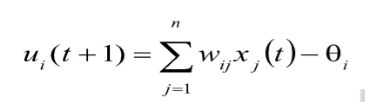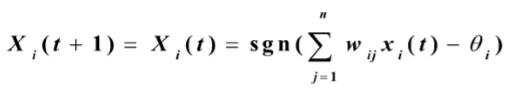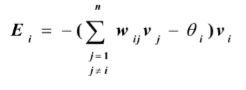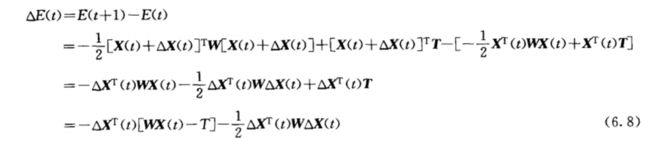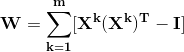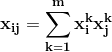反馈式神经网络之HNN
反馈式神经网络之HNN
神经网络
神经网络的简介
人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Network,即ANN ),它从信息处理角度对人脑神经元网络进行抽象, 建立某种简单模型,按不同的连接方式组成不同的网络。同时也直接简称为神经网络或类神经网络。神经网络是一种运算模型,由大量的节点(或称神经元)之间相互联接构成。每个节点代表一种特定的输出函数,称为激励函数(activation function)。每两个节点间的连接都代表一个对于通过该连接信号的加权值,称之为权重,这相当于人工神经网络的记忆。网络的输出则依网络的连接方式,权重值和激励函数的不同而不同。而网络自身通常都是对自然界某种算法或者函数的逼近,也可能是对一种逻辑策略的表达。
神经网络的类型
人工神经网络模型主要考虑网络连接的拓扑结构、神经元的特征、学习规则等。所以我们根据连接的拓扑结构,神经网络模型可以分为:
-
前向网络
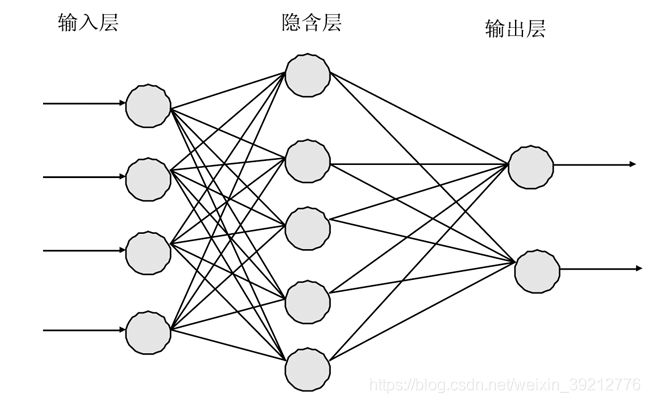
网络中的各个神经元(节点)接收前一级的输入,加权叠加后并输入到下一级,网络中没有反馈,网络的拓扑结构可以用一个有向无环图表示。这种网络实现信号从输入空间到输出空间的变换,它的信息处理能力来自于简单非线性函数的多次复合。网络结构简单,易于实现。反传网络(BP)是一种典型的前向网络。如图1所示:
-
反馈网络
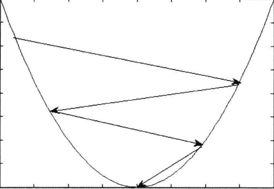
网络内神经元间有反馈,可以用一个无向的完备图表示。这种神经网络的信息处理是状态的变换,可以用动力学系统理论处理。系统的稳定性与联想记忆功能有密切关系。Hopfield网络(HNN)、波耳兹曼机均属于这种类型。如图2(HNN的拓扑结构图)所示:
反馈式神经网络
反馈神经网络是一种反馈动力学系统。在这种网络中,每个神经元同时将自身的输出信号作为输入信号反馈给其他神经元,它需要工作一段时间才能达到稳定。
Hopfield神经网络(HNN)
美国加州理工学院物理学家J.J.Hopfield教授于1982年提出一种单层反馈神经网络,后来人们将这种反馈网络称作Hopfield 网。Hopfield神经网络是(HNN)反馈网络中最简单且应用广泛的模型,它具有联想记忆和解决快速寻优问题的功能。
HNN的状态
对于HNN中的每一个节点只有两种状态:0 或者 1,代表闭或开,节点之间彼此互相连接,所有神经元状态的集合就构成反馈网络的状态,但是这种网络是很难分析的,其可能的状态有:
HNN的能量函数与吸引子
研究发现如果模型是对称的,那么整个网络就会存在一个全局能量函数,系统能够收敛到一个最低能量处。因此,我们研究的 Hopfield 网络是一个对称网络。这里所谓的对称即每个节点的输出状态都反馈回来作为除自身外每一个节点的输入。
-
对于每一个神经元,我们知道其输入与输出的关系为:
-
离散型(DHNN)与连续型(DHNN)
根据激励函数的选取我们可以把神经网络定义成离散型与连续型:
DHNN: 作用函数为符号函数,主要用于联想记忆。
CHNN:作用函数为S形函数(sigmoid),主要用于优化计算。
-
DHNN
对于每个神经元,其输出状态为:
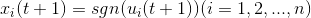
-
DHNN的状态变化
- 每一个神经元有两种状态(0或1),所有对于N个节点的HNN有2的N次方个可能的状态,即整个网络的状态可以用一个包含0和1的向量表示。
- 节点的状态更新包括三种情况:0—>1; 1—>0; 保持不变
- 按照单元异步更新方式,某一时刻网络只有一个节点被选择进行状态更新,当该节点状态变化时,网络状态就以一定概率转移到另一状态;当该节点保持时,网络状态的更新结果保持前一时刻的状态。
因为我们用权值和阈值训练整个网络,所以,一旦给出确定的HNN权值和神经元的阈值,网络的状态转移序列就确定了,也就是网络的状态就确定了。
HNN的能量函数
按照能量变化为负的思路,可将定义节点i的能量为:
