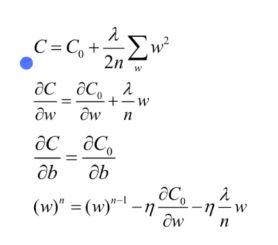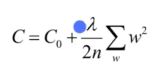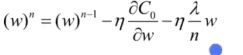9- 深度学习之神经网络核心原理与算法-全连接网络GPU实现
全连接网络GPU实现
- 加入Dropout
- 封装全连接层
之前我们的全连接网络只能运行在cpu上,我们改造为gpu实现。
封装全连接层到一个类里面。
因为我们要用到theano
WARNING (theano.configdefaults): g++ not available, if using conda: `conda install m2w64-toolchain`
D:\softEnvDown\Anaconda2\envs\py3\lib\site-packages\theano\configdefaults.py:560: UserWarning: DeprecationWarning: there is no c++ compiler.This is deprecated and with Theano 0.11 a c++ compiler will be mandatory
warnings.warn("DeprecationWarning: there is no c++ compiler."
WARNING (theano.configdefaults): g++ not detected ! Theano will be unable to execute optimized C-implementations (for both CPU and GPU) and will default to Python implementations. Performance will be severely degraded. To remove this warning, set Theano flags cxx to an empty string.
WARNING (theano.tensor.blas): Using NumPy C-API based implementation for BLAS functions.
根据报错,我们安装conda install -c msys2 m2w64-toolchain
因为我们要把我们的代码放在gpu上进行计算,所以我们引入theano
import theano.tensor as T
from theano.tensor import shared_randomstreams
from theano.tensor.nnet import sigmoid
引入theano里面的tensor提供了许多数学相关的函数。shared_randomstreams帮我们取随机值。使用提供的sigmoid激励函数。
# 是否使用GPU
GPU = True
if GPU:
print("Trying to run under a GPU. If this is not desired, then modify " + \
"network3.py\nto set the GPU flag to False.")
try:
theano.config.device = 'gpu'
except:
pass # it's already set
theano.config.floatX = 'float32'
else:
print("Running with a CPU. If this is not desired, then the modify " + \
"network3.py to set\nthe GPU flag to True.")
如果使用gpu的话,定义两个theano的变量theano.config.device 和theano.config.floatX = 'float32'
报错:
You can find the C code in this temporary file: C:\Users\mtian\AppData\Local\Temp\theano_compilation_error__dohjzex
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:\softEnvDown\Anaconda2\envs\py3\lib\site-packages\theano\gof\lazylinker_c.py", line 75, in
raise ImportError()
ImportError
解决方案;
conda install mingw libpython
全连接的实现被我们封装进了一个类里面:
class FullyConnectedLayer(object):
def __init__(self, n_in, n_out, activation_fn=sigmoid, p_dropout=0.0):
# 前一层神经元个数
self.n_in = n_in
# 后一层神经元个数
self.n_out = n_out
# 激励函数
self.activation_fn = activation_fn
# dropout
self.p_dropout = p_dropout
# 初始化权重
self.w = theano.shared(
np.asarray(
np.random.normal(
loc=0.0, scale=np.sqrt(1.0 / n_out), size=(n_in, n_out)),
dtype=theano.config.floatX),
name='w', borrow=True)
# 初始化偏置
self.b = theano.shared(
np.asarray(np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(n_out,)),
dtype=theano.config.floatX),
name='b', borrow=True)
self.params = [self.w, self.b]
def set_inpt(self, inpt, inpt_dropout, mini_batch_size):
# reshape输入
self.inpt = inpt.reshape((mini_batch_size, self.n_in))
# 输出
self.output = self.activation_fn(
(1 - self.p_dropout) * T.dot(self.inpt, self.w) + self.b)
# 取最大值
self.y_out = T.argmax(self.output, axis=1)
# dropout输入dropout
self.inpt_dropout = dropout_layer(
inpt_dropout.reshape((mini_batch_size, self.n_in)), self.p_dropout)
# dropout输出
self.output_dropout = self.activation_fn(
T.dot(self.inpt_dropout, self.w) + self.b)
def accuracy(self, y):
return T.mean(T.eq(y, self.y_out))
n_in表示前一层网络有多少神经元, n_out表示后一层一共有多少神经元, 激励函数(默认使用sigmoid函数) p_Dropout 抛弃多少神经元(百分比)
保存传入的参数到类的私有变量。
初始化权重self.w
使用theano.shared方法可以把我们的权重值放在gpu上运算。这里我们使用正态分布,均值为0,方差为(1/后一层神经元个数)开根号。总共有多少个权重 (n_in, n_out)前一层乘以后一层。数组的数据类型可以用theano里面的floatx来表示(方便放在gpu上运行)。设置一个名字name w。borrow设置为true表示共享变量。
https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/theano-users/XWDOoKdpn5I
初始化偏置self.b
使用均值为0,方差为1的正态分布初始化数组,数组的size是n_out.偏置等于下一层神经元的个数。数组的数据类型可以用theano里面的floatx来表示(方便放在gpu上运行)。
self.params 将刚才初始化的w和b放在一个列表里面。
set_input函数
通过这个方法设置我们需要的值。
