Background Matting-v2
一、要解决的问题
- 抠图问题: I = α ∗ F + ( 1 − α ) ∗ B I=\alpha*F+(1-\alpha)*B I=α∗F+(1−α)∗B
- 输出高质量alpha,保留发丝细节
二、创新点
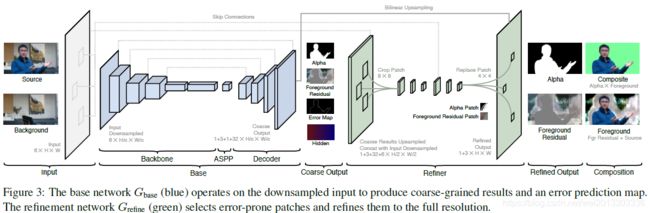
- 两阶段抠图:base-matting与refine-matting,由粗到细
- base阶段预测额外预测Error Map,用于表征需要refine的区域
- 两个数据集:图像数据集PhotoMatte85和视频数据集VideoMatte240K
三、具体细节
MattingBase网络:
Base网络是基于Deeplabv3+修改的Encoder-Decoder网络。Encoder部分的Backbone为Resnet50,同时作者的代码提供了Resnet101和Mobilenetv2作为可选backbone用于对精度和速度的不同要求。
Resnet50 backbone后接Deeplabv3的ASPP模块,空洞卷积的dilate_rate=[3,6,9]。
Decoder部分采用上采样+3*3conv+BN+ReLU套装。同时与Encoder的中间输出进行跳层链接。
Base网络共四个输出:
- coarse-grained alpha matte α c \alpha_c αc
- foreground residual F c R F_c^R FcR
- error prediction map E c E_c Ec
- 32-channel hidden features H c H_c Hc
MattingRefine网络:
Refine网络的目的是减少过多的网络计算,同时回复高分辨率的抠图细节。Base网络基于全图进行抠图操作,Refine网络则是根据error prediction map E c E_c Ec选取patches进行抠图refine操作。Refine包括 1 2 \frac{1}{2} 21原分辨率的操作和全分辨率refine两个过程。
patches的选择:resample E c E_c Ec到原分辨率的 1 4 \frac{1}{4} 41,即 E 4 E_4 E4。这样 E 4 E_4 E4中的每个像素表示原分辨率上4*4的patches。选取 E 4 E_4 E4中误差最大的top-k个元素作为refine网路的输入,这样在原分辨率上相当于对16k个像素进行refine.
2-stage Refine过程:首先,对 α c \alpha_c αc、 F c R F_c^R FcR、 H c H_c Hc、input image I I I、 background B B B进行双线性插值,到原分辨率的 1 2 \frac{1}{2} 21,并Concatenate到一起。
然后在选曲的误差较大的区域截取8*8的patches,然后送入2个3*3卷积+BN+ReLU套装,并降低到4*4,得到中间特征(intermediate features).
intermediate features再进行上采样到8*8,并和从原分辨率的 I I I和 B B B中截取的8*8patches concatenate到一起,送入2个3*3卷积+BN+ReLU套装,得到4*4的patches alpha prediction 和 foreground residuals。
最后,把 α c \alpha_c αc和 F c R F_c^R FcR上采样到原分辨率,并在选取的refine区域,将上采样的patches换成refine得到4*4的patches alpha prediction 和 foreground residuals。
四、代码
Base部分
RenNetEncoder定义在model/resnet.py中,继承自pytorch官方Renset。只是输入的channel从3变成6( I _ c h a n n e l + B _ c h a n n e l = 6 I\_channel+B\_channel=6 I_channel+B_channel=6)
并在forward的过程中保留中间block输出,用于skip connection。
def forward(self, x):
x0 = x # 1/1
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x1 = x # 1/2
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x2 = x # 1/4
x = self.layer2(x)
x3 = x # 1/8
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x4 = x # 1/16
return x4, x3, x2, x1, x0
ASPP直接从官方Pytorch中引入,输入的dilate_rate=[3, 6, 9]
Decoder则是自定义的interpolate+3*3conv+BN+ReLU套装,共4次上采样, 对应Encoder的4次2倍缩放。
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(feature_channels[0] + channels[0], channels[1], 3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[1])
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(feature_channels[1] + channels[1], channels[2], 3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[2])
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(feature_channels[2] + channels[2], channels[3], 3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[3])
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(feature_channels[3] + channels[3], channels[4], 3, padding=1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(True)
...
