UNet代码练习
UNet代码练习
- 1 运行环境和目的
- 2 数据加载
-
- 2.1 源码下载
- 2.2 常用的数据加载代码格式:
- 2.3 本代码数据集内容
- 2.4 数据加载代码如下:
- 3.模型搭建
-
- 3.1 查看网络结构图:
- 3.2 代码编写:
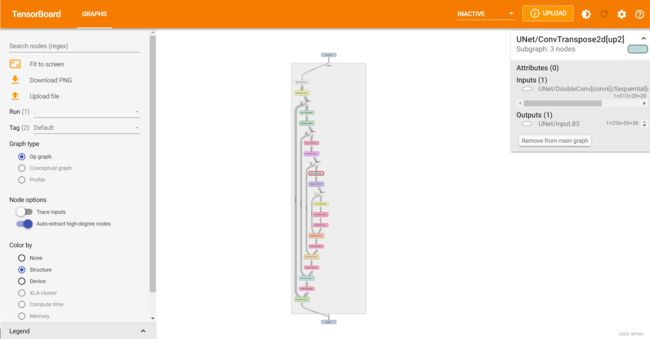
- 3.3 网络结构展示:
-
- 3.3.1 直接打印的网络结构
- 3.3.2 Tensorboard展示:
- 4 模型训练
-
- 4.1训练结果
- 5 模型预测
-
- 5.1展示预测结果
1 运行环境和目的
1.自己电脑没有显卡,训练会慢的离谱,白嫖了Kaggle训练平台上的GPU,自己已经上传了原始的代码和数据集,下面演示的是自己跟着师兄重新写的代码,会稍微简单好入门一点。
2.实现对细胞结构进行图像分割。
2 数据加载
2.1 源码下载
源代码和数据集已经放在kaggle平台上,点击使用
点击使用该数据集,结构如下:
2.2 常用的数据加载代码格式:
# You should build your custom dataset as below.
class CustomDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self):
# TODO
# 1. Initialize file paths or a list of file names.
pass
def __getitem__(self, index):
# TODO
# 1. Read one data from file (e.g. using numpy.fromfile, PIL.Image.open).
# 2. Preprocess the data (e.g. torchvision.Transform).
# 3. Return a data pair (e.g. image and label).
pass
def __len__(self):
# You should change 0 to the total size of your dataset.
return 0
# You can then use the prebuilt data loader.
custom_dataset = CustomDataset()
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=custom_dataset,
batch_size=64,
shuffle=True)
2.3 本代码数据集内容
我使用的数据集包含了训练集和测试集,各30张图片,且训练集已对图片进行了label操作
2.4 数据加载代码如下:
# dataset.py 数据加载使用
import torch
import cv2
import os
import glob
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import random
class ISBI_Loader(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_path):
# 初始化函数,读取所有data_path下的图片
self.data_path = data_path
# glob.glob(pathname)返回所有匹配的文件路径列表,字符串前面加r是让字符串不转义,这里获取”data_path/image/*.png下所有文件“
self.imgs_path = glob.glob(os.path.join(data_path, 'image/*.png'))
# glob.iglob 返回一个可以遍历的对象
def augment(self, image, flipCode): # augment 图像增强库 (self,图片,增强类型)
# 使用cv2.flip进行数据增强,filpCode为1水平翻转,0垂直翻转,-1水平+垂直翻转
flip = cv2.flip(image, flipCode) # cv2.flip是图片反转韩式
return flip
def __getitem__(self, index):
# 根据index读取图片
image_path = self.imgs_path[index]
# 根据image_path生成label_path
# 放在同一个文件夹下,然后将image换成label,找到标签图片
label_path = image_path.replace('image', 'label')
# 读取训练图片和标签图片
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
label = cv2.imread(label_path)
# 将数据转为单通道的图片 cv2.cvtColor是颜色空间转换函数,(1,2) 2为转换为何种格式,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY是灰度图 cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB是RGN格式
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
label = cv2.cvtColor(label, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# image.shape 是一个元组,0为垂直尺寸,1为水平尺寸,2为通道数
image = image.reshape(1, image.shape[0], image.shape[1])
label = label.reshape(1, label.shape[0], label.shape[1])
# print(label) 这时候读出来的数据是三维矩阵
# 处理标签,将像素值为255的改为1
if label.max() > 1: # 数组中最大的数据大于1时,则进行灰度处理
label = label / 255
# 随机进行数据增强,为2时不做处理
flipCode = random.choice([-1, 0, 1, 2]) # 数据随机生成
if flipCode != 2:
image = self.augment(image, flipCode)
label = self.augment(label, flipCode)
return image, label
def __len__(self):
# 返回训练集大小
return len(self.imgs_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
isbi_dataset = ISBI_Loader("../input/unet-train/lesson-2/data/train")
print("数据个数:", len(isbi_dataset))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=isbi_dataset,
batch_size=2,
shuffle=True) # 每次迭代 数据洗牌
for image, label in train_loader: # 这里的2.1.512.512 是 两个图片,一个通道,大小512*512
print(image.shape)
3.模型搭建
3.1 查看网络结构图:
请注意: 只需要关注输入输出的通道就可以了,不用去关注下面的图片大小,那些572*572的数字,这些图片大小是在写论文时候,将网络和具体的输入结合后画的网络图。
3.2 代码编写:
import torch.nn as nn
# 双卷积进行封装
class DoubleConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_ch,out_ch):
super(DoubleConv, self).__init__()
