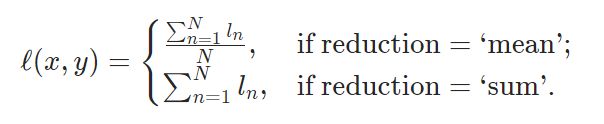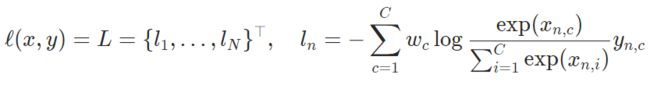【源码解析】如何从零实现一个分类模型?
说明:本文源代码来源于MACHINE LEARNING 2022 SPRING课程,我只是针对源代码进行了一些加工处理。感谢互联网,让我们能免费接触到这些优秀的课程。
前置知识
- 什么是分类模型?简单说就是模型将输入分类为已知的类别之一。一般采用SoftMax作为网络结构的最后一层,再选取概率最大的作为结果。
目标
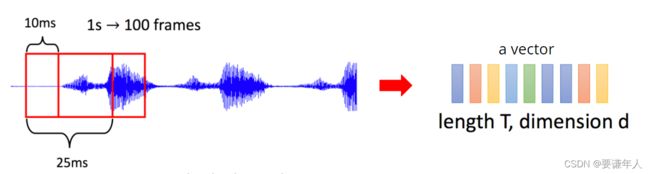
- 模型输出声音信号的每一帧的音素(phoneme)
- 音素的介绍(phoneme):能够被用来识别一个语言中的某个词汇的声音单元。
任务描述
-
数据预处理:从原始声波信号提取MFCC特征(已完成)
-
分类:使用预先提取的MFCC特征进行每一帧音素的分类
数据组成
- 数据集:LibriSpeech (train-clean-100的子集)
- 训练集:4268个带标签的经预处理的声音特征
- 测试集:1078个经预处理的声音特征
- 类别:41个类别,每个类别代表一个音素
性能指标
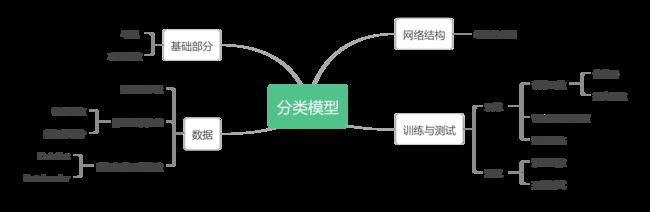
实现思路
源码解析
基础部分
导包
import numpy as np
import os
import random
import pandas as pd
import torch
from tqdm import tqdm
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import gc
功能函数
# 固定随机数种子,保证训练结果可复现
def same_seeds(seed):
torch.manual_seed(seed)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
数据
数据的下载
从谷歌云盘下载.zip格式的数据集,并解压
解压后得到如下文件:
libriphone/train_split.txtlibriphone/train_labelslibriphone/test_split.txtlibriphone/feat/train/*.pt: training featurelibriphone/feat/test/*.pt: testing feature
# 指令前的加的 ! 是因为在jupyter环境下执行终端指令
# 主链接
!wget -O libriphone.zip "https://github.com/xraychen/shiny-robot/releases/download/v1.0/libriphone.zip"
# 备选链接 0
# !pip install --upgrade gdown
# !gdown --id '1o6Ag-G3qItSmYhTheX6DYiuyNzWyHyTc' --output libriphone.zip
# 备选链接 1
# !pip install --upgrade gdown
# !gdown --id '1R1uQYi4QpX0tBfUWt2mbZcncdBsJkxeW' --output libriphone.zip
# 备选链接 2
# !wget -O libriphone.zip "https://www.dropbox.com/s/wqww8c5dbrl2ka9/libriphone.zip?dl=1"
# 备选链接 3
# !wget -O libriphone.zip "https://www.dropbox.com/s/p2ljbtb2bam13in/libriphone.zip?dl=1"
# 解压并打印
!unzip -q libriphone.zip
!ls libriphone
数据的预处理(特征选取、数据划分)
# 加载以.pt格式存储的原始数据到torch.tensor格式
# path:路径
def load_feat(path):
feat = torch.load(path)
return feat
# 将x中每一行向前或向后移动|n|行
# 当n=0时,返回原始的x
# 当n<0时,将x所有行向下移动|n|行,前面空出的|n|行由原有的第一行重复|n|次填充
# 当n>0时,将x所有行向上移动n行,后面空出的n行由原有的最后一行重复n次填充
# 以上描述进行了一定的抽象,并不准确对应实际操作
def shift(x, n):
if n < 0:
left = x[0].repeat(-n, 1)
right = x[:n]
elif n > 0:
right = x[-1].repeat(n, 1)
left = x[n:]
else:
return x
return torch.cat((left, right), dim=0)
def concat_feat(x, concat_n):
# 确保concat_n为奇数,否则报错
assert concat_n % 2 == 1
if concat_n < 2:
return x
# 序列长度、特征维度(39)
seq_len, feature_dim = x.size(0), x.size(1)
# torch.repeat沿着指定的维度重复这个tensor
# 此处的作用就是将 x 的特征维“重复”concat_n次
x = x.repeat(1, concat_n)
# torch.view将tensor“变形”为指定的形状,必须确保变形后的元素数与原始tensor一致
# torch.permute重新排列tensor的各个维度
# 此处x经处理后的形状为(concat_n, seq_len, feature_dim)
x = x.view(seq_len, concat_n, feature_dim).permute(1, 0, 2)
# 找到“中间”的一帧
mid = (concat_n // 2)
# 此处的设置十分巧妙
for r_idx in range(1, mid+1):
x[mid + r_idx, :] = shift(x[mid + r_idx], r_idx)
x[mid - r_idx, :] = shift(x[mid - r_idx], -r_idx)
# 返回的X,最终达成每行对应concat_n*feature_dim个元素
# 即每一行数据分别包含前、后concat_n//2帧的声音数据
return x.permute(1, 0, 2).view(seq_len, concat_n * feature_dim)
# 数据预处理
# split: 数据集的属性,取值有:train/test/val
# feat_dir: 所有.pt源文件所在的路径
# phone_path: 存储训练集、测试集划分及标签.txt源文件所在的路径
# concat_nframes: 一个训练数据拼接的帧数,必须设为奇数(2n+1)
# train_ratio: 数据集划分时,训练集占比(默认为0.8)
# train_val_seed: 读取数据集并进行shuffle操作时,random函数的随机数种子(默认为1337)
def preprocess_data(split, feat_dir, phone_path, concat_nframes, train_ratio=0.8, train_val_seed=1337):
# 音素类别数,已知
class_num = 41
# 判断当前模式,“train”或者“test”
mode = 'train' if (split == 'train' or split == 'val') else 'test'
# 存储标签的空字典
label_dict = {}
# 非“test”模式时:按行对应的标签文件
if mode != 'test':
phone_file = open(os.path.join(phone_path, f'{mode}_labels.txt')).readlines()
