赫夫曼树赫夫曼编码的创建
目录
- 基础知识点
-
- 最优二叉树
- 如何构造赫夫曼树
- 赫夫曼编码
- 编码与压缩文件
- 代码
-
- 结构体设计
- 创建赫夫曼树
- 创建构建赫夫曼编码
基础知识点
赫夫曼树又称为最优树,是一种带权路径长短最短的树,有着广泛的应用。
最优二叉树
我们给出路径和路径长度的概念。从树的一个结点到另一个结点之间的分治构成这两个结点之间的路径,路径上的分支数目称作路径长度。树的路径长度是从树根到每一个结点的路径长度之和。完全二叉树就是这种路径长度最短的二叉树。带权路径的长度从结点到树根之间的路径长度域结点上权值的乘积。树的带权路径长度为树中所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和。
WPL=(W1L1+W2L2+W3L3+…+WnLn)
例如下图:
WPL=24+34+43+92+72+82=80
下图是叶子节点权值相同路径不同的三棵二叉树,计算他们的权值如下:
2*(9+4+5+2)=40
14+22+35+39=50
91+52+43+23=37
我们发现不同路径权值相同,其带权路径长度不同,而最小的便是我们的赫夫曼树。

如何构造赫夫曼树
赫夫曼最早给出了一个带有一般规律的算法,俗称赫夫曼算法。如下
- 根据给定的n个权值{w1,w2,……,wn}构成n棵二叉树的集合F={T1,T2……Tn},其中每棵二叉树Ti中只有一个带权为wi的根结点,其左右子树均为空。
- 在F中选取两棵根节点的权值最小的树作为左右子树构造一棵新的二叉树,且置新的二叉树的根节点的权值为其左,右子树上根节点的权值之和
- 在F中删除这棵树,同时将新得到的二叉树加入F中。
- 重复2,3步骤,直到F只含一棵树为止,这棵树便是赫夫曼树。
我们可以进行举例:已知某系统联络中只可能出现8{a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h}种字符,其出现的概率为0.05,0.29,0.07,0.08,0.14,0.23,0.03,0.11,试设计赫夫曼树。
设权w={5,29,7,8,14,23,3,11},n=8,则m=15,按照以上算法可构造以可赫夫曼树。
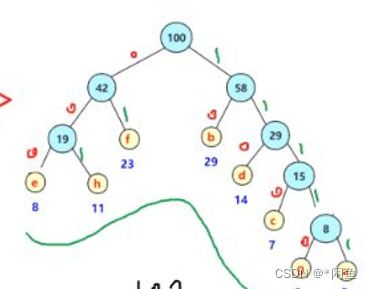
下图的结点均为叶子节点,我们首先在其中找到权值最小的两个结点,构造一棵而二叉树,比如下面结点我们以做一个左孩子权值为3右孩子权值为5,双亲权值为8的二叉树,然后将权值为8左孩子和右孩子编号为7和1的结点加入下面结点中,就这样选过的不再继续选,将新建立的结点加入其中,每次选出权值最小的两个结点,一直循环下去,直到遍历完所有的结点即可。

构建完成之后的哈夫曼树:
赫夫曼编码
我们根据二叉树的左右孩子进行变码,左为0,右为1,e的变码便是000,h的编码便是001。从根节点依次向下读取即可。
编码与压缩文件
文件压缩流程:
- 统计文件中所有字符出现的频次
- 将字符作为节点的值,字符出现的频次作为节点的权,构建哈夫曼树
- 将哈夫曼树的每个节点的字符与对应的 01 编码作为映射存储到字典中
- 再次读取文件,将每个字符转化为 01 编码的字符串格式
- 将这个文件对应的 01 编码字符串转换为真正的比特并写入到文件中,完成压缩
解压流程:
- 读取压缩文件,将压缩文件转换为 01 的字符串形式
- 将哈夫曼树的每个节点对应的 01 编码与字符值作为映射存储到字典中(HashMap)
- 对压缩文件转换成的字符串进行遍历;使用两个指针 i,j,第一个指针 i 指向起始点,第二个指针 j 以 i 所在的位置开始从左向右逐一扫描。如果 i~j 对应的字符串在字典中有匹配的 key,那么就在字典中取出对应的 value 写入到还原的文件中,并更新指针 i 的位置;无匹配的 key 则继续移动 j 指针直至匹配。当 i 移动到字符串最后的位置时,结束遍历,解压完成。
代码
结构体设计
#pragma once
const int n = 8;
const int m = n * 2;
typedef unsigned int WeigthType;
typedef unsigned int NodeType;
typedef struct {
WeigthType weight;
NodeType parent, leftchild, rightchild;
}HTNode;
typedef HTNode HuffManTree[m];
typedef struct
{
char ch;
char code[n + 1];
}HuffCodeNode;
typedef HuffCodeNode HuffCoding[n + 1];
struct IndexWeigth
{
int index;
WeigthType weight;
operator WeigthType() const { return weight; }
};
创建赫夫曼树
void InitHuffManTree(HuffManTree hft, WeigthType *w) {
memset(hft,0, sizeof(HuffManTree));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
hft[i+1].weight = w[i];
}
}
void PrintHuffManTree(HuffManTree hft) {
for (int i = 1; i <m; ++i) {
printf("index %3d weight: %3d parent %3d Lchild %3d Rchild %3d\n"
,i,hft[i].weight,hft[i].parent,hft[i].leftchild,hft[i].rightchild);
}
}
void CreateHuffManTree(HuffManTree hft) {
priority_queue<IndexWeigth, vector<IndexWeigth>, std::greater<IndexWeigth> >qu;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
qu.push(IndexWeigth{i,hft[i].weight});
}
int k = n + 1;
while (!qu.empty()) {
if (qu.empty()) break;
IndexWeigth left = qu.top(); qu.pop();
if (qu.empty()) break;
IndexWeigth right = qu.top(); qu.pop();
hft[k].weight = left.weight + right.weight;
hft[k].leftchild = left.index;
hft[k].rightchild = right.index;
hft[left.index].parent = k;
hft[right.index].parent = k;
qu.push(IndexWeigth{k,hft[k].weight});
k += 1;
}
}
创建构建赫夫曼编码
void InitHuffManCode(HuffCoding hc, char* ch) {
memset(hc,0,sizeof(HuffCoding));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
hc[i].ch = ch[i-1];
hc[i].code[0] = '\0';
}
}
void PrintHuffManCode(HuffCoding hc) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
printf("data: %c => code : %s \n", hc[i].ch, hc[i].code);
}
}
void CreateHuffManCode(HuffManTree hft, HuffCoding hc) {
char code[n + 1] = { 0 };
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int k = n;
code[k] = '\0';
int c = i;
int pa = hft[c].parent;
while (pa != 0) {
code[--k] = hft[pa].leftchild==c?'0' : '1';
c = pa;
pa = hft[c].parent;
}
strcpy_s(hc[i].code,n,&code[k]);
}
}