self.in_ch = in_ch
self.out_ch = out_ch
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_ch, out_channels=self.out_ch, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_ch),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.out_ch, out_channels=self.out_ch, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_ch),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self,x):
return self.conv(x)
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_ch,out_ch):
super(UNet,self).__init__()
self.in_ch = in_ch
self.out_ch = out_ch
self.conv1 = DoubleConv(in_ch = self.in_ch,out_ch = 64)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv2 = DoubleConv(64,128)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv3 = DoubleConv(128,256)
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv4 = DoubleConv(256,512)
self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv5 = DoubleConv(512,1024)
self.up1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv6 = DoubleConv(1024,512)
self.up2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=256, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv7 = DoubleConv(512,256)
self.up3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv8 = DoubleConv(256,128)
self.up4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=64, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv9 = DoubleConv(128,64)
self.conv_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=self.out_ch,kernel_size=1),
#nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self,x):
conv1 = self.conv1(x)
pool1 = self.pool1(conv1)
conv2 = self.conv2(pool1)
pool2 = self.pool2(conv2)
conv3 = self.conv3(pool2)
pool3 = self.pool3(conv3)
conv4 = self.conv4(pool3)
pool4 = self.pool4(conv4)
conv5 = self.conv5(pool4)
up1 = self.up1(conv5)
cat1 = torch.cat([conv4,up1],dim = 1)
conv6 = self.conv6(cat1)
up2 = self.up2(conv6)
cat2 = torch.cat([conv3,up2],dim = 1)
conv7 = self.conv7(cat2)
up3 = self.up3(conv7)
cat3 = torch.cat([conv2,up3],dim = 1)
conv8 = self.conv8(cat3)
up4 = self.up4(conv8)
cat4 = torch.cat([conv1,up4],dim = 1)
conv9 = self.conv9(cat4)
conv_out = self.conv_out(conv9)
return conv_out
#打印模型,查看整体结构
net = UNet(1,1)
print(net)
3.3 网络结构展示:
3.3.1 直接打印的网络结构
UNet(
(conv1): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv2): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv3): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(pool3): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv4): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(pool4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv5): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(512, 1024, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(1024, 1024, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(up1): ConvTranspose2d(1024, 512, kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
(conv6): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1024, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(up2): ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
(conv7): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(up3): ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
(conv8): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(up4): ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
(conv9): DoubleConv(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(128, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(4): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
)
(conv_out): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(64, 1, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
