y 3 2 d =\frac{x_1y_1+x_2y_2+x_3y_3}{\sqrt{x_1^2 + x_2^2 + x_3^2} * \sqrt{y_1^2 + y_2^2 + y_3^2}} d=x12+x22+x32∗y12+y22+y32x1y1+x2y2+x3y3
直接上例子:

总结(summary)
事实上:
Boolean-based representation
Count-based representation
Tf-idf representation
属于:
One-hot representation
是稀疏(sparsity)的表示方法
缺点:
- 不能表示语义的相似度
- 向量过于稀疏
拿前面的例子:

利用上述的向量来计算
欧氏距离:均为 2 \sqrt{2} 2
余弦相似度:均为 0
所以还是不足以去帮助计算机理解我们的语言含义