参数: 前一层的输出,和前一层经过Dropout之后的输出当做本层的输入,mini_batch的大小。
reshape一下inpt。总共是有mini_batch条数据,每条数据有n_in这么多列。
本层全连接层的输出,线性部分wx+b经过激励函数。
引入了dropout。也就是输出的时候要保留多少个神经元的结果。
取一下输出的最大值。如果仍做手写数字的识别,输出一共有10种0-9。取最大值也就是它最大的可能性。
对于全连接层输入的时候我们要做一下Dropout reshape。
drop_layer函数在下面实现:
def dropout_layer(layer, p_dropout):
srng = shared_randomstreams.RandomStreams(
np.random.RandomState(0).randint(999999))
mask = srng.binomial(n=1, p=1 - p_dropout, size=layer.shape)
return layer * T.cast(mask, theano.config.floatX)
就是要保留多少数据。
输出的时候也要做一下Dropout
直接和输入时的Dropout和w做内积再加上偏置。
计算一下本层的输出和做完Dropout之后的输出。
定义一个计算准确率的函数
def accuracy(self, y):
return T.mean(T.eq(y, self.y_out))
传入网络的真实值与预测值进行比较。取平均值,得到准确率。
我们Network类的修改;
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, layers, mini_batch_size):
self.layers = layers
self.mini_batch_size = mini_batch_size
# 把每一层的参数放到一个list里
self.params = [param for layer in self.layers for param in layer.params]
# 初始化x, y
self.x = T.matrix("x")
self.y = T.ivector("y")
# 初始化第一层
init_layer = self.layers[0]
init_layer.set_inpt(self.x, self.x, self.mini_batch_size)
# 初始化后面每层
for j in range(1, len(self.layers)):
prev_layer, layer = self.layers[j - 1], self.layers[j]
layer.set_inpt(
prev_layer.output, prev_layer.output_dropout, self.mini_batch_size)
# 最后一层的输出
self.output = self.layers[-1].output
self.output_dropout = self.layers[-1].output_dropout
构造函数,总共传入多少层。将每一层的参数放入一个list中。
首先遍历每一层,然后在每一层里面取每一层的参数。
初始化一下训练数据和它对应的标签。标签是一个0-9向量 x是一个28,28的矩阵。
设置一下网络第一次的输入,经过Dropout之后的输入。因为这里是第一层,此时原始的图片中第一个参数和第二个参数是一样的。
初始化后面的每一层网络。从第二层开始一直到最后一层。
取一下本层的网络的前一层和当前层。为当前层的网络设置参数: 前一层的输出,前一层的Dropout输出。
我们保留一下最后一层的output。最后一层Dropout之后的输出。-1是取最后一层。
梯度下降函数
def SGD(self, training_data, epochs, mini_batch_size, eta,
validation_data, test_data, lmbda=0.0):
training_x, training_y = training_data
validation_x, validation_y = validation_data
test_x, test_y = test_data
num_training_batches = size(training_data) / mini_batch_size
num_validation_batches = size(validation_data) / mini_batch_size
num_test_batches = size(test_data) / mini_batch_size
eta学习率 验证数据集是帮助我们网络在训练的时候调整参数的,让你发现哪些超参数有问题。
测试数据集是帮我们验证我们最后训练出来的模型的好坏的。lmbda是做正则化用的参数
保存一下训练数据集和验证数据集分别对应的x和y。
我们计算一下验证,测试,训练总共要分成多少个batches
L2正则化
原始的损失函数+加号后面这一项: L2正则项
w的平方累加和,
原始的C0 和 我们的L2正则化项。
计算偏导。
原来我们是手工实现的,直接调用theano里面提供的方法grad计算梯度
参数: 损失,每层神经元的参数w和b
更新每一层的参数:
w-学习率* 偏导。
设置更新方程
index 就是一个标量i
第一个参数是i,第二层个参数是cost,第三个参数是上面的更新参数
输入时训练数据集的x, 0-60 60-120
验证数据集上的准确率。调用最后一层。如果最后一层是全连接层的话,调用
全连接层我们刚实现的计算准确率的函数。把x对应的实际标签y丢进去。
组织一下batches
开始训练
# 开始训练
best_validation_accuracy = 0.0
for epoch in range(epochs):
for minibatch_index in range(num_training_batches):
iteration = num_training_batches * epoch + minibatch_index
if iteration % 1000 == 0:
print("Training mini-batch number {0}".format(iteration))
cost_ij = train_mb(minibatch_index)
if (iteration + 1) % num_training_batches == 0:
validation_accuracy = np.mean(
[validate_mb_accuracy(j) for j in range(num_validation_batches)])
print("Epoch {0}: validation accuracy {1:.2%}".format(
epoch, validation_accuracy))
if validation_accuracy >= best_validation_accuracy:
print("This is the best validation accuracy to date.")
best_validation_accuracy = validation_accuracy
best_iteration = iteration
if test_data:
test_accuracy = np.mean(
[test_mb_accuracy(j) for j in range(num_test_batches)])
print('The corresponding test accuracy is {0:.2%}'.format(
test_accuracy))
print("Finished training network.")
print("Best validation accuracy of {0:.2%} obtained at iteration {1}".format(
best_validation_accuracy, best_iteration))
print("Corresponding test accuracy of {0:.2%}".format(test_accuracy))
总共训练多少轮,每轮里面训练多少个把batch 每次取一个batch进行训练。
每隔多少步打印一下。当前训练到了多少个minibatch。调用我们的train_mb函数进行训练。
每训练完一轮,就使用我们的验证数据集进行验证。之前这一轮在验证数据集上的准确率。
如果验证数据集上的准确率大于以往的最佳验证数据集准确率。表示更新了。
并且保存它训练的步数。