所以对于整个网络,其总能量为:
显然E是对所有的Ei按照某种方式求和得到。因为离散HNN中,wij = wji (单层对称网络),如果直接计算E,将会对Ei中的每一项计算两次。所以在前面有个1/2的因子。
对于能量函数,我们可以改写为:
定义两个差值变量:
则可得出能量变化为:
我们假设t时刻,只有1个神经元调整状态(串行方式工作),假设神经元为j,则此时:
![]() 带入上式,得到:
带入上式,得到:
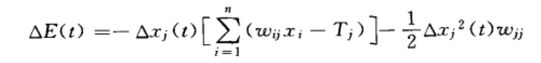
因为神经元不存在自反馈,所以wii为0,则最终能量变化为:
我们考虑:
因此能量E是不断减少的。
吸引子
网络达到稳定时的状态X,称为网络的吸引子。在上述推导中我们证明了网络中的能量是逐渐减少的,通过能量变化公式可知,当能量稳定时(极小点),整个网络的状态也稳定了。我们称此时的状态为网络的吸引子,也就是说此时网络具有了记忆的功能。如果将记忆的样本信息存储于不同的能量极小点,当输入某一模式时,网络就能实现“联想记忆”与其相关的存储样本,实现联想记忆。
权值的设计
通过上面的推导,我们知道HNN主要是通过训练(或者确定)连接权和阈值就可以达到存储序列的目的,在实际的过程中我们可令阈值为0,这样一来我们只需要训练连接权就可达到记忆相应的序列的目的。所以,我们下面的问题就是怎么去设计这个权值。
通常训练权值的方法有外积法、伪逆法、正交设计法等。下面讲解了最常用的外积法(Hebb学习法则)。
Hebb学习法则
Hebb学习法则是一种比较简单,在一定条件下行之有效的设计劝着的方法。当神经元输入与输出节点的状态相同(即同时兴奋或抑制)时,从第 j 个到第 i 个神经元之间的连接强度则增强,否则则减弱。海布(Hebb)法则是一种无指导的死记式学习算法。学习的目的:对具有 q 个不同的输入样本组X^k = [x1,x2,…,x^k],希望通过调节计算有限的权值矩阵 W,使得当每一组输入样本 X^k,作为系统的初始值,经过网络循环,系统能够收敛到各自输入样本矢量本身。
根据上式,我们可以根据目的存储序列设计出相应的连接权。
HNN的实现
不管采取什么工作方式,基本运行步骤是类似的,下面以串行工作方式为例。
HNN的实现流程
- 第一步:对网络进行初始化
- 第二步:使用Hebbo法则确定权值
- 第三步:进行预测
训练集
zero = [0, 1, 1, 1, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
0, 1, 1, 1, 0]
one = [0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
two = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
训练板块
# Hopfield Class
class HOP(object):
def __init__(self, N):
# Bit Dimension
self.N = N
# Weight Matrix
self.W = np.zeros((N, N), dtype = floatType)
# Calculate Kronecker Square Product of [factor] itself OR use np.kron()
def kroneckerSquareProduct(self, factor):
ksProduct = np.zeros((self.N, self.N), dtype=floatType)
# Calculate
for i in range(0, self.N):
ksProduct[i] = factor[i] * factor
return ksProduct
# Training a single stableState once a time, mainly to train [W]
def trainOnce(self, inputArray):
# Learn with normalization
mean = float(inputArray.sum()) / inputArray.shape[0]
self.W = self.W + self.kroneckerSquareProduct(inputArray - mean) / (self.N * self.N) / mean / (1 - mean)
# Erase diagonal self-weight
index = range(0, self.N)
self.W[index, index] = 0.
