常见集成学习及其代码实现
文章来源于Coggle数据科学 ,作者Coggle
文章来源于Coggle数据科学 ,作者Coggle
集成学习简介
集成学习是指结合两个或多个模型的机器学习模型。集成学习是机器学习的分支,通常在追求更强预测的能力时使用。现代机器学习库(scikit-learn、XGBoost)内部已经结合了常见的集成学习方法。
常见的集成学习技术有三类:
- Bagging, 如. Bagged Decision Trees and Random Forest.
- Boosting, 如. Adaboost and Gradient Boosting
- Stacking, 如. Voting and using a meta-model.
使用集成学习可以减少预测结果的方差,同时也比单个模型更好的性能。
1.Bagging
Bagging通过对训练集进行采样,用得到的样本训练得到多样的模型,进而得到多样的预测结果。在结合模型的预测结果时,可以对单个模型预测结果进行投票或平均。
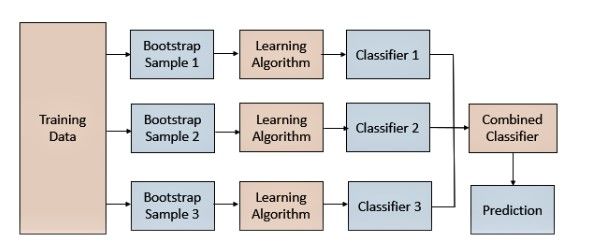
Bagging的关键是对数据集的采样方法。常见的方式可以从行(样本)维度进行采样,这里进行的是有放回采样。
Bagging可通过BaggingClassifier和BaggingRegressor使用,默认情况下它们使用决策树作为基本模型,可以通过n_estimators参数指定要创建的树的数量。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
import numpy as np
# 创建样例数据集
X, y = make_classification(random_state=1)
# 创建bagging模型
model = BaggingClassifier(n_estimators=50)
# 设置验证集数据划分方式
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
# 验证模型精度
n_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1)
# 打印模型的精度
print('Mean Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (np.mean(n_scores), np.std(n_scores)))
2.Random Forest
随机森林是 Bagging与树模型的结合:
- 随机森林集成在训练集的不同引导样本上拟合决策树。
- 随机森林还将对每个数据集的特征(列)进行采样。
在构建每个决策树时,随机森林不是在选择分割点时考虑所有特征,而是将特征限制为特征的随机子集。
随机森林集成可通过RandomForestClassifier和RandomForestRegressor类在 scikit-learn 中获得。可以通过n_estimators参数指定要创建的树的数量,并通过max_features参数指定要在每个分割点考虑的随机选择的特征的数量。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
import numpy as np
# 创建样例数据集
X, y = make_classification(random_state=1)
# 创建随机森林模型
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50)
# 设置验证集数据划分方式
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
# 验证模型精度
n_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1)
# 打印模型的精度
print('Mean Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (np.mean(n_scores), np.std(n_scores)))
3.AdaBoost
Boosting在迭代过程中尝试纠正先前模型所产生的错误,迭代次数越多集成产生的错误就越少,至少在数据支持的限制范围内并且在过度拟合训练数据集之前。

Boosting想法最初是作为一种理论思想发展起来的,AdaBoost算法是第一个成功实现基于Boosting的集成算法的方法。
AdaBoost在加权训练数据集的版本上拟合决策树,以便树更多地关注先前成员出错的示例。AdaBoost不是完整的决策树,而是使用非常简单的树,在做出预测之前对一个输入变量做出单一决策。这些短树被称为决策树桩。
AdaBoost可通过AdaBoostClassifier和AdaBoostRegressor使用,它们默认使用决策树(决策树桩)作为基本模型,可以通过n_estimators参数指定要创建的树的数量。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
import numpy as np
# 创建样例数据集
X, y = make_classification(random_state=1)
# 创建adaboost模型
model = AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=50)
# 设置验证集数据划分方式
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
# 验证模型精度
n_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1)