#forward
x = F.interpolate(x4, size=x3.shape[2:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
x = torch.cat([x, x3], dim=1)
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
...
整个Base的代码如下:
self.backbone = ResNetEncoder(in_channels, variant=backbone)
self.aspp = ASPP(2048, [3, 6, 9])
self.decoder = Decoder([256, 128, 64, 48, out_channels], [512, 256, 64, in_channels])
...
# 4个输出
def forward(self, src, bgr):
x = torch.cat([src, bgr], dim=1)
x, *shortcuts = self.backbone(x)
x = self.aspp(x)
x = self.decoder(x, *shortcuts)
pha = x[:, 0:1].clamp_(0., 1.) # alpha_c
fgr = x[:, 1:4].add(src).clamp_(0., 1.) # F_c
err = x[:, 4:5].clamp_(0., 1.) # E_c
hid = x[:, 5: ].relu_() # hidden_feature
return pha, fgr, err, hid
Refine部分
Refine部分的代码在 model/refiner.py文件中。按照论文中的描述,首先在 E 4 E_4 E4上选取前k个refine点。
def select_refinement_regions(self, err: torch.Tensor):
"""
Select refinement regions.
Input:
err: error map (B, 1, H, W)
Output:
ref: refinement regions (B, 1, H, W). FloatTensor. 1 is selected, 0 is not.
"""
if self.mode == 'sampling':
# Sampling mode.
b, _, h, w = err.shape
err = err.view(b, -1)
idx = err.topk(self.sample_pixels // 16, dim=1, sorted=False).indices # 选取topk个refine点
ref = torch.zeros_like(err)
ref.scatter_(1, idx, 1.) # 使用类似one-hot的方式,1表示需要优化的点,0表示不需要优化的点
if self.prevent_oversampling:
ref.mul_(err.gt(0).float())# 删除0点
ref = ref.view(b, 1, h, w)
else:
# Thresholding mode.
ref = err.gt(self.threshold).float()
return ref
def crop_patch(self,
x: torch.Tensor,
idx: Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],
size: int,
padding: int):
"""
Crops selected patches from image given indices.
Inputs:
x: image (B, C, H, W).
idx: selection indices Tuple[(P,), (P,), (P),], where the 3 values are (B, H, W) index.
size: center size of the patch, also stride of the crop.
padding: expansion size of the patch.
Output:
patch: (P, C, h, w), where h = w = size + 2 * padding.
"""
if padding != 0:
x = F.pad(x, (padding,) * 4)
if self.patch_crop_method == 'unfold':
# Use unfold. Best performance for PyTorch and TorchScript.
# 先按照H方向滑动窗口unfold出8*w的patch
# 再按照W方向滑动窗口unfold出8*8的patch
# 最后按照筛选出topk的refine点位置取出对应patch
return x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1) \
.unfold(1, size + 2 * padding, size) \
.unfold(2, size + 2 * padding, size)[idx[0], idx[1], idx[2]]
else:
# Use roi_align. Best compatibility for ONNX.
# roi_align更好地兼容ONNX,采用Mask-RCNN的roi_align,输出[K, C, output_size[0], output_size[1]]
idx = idx[0].type_as(x), idx[1].type_as(x), idx[2].type_as(x)
b = idx[0]
x1 = idx[2] * size - 0.5
y1 = idx[1] * size - 0.5
x2 = idx[2] * size + size + 2 * padding - 0.5
y2 = idx[1] * size + size + 2 * padding - 0.5
boxes = torch.stack([b, x1, y1, x2, y2], dim=1)
return torchvision.ops.roi_align(x, boxes, size + 2 * padding, sampling_ratio=1)
def replace_patch(self,
x: torch.Tensor,
y: torch.Tensor,
idx: Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]):
"""
Replaces patches back into image given index.