# 处理按行读入的标签,原始格式为:文件名 one-hot向量
# 经处理后,存储label_dict的格式为:{文件名1:[one-hot向量],文件名2:[one-hot向量]....}
for line in phone_file:
line = line.strip('\n').split(' ')
label_dict[line[0]] = [int(p) for p in line[1:]]
if split == 'train' or split == 'val':
# 划分 train 和 val
usage_list = open(os.path.join(phone_path, 'train_split.txt')).readlines()
random.seed(train_val_seed)
random.shuffle(usage_list)
percent = int(len(usage_list) * train_ratio)
usage_list = usage_list[:percent] if split == 'train' else usage_list[percent:]
elif split == 'test':
usage_list = open(os.path.join(phone_path, 'test_split.txt')).readlines()
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid \'split\' argument for dataset: PhoneDataset!')
# 移除保存usage_line存储的文件名中的换行符
usage_list = [line.strip('\n') for line in usage_list]
print('[Dataset] - # phone classes: ' + str(class_num) + ', number of utterances for ' + split + ': ' + str(len(usage_list)))
max_len = 3000000
# 创建存储音素数据的tensor矩阵,max_len设很大的原因是留充足的空间存储数据
X = torch.empty(max_len, 39 * concat_nframes)
if mode != 'test':
# 创建存储标签的tensor矩阵
y = torch.empty(max_len, dtype=torch.long)
# 下面的for循环完成后,X存储了所有的数据,每一行对应一条
# 若y有定义,则是X中对应数据的标签
idx = 0
for i, fname in tqdm(enumerate(usage_list)):
feat = load_feat(os.path.join(feat_dir, mode, f'{fname}.pt'))
cur_len = len(feat)
feat = concat_feat(feat, concat_nframes)
# 若不是测试集,则返回数据集对应的标签
if mode != 'test':
label = torch.LongTensor(label_dict[fname])
X[idx: idx + cur_len, :] = feat
if mode != 'test':
y[idx: idx + cur_len] = label
idx += cur_len
# 清理分配给X、y的多余的空间
X = X[:idx, :]
if mode != 'test':
y = y[:idx]
print(f'[INFO] {split} set')
print(X.shape)
if mode != 'test':
print(y.shape)
return X, y
else:
return X
数据加载器的构造(DataSet、DataLoader)
# 标准的数据集类定义,实现__getitem__、__len__
class LibriDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, X, y=None):
self.data = X
if y is not None:
self.label = torch.LongTensor(y)
else:
self.label = None
def __getitem__(self, idx):
if self.label is not None:
return self.data[idx], self.label[idx]
else:
return self.data[idx]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
# 设置有关数据集的参数
concat_nframes = 1 # 数据集预处理时拼接的帧数, 必须为奇数
train_ratio = 0.8 # 用于训练的数据集的比例,剩余的全用于验证集
# 预处理数据
# 加载训练集、验证机、测试集
train_X, train_y = preprocess_data(split='train', feat_dir='./libriphone/feat', phone_path='./libriphone', concat_nframes=concat_nframes, train_ratio=train_ratio)
val_X, val_y = preprocess_data(split='val', feat_dir='./libriphone/feat', phone_path='./libriphone', concat_nframes=concat_nframes, train_ratio=train_ratio)
test_X = preprocess_data(split='test', feat_dir='./libriphone/feat', phone_path='./libriphone', concat_nframes=concat_nframes)
# 获取数据集类的实例
train_set = LibriDataset(train_X, train_y)
val_set = LibriDataset(val_X, val_y)
test_set = LibriDataset(test_X, None)
# 移除原始数据,节省内存
del train_X, train_y, val_X, val_y
# 执行垃圾回收,清理内存
gc.collect()
# 获取数据加载器(DataLoader)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
网络结构
结构的实现
# 网络基础块的定义,包含一个全连接层、一个ReLU
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.block(x)
return x
# 分类器网络结构的实现
# 全连接层数=hidden_layers+2
class Classifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim=41, hidden_layers=1, hidden_dim=256):
super(Classifier, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(input_dim, hidden_dim),
*[BasicBlock(hidden_dim, hidden_dim) for _ in range(hidden_layers)],
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc(x)
return x
训练与预测
训练参数的设置
# 训练参数
seed = 0 # random seed
batch_size = 512 # batch size
num_epoch = 5 # the number of training epoch