# 打印模型的精度
print('Mean Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (np.mean(n_scores), np.std(n_scores)))
4.Gradient Boosting
Gradient Boosting是一个用于提升集成算法的框架,是对AdaBoosting的扩展。Gradient Boosting定义为统计框架下的加法模型,并允许使用任意损失函数以使其更加灵活,并允许使用损失惩罚(收缩)来减少过度拟合。
Gradient Boosting引入了Bagging的操作,例如训练数据集行和列的采样,称为随机梯度提升。
对于结构化或表格数据来说,Gradient Boosting一种非常成功的集成技术,尽管由于模型是按顺序添加的,因此拟合模型可能会很慢。已经开发了更有效的实现,如XGBoost、LightGBM。
Gradient Boosting可以通过GradientBoostingClassifier和GradientBoostingRegressor使用,默认使用决策树作为基础模型。您可以通过n_estimators参数指定要创建的树的数量,通过learning_rate参数控制每棵树的贡献的学习率。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
import numpy as np
# 创建样例数据集
X, y = make_classification(random_state=1)
# 创建GradientBoosting模型
model = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=50)
# 设置验证集数据划分方式
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
# 验证模型精度
n_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1)
# 打印模型的精度
print('Mean Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (np.mean(n_scores), np.std(n_scores)))
5.Voting
Voting使用简单的统计数据来组合来自多个模型的预测。
- 硬投票:对预测类别进行投票;
- 软投票:对预测概率进行求均值;
Voting可通过VotingClassifier和VotingRegressor使用。可以将基本模型列表作为参数,列表中的每个模型都必须是具有名称和模型的元组。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import numpy as np
# 创建数据集
X, y = make_classification(random_state=1)
# 模型列表
models = [('lr', LogisticRegression()), ('nb', GaussianNB())]
# 创建voting模型
model = VotingClassifier(models, voting='soft')
# 设置验证集数据划分方式
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
# 验证模型精度
n_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1)
# 打印模型的精度
print('Mean Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (np.mean(n_scores), np.std(n_scores)))
6.Stacking
Stacking组合多种不同类型的基本模型的预测,和Voting类似。但Stacking可以根据验证集来调整每个模型的权重。
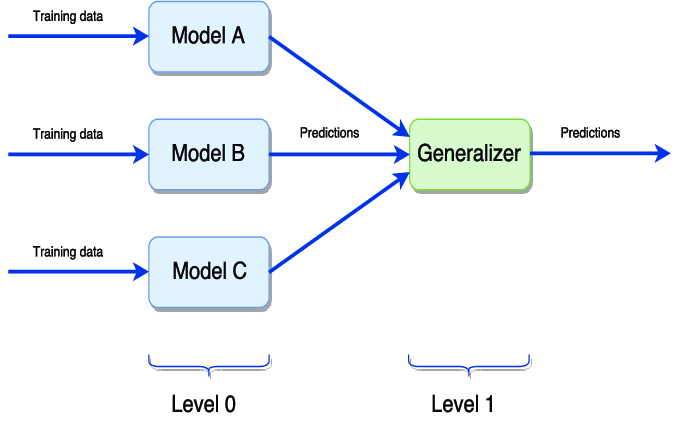
Stacking需要和交叉验证搭配使用,也可以通过StackingClassifier和StackingRegressor使用,可以将基本模型作为模型的参数提供。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.ensemble import StackingClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import numpy as np
# 创建数据集
X, y = make_classification(random_state=1)
# 模型列表
models = [('knn', KNeighborsClassifier()), ('tree', DecisionTreeClassifier())]
# 创建Stacking模型
model =StackingClassifier(estimators=models, final_estimator=LogisticRegression())
# 设置验证集数据划分方式
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
# 验证模型精度
n_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1)
# 打印模型的精度
print('Mean Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (np.mean(n_scores), np.std(n_scores)))