Inputs:
x: image (B, C, H, W)
y: patches (P, C, h, w)
idx: selection indices Tuple[(P,), (P,), (P,)] where the 3 values are (B, H, W) index.
Output:
image: (B, C, H, W), where patches at idx locations are replaced with y.
"""
xB, xC, xH, xW = x.shape
yB, yC, yH, yW = y.shape
if self.patch_replace_method == 'scatter_nd':
# Use scatter_nd. Best performance for PyTorch and TorchScript. Replacing patch by patch.
x = x.view(xB, xC, xH // yH, yH, xW // yW, yW).permute(0, 2, 4, 1, 3, 5)
x[idx[0], idx[1], idx[2]] = y
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 4, 2, 5).view(xB, xC, xH, xW)
return x
else:
# Use scatter_element. Best compatibility for ONNX. Replacing pixel by pixel.
iH, iW = xH // yH, xW // yW
i = self.crop_patch(torch.arange(0, xB * xC * xH * xW).view(xB, xC, xH, xW).type_as(x), idx, 4, 0)
i, x, y = i.view(-1), x.view(-1), y.view(-1)
x.scatter_(0, i.long(), y)
x = x.view(xB, xC, xH, xW)
return x
# refine开始
# 上采样E到1/4 E_4
err = F.interpolate(err, (H_quat, W_quat), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
ref = self.select_refinement_regions(err)
idx = torch.nonzero(ref.squeeze(1))
idx = idx[:, 0], idx[:, 1], idx[:, 2] # 计算refine点位置,(B:list, H:list, W:list)
if idx[0].size(0) > 0:
# 1. Hid, F_c, alpha_c concatenate
# 2. 把Hid, F_c, alpha_c上采样到1/2
# 3. crop_patches
x = torch.cat([hid, pha, fgr], dim=1)
x = F.interpolate(x, (H_half, W_half), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
x = self.crop_patch(x, idx, 2, 3 if self.kernel_size == 3 else 0)
# 1. .
# 2. src_bgr(F,B)上采样到1/2
# 3. crop_patches
y = F.interpolate(src_bgr, (H_half, W_half), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
y = self.crop_patch(y, idx, 2, 3 if self.kernel_size == 3 else 0)
# 4. 3*3卷积+BN+ReLU套装
x = self.conv1(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1))
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.relu(x)
# 5. 套装输出的结果再次上采样到8*8
# 6. 对src_bgr 的refine点crop patches(center_size=4, padding=2)
x = F.interpolate(x, 8 if self.kernel_size == 3 else 4, mode='nearest')
y = self.crop_patch(src_bgr, idx, 4, 2 if self.kernel_size == 3 else 0)
# 7. 套装
x = self.conv3(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1))
x = self.bn3(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
# 8. 上采样alpha_c, FR_c到原分辨率
out = torch.cat([pha, fgr], dim=1)
out = F.interpolate(out, (H_full, W_full), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# 9. refine点替换
out = self.replace_patch(out, x, idx)
pha = out[:, :1]
fgr = out[:, 1:]
else:
pha = F.interpolate(pha, (H_full, W_full), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
fgr = F.interpolate(fgr, (H_full, W_full), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
训练过程损失函数
![]()
同v1一样,alpha损失采用了L1 Loss和Gradient Loss(Sobel)。
![]()
网络输出前景残差 F R F^R FR,然后计算 F = m a x ( m i n ( F R + I , 1 ) , 0 ) F=max(min(F^R+I,1),0) F=max(min(FR+I,1),0),再将F与ground truth F ∗ F^* F∗计算L1 Loss,这里计算的时候只考虑alpha>0的区域。
![]()
Error map的Ground truth E ∗ E^* E∗由ground truth α ∗ \alpha^* α∗和预测的 α \alpha α计算得来, E ∗ = ∣ α − α ∗ ∣ E^*=|\alpha-\alpha^*| E∗=∣α−α∗∣,E主要为了表征预测的 α \alpha α与实际 α \alpha α的Error区域,不需要明确的边界,所以采用L2 Loss(MSE)。同时,差别越大的区域损失值也越大。
Base网络的整体损失函数:
Refine网络的整体损失函数:
五、参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/381917042