learning_rate = 0.0001 # learning rate
model_path = './model.ckpt' # the path where the checkpoint will be saved
# 模型参数
input_dim = 39 * concat_nframes # the input dim of the model, you should not change the value
hidden_layers = 1 # the number of hidden layers
hidden_dim = 256 # the hidden dim
device = 'cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f'DEVICE: {device}')
# 固定随机数种子
same_seeds(seed)
# create model, define a loss function, and optimizer
model = Classifier(input_dim=input_dim, hidden_layers=hidden_layers, hidden_dim=hidden_dim).to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
开始训练
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(num_epoch):
train_acc = 0.0
train_loss = 0.0
val_acc = 0.0
val_loss = 0.0
# training
model.train() # set the model to training mode
for i, batch in enumerate(tqdm(train_loader)):
features, labels = batch
features = features.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(features)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, train_pred = torch.max(outputs, 1) # get the index of the class with the highest probability
train_acc += (train_pred.detach() == labels.detach()).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
# validation
if len(val_set) > 0:
model.eval() # set the model to evaluation mode
with torch.no_grad():
for i, batch in enumerate(tqdm(val_loader)):
features, labels = batch
features = features.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(features)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
_, val_pred = torch.max(outputs, 1)
val_acc += (val_pred.cpu() == labels.cpu()).sum().item() # get the index of the class with the highest probability
val_loss += loss.item()
print('[{:03d}/{:03d}] Train Acc: {:3.6f} Loss: {:3.6f} | Val Acc: {:3.6f} loss: {:3.6f}'.format(
epoch + 1, num_epoch, train_acc/len(train_set), train_loss/len(train_loader), val_acc/len(val_set), val_loss/len(val_loader)
))
# if the model improves, save a checkpoint at this epoch
if val_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = val_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
print('saving model with acc {:.3f}'.format(best_acc/len(val_set)))
else:
print('[{:03d}/{:03d}] Train Acc: {:3.6f} Loss: {:3.6f}'.format(
epoch + 1, num_epoch, train_acc/len(train_set), train_loss/len(train_loader)
))
# 若未设置验证集,则保存最后一个epoch的模型参数
if len(val_set) == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
print('saving model at last epoch')
开始测试
# 实例化模型,并加载预训练的参数进行初始化
model = Classifier(input_dim=input_dim, hidden_layers=hidden_layers, hidden_dim=hidden_dim).to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
test_acc = 0.0
test_lengths = 0
pred = np.array([], dtype=np.int32)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for i, batch in enumerate(tqdm(test_loader)):
features = batch
features = features.to(device)
outputs = model(features)
_, test_pred = torch.max(outputs, 1) # get the index of the class with the highest probability
# 将所有的测试集输出存储到pred一个矩阵中
pred = np.concatenate((pred, test_pred.cpu().numpy()), axis=0)
# 将pred写入到.csv文件中保存
with open('prediction.csv', 'w') as f:
f.write('Id,Class\n')
for i, y in enumerate(pred):
f.write('{},{}\n'.format(i, y))
.to(device)
outputs = model(features)
_, test_pred = torch.max(outputs, 1) # get the index of the class with the highest probability
# 将所有的测试集输出存储到pred一个矩阵中
pred = np.concatenate((pred, test_pred.cpu().numpy()), axis=0)
将pred写入到.csv文件中保存
with open(‘prediction.csv’, ‘w’) as f:
f.write(‘Id,Class\n’)
for i, y in enumerate(pred):
f.write(’{},{}\n’.format(i, y))