使用Opencv+Python的AR小demo
摘要
浅浅了解一下 Python OpenCV,试着给自己的 iphone 8 做一下相机标定
定义
增强现实( AR ) 是一种真实世界环境的交互式体验,其中存在于现实世界中的对象通过计算机生成的感知信息得到增强,有时跨越多种感官模式,包括视觉、听觉、触觉、体感和嗅觉。AR 可以定义为一个包含三个基本特征的系统:真实和虚拟世界的结合、实时交互以及虚拟和真实对象的准确 3D 配准。重叠的感觉信息可以是建设性的(即对自然环境的补充)或破坏性的(即对自然环境的掩蔽)。这种体验与物理世界无缝交织,因此被视为真实环境的沉浸式体验。[4]通过这种方式,增强现实改变了人们对现实世界环境的持续感知,而虚拟现实完全用模拟环境取代了用户的现实世界环境。增强现实与两个主要同义词相关:混合现实和计算机介导的现实。
——以上内容来自Wiki百科
类别
Vision based AR(基于计算机视觉的AR)
Marker-Based AR (基于标定的AR)
如:
Marker-Less AR(基于特征点的AR)
如:
LBS based AR(基于地理位置信息的AR)
如:
本文将具体讲解和实验基于特征点的AR技术
Demo 演示
1. 演示环境
2. 准备图片
3. 相机标定原理
从世界坐标系转换到图像坐标系,求投影矩阵 P P P 的过程
分为两步
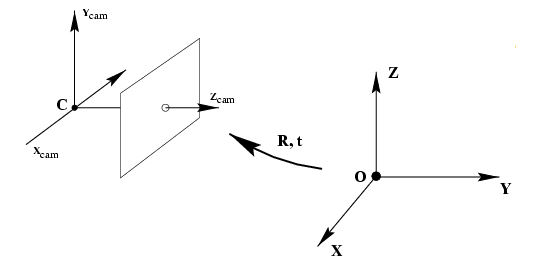
3.1 从世界坐标系转换为相机坐标系
这一步是三维点到三维点的转换,包括 R , t R,t R,t (相机外参)等参数
X ~ c a m = R ( X ~ − C ~ ) \widetilde{X}_{c a m}=R(\widetilde{X}-\widetilde{C}) X cam=R(X −C )
- X ~ \widetilde{X} X 为 X X X 在世界坐标中的位置
- R R R 为旋转矩阵
- C ~ \widetilde{C} C 为相机原点 C C C 所在世界坐标中的位置
- X ~ c a m \widetilde{X}_{c a m} X cam 为 $ X $ 在相机坐标系中的位置
3.2 从相机坐标系转换为图像坐标系
这一步是三维点到二维点的转换,包括 K K K(相机内参)等参数
-
C C C 为相机的中心点,也是相机坐标系的中心点
-
Z Z Z 为相机的主轴
-
p p p 为相机的像平面,也就是图片坐标系所在的二维平面
-
C C C 点到 p p p 点的距离 f f f,为相机的焦距
可得到
x = f X / Z y = f Y / Z ( X , Y , Z ) ↦ ( f X / Z , f Y / Z ) \begin{aligned} x &=f X / Z \\ y &=f Y / Z \\ (X, \quad Y, \quad Z) & \mapsto(f X / Z, \quad f Y / Z) \end{aligned} xy(X,Y,Z)=fX/Z=fY/Z↦(fX/Z,fY/Z)
由图可知偏移量
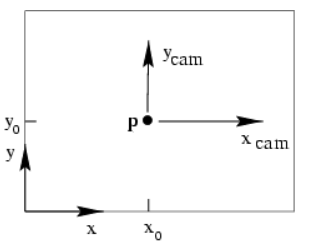
( X , Y , Z ) ↦ ( f X / Z + p x , f Y / Z + p y ) (X, \quad Y, \quad Z) \mapsto\left(f X / Z+p_{x}, \quad f Y / Z+p_{y}\right) (X,Y,Z)↦(fX/Z+px,fY/Z+py)
矩阵形式为
( X Y Z 1 ) ↦ ( f X + Z p x f Y + Z p y Z ) = [ f p x 0 f p y 0 1 0 ] ( X Y Z 1 ) \left(\begin{array}{c} X \\ Y \\ Z \\ 1 \end{array}\right) \mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c} f X+Z p_{x} \\ f Y+Z p_{y} \\ Z \end{array}\right)=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} f & p_{x} & 0 \\ & f & p_{y} & 0 \\ & & 1 & 0 \end{array}\right]\left(\begin{array}{c} X \\ Y \\ Z \\ 1 \end{array}\right) ⎝ ⎛XYZ1⎠ ⎞↦⎝ ⎛fX+ZpxfY+ZpyZ⎠ ⎞=⎣ ⎡fpxf0py100⎦ ⎤⎝ ⎛XYZ1⎠ ⎞