)
3.3.2 Tensorboard展示:
4 模型训练
from torch import optim
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
def train_net(net, device, data_path, epochs=40, batch_size=1, lr=0.00001):
# 加载训练集
isbi_dataset = ISBI_Loader(data_path)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=isbi_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True)
# 定义RMSprop算法
optimizer = optim.RMSprop(net.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=1e-8, momentum=0.9) # 常用的优化器
# 定义Loss算法
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss() # 就是一个将sigmoid函数和BCELOSS函数结合的一种loss函数
# best_loss统计,初始化为正无穷
best_loss = float('inf')
# 训练epochs次
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 训练模式
net.train() # 打开训练模式
i = 1
# 按照batch_size开始训练
for image, label in train_loader:
i = i + 1
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 将数据拷贝到device中
image = image.to(device=device, dtype=torch.float32)
label = label.to(device=device, dtype=torch.float32)
# 使用网络参数,输出预测结果
pred = net(image)
# 计算loss
loss = criterion(pred, label)
if i==30 :
print('Loss/train', loss.item())
# 保存loss值最小的网络参数
if loss < best_loss:
best_loss = loss
torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'best_model.pth')
# 更新参数
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 选择设备,有cuda用cuda,没有就用cpu
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 加载网络,图片单通道1,分类为1。
net = UNet(1,1)
# 将网络拷贝到deivce中
net.to(device=device)
# 指定训练集地址,开始训练
data_path = "../input/unet-train/lesson-2/data/train"
train_net(net, device, data_path)
4.1训练结果
5 模型预测
import glob
import numpy as np
import torch
import os
import cv2
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 选择设备,有cuda用cuda,没有就用cpu
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 加载网络,图片单通道,分类为1。
net = UNet(1, 1)
# 将网络拷贝到deivce中
net.to(device=device)
# 加载模型参数
net.load_state_dict(torch.load('./best_model.pth', map_location=device))
# 测试模式
net.eval()
# 读取所有图片路径
tests_path = glob.glob('../input/unet-train/lesson-2/data/test/*.png')
print(tests_path)
# 遍历素有图片
for test_path in tests_path:
# 保存结果地址
save_res_path = test_path.split('/')[6] + '_res.png'
print(save_res_path)
# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread(test_path)
# 转为灰度图
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# 转为batch为1,通道为1,大小为512*512的数组
img = img.reshape(1, 1, img.shape[0], img.shape[1])
# 转为tensor
img_tensor = torch.from_numpy(img)
# 将tensor拷贝到device中,只用cpu就是拷贝到cpu中,用cuda就是拷贝到cuda中。
img_tensor = img_tensor.to(device=device, dtype=torch.float32)
# 预测
pred = net(img_tensor)
# 提取结果
pred = np.array(pred.data.cpu()[0])[0]
# 处理结果
pred[pred >= 0.5] = 255
pred[pred < 0.5] = 0
# 保存图片
cv2.imwrite(save_res_path, pred)
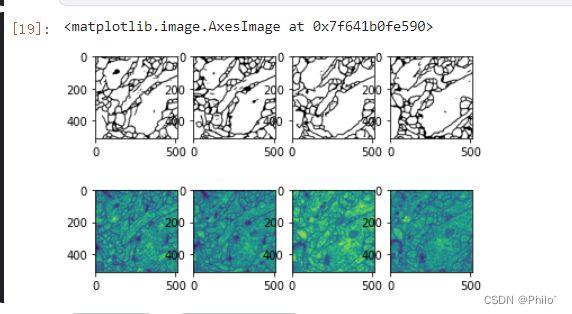
5.1展示预测结果
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.subplot(2, 4, 1)
im = plt.imread('./7.png_res.png')
plt.imshow(im, cmap="gray")
plt.subplot(2, 4, 2)
im = plt.imread('./6.png_res.png')
plt.imshow(im, cmap="gray")
plt.subplot(2, 4, 3)
im = plt.imread('./5.png_res.png')
plt.imshow(im, cmap="gray")
plt.subplot(2, 4, 4)
im = plt.imread('./4.png_res.png')
plt.imshow(im, cmap="gray")
plt.subplot(2, 4, 5)
im = plt.imread('../input/unet-train/lesson-2/data/test/7.png')
plt.imshow(im)
plt.subplot(2, 4, 6)
im = plt.imread('../input/unet-train/lesson-2/data/test/6.png')
plt.imshow(im)
plt.subplot(2, 4, 7)
im = plt.imread('../input/unet-train/lesson-2/data/test/5.png')
plt.imshow(im)
plt.subplot(2, 4, 8)
im = plt.imread('../input/unet-train/lesson-2/data/test/4.png')
plt.imshow(im)