# Overall training function
def hopTrain(self, stableStateList):
# Preprocess List to Array type
stableState = np.asarray(stableStateList, dtype=uintType)
# Exception
if np.amin(stableState) < 0 or np.amax(stableState) > 1:
print('Vector Range ERROR!')
return
# Train
if len(stableState.shape) == 1 and stableState.shape[0] == self.N:
print('stableState count: 1')
self.trainOnce(stableState)
elif len(stableState.shape) == 2 and stableState.shape[1] == self.N:
print('stableState count: ' + str(stableState.shape[0]))
for i in range(0, stableState.shape[0]):
self.trainOnce(stableState[i])
else:
print('SS Dimension ERROR! Training Aborted.')
return
print('Hopfield Training Complete.')
# Run HOP to output
def hopRun(self, inputList):
# Preprocess List to Array type
inputArray = np.asarray(inputList, dtype=floatType)
# Exception
if len(inputArray.shape) != 1 or inputArray.shape[0] != self.N:
print('Input Dimension ERROR! Runing Aborted.')
return
# Run
matrix = np.tile(inputArray, (self.N, 1))
matrix = self.W * matrix
# print("matrix:",matrix.shape)
outputArray = matrix.sum(1)
# print("outputArray:",outputArray.shape)
# Normalize
m = float(np.amin(outputArray))
M = float(np.amax(outputArray))
outputArray = (outputArray - m) / (M - m)
# Binary
''' \SWITCH/ : 1/-1 OR 1/0
outputArray[outputArray < 0.5] = -1.
''' # \Division/
outputArray[outputArray < 0.5] = 0.
# ''' # \END/
outputArray[outputArray > 0] = 1.
return np.asarray(outputArray, dtype=uintType)
# Reset HOP to initialized state
def hopReset(self):
# Weight Matrix RESET
self.W = np.zeros((self.N, self.N), dtype = floatType)
输出格式定义
# Utility routine for printing the input vector: [NperGroup] numbers each piece
def printFormat(vector, NperGroup):
string = ''
for index in range(len(vector)):
if index % NperGroup == 0:
'''
\SWITCH/ : Single-Row OR Multi-Row
string += ' '
'''
# \Division/
string += '\n'
if str(vector[index]) == '0':
string += ' '
elif str(vector[index]) == '1':
string += '*'
else:
string += str(vector[index])
string += '\n'
print(string)
进行测试
# DEMO of Hopfield Net
def HOP_demo():
zero = [0, 1, 1, 1, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
0, 1, 1, 1, 0]
one = [0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
two = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
hop = HOP(5 * 6)
hop.hopTrain([zero, one, two])
half_zero = [0, 1, 1, 1, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
print('Half-Zero:')
printFormat(half_zero, 5)
result = hop.hopRun(half_zero)
print('Recovered:')
printFormat(result, 5)
half_two = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
print('Half-Two:')
printFormat(half_two, 5)
result = hop.hopRun(half_two)
print('Recovered:')
printFormat(result, 5)
half_two = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
print('Another Half-Two:')
printFormat(half_two, 5)
result = hop.hopRun(half_two)
print('Recovered:')
printFormat(result, 5)
入口程序
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.clock()
HOP_demo()
end = time.clock()
print("time: ", end-start)
输出结果
stableState count: 3
Hopfield Training Complete.
Half-Zero:
***
* *
* *
Recovered:
***
* *
* *
* *
* *
***
Half-Two:
**
*
*****
Recovered:
***
*
*
**
*
*****
Another Half-Two:
***
*
*
Recovered:
***
*
*
**
*
*****
time: 0.02231466803018272
附录
参考文档
Hopfield 网络
Hopfield 网络(上)
Hopfield 网络(下)
Hopfield神经网络详解
【Python】改进Hopfield网络代码实现
一种设计离散型Hopfield神经网络权值的新方法