化简得
( f X + Z p x f Y + Z p y Z ) = [ f p x f p y 1 ] [ 1 0 1 0 1 0 ] ( X Y Z 1 ) \left(\begin{array}{c} f X+Z p_{x} \\ f Y+Z p_{y} \\ Z \end{array}\right)=\left[\begin{array}{cc} f & p_{x} \\ & f & p_{y} \\ & & 1 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{llll} 1 & & & 0 \\ & 1 & & 0 \\ & & 1 & 0 \end{array}\right]\left(\begin{array}{l} X \\ Y \\ Z \\ 1 \end{array}\right) ⎝ ⎛fX+ZpxfY+ZpyZ⎠ ⎞=⎣ ⎡fpxfpy1⎦ ⎤⎣ ⎡111000⎦ ⎤⎝ ⎛XYZ1⎠ ⎞
则
K = [ f p x f p y 1 ] K=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} f & & p_{x} \\ & f & p_{y} \\ & & 1 \end{array}\right] K=⎣ ⎡ffpxpy1⎦ ⎤
设旋转矩阵 R R R 为单位矩阵 I I I,平移矩阵 t t t 为0
P = K [ R ∣ t ] = K [ I ∣ 0 ] \begin{aligned} P &=K[R \mid t] \\ &=K[I \mid 0] \end{aligned} P=K[R∣t]=K[I∣0]
畸变参数本例未考虑到,不作讨论
4. 获得相机标定矩阵
4.1 手动对焦,固定焦距,拍摄各个方面的标定板
4.2 具体过程
- 提取角点 本例使用的标定板来自 calib 有13 * 9 个角点
- 提取亚像素角点 提高精度
- 标定
4.3 结果
得到 iphone 8 的相机标定矩阵为 (代码见camera_calibration.py)
[[1.09358481e+03 0.00000000e+00 5.12119524e+02]
[0.00000000e+00 1.08983166e+03 6.61345525e+02]
[0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 1.00000000e+00]]
5. 特征处理
5.1 特征检测
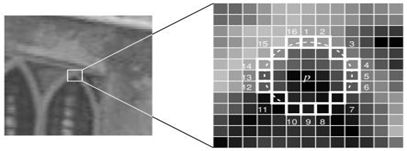
使用ORB法进行特征检测,ORB基于FAST算法,FAST算法的原理如下
任选图像中的一点 P P P,以该点为圆形, r r r为半径确定一个圆,在圆上均匀取 m m m个像素点,设定一个阈值 t t t,如果 m m m个像素点中,有连续 N N N个像素点的大小均大于或小于 t t t,则这个点就是角点。但是在进行FAST进行角点检测时,边缘位置的部分易混淆,针对这种情况,ORB算法通过增加图像金字塔和计算角度的方法,用Harris角点检测器把 N N N个关键点进行等级排序,使用者可提取前n个自己需要的点。不同的是,ORB在进行特征点匹配时,检测出的角点需要满足尺度不变形和旋转不变性。
- 尺度不变形
通过对初始图像的按1/2的比例不断下采样(即按1/2的比例不断缩放),得到一系列图像,形成图像金字塔。对每层图像,进行FAST角点检测
- 旋转不变形
采用灰度质心法进行计算每个特征点的主方向
m p q = ∑ x , y x p y q I ( x , y ) \mathrm{m}_{p q}=\sum_{x, y} x^{p} y^{q} I(x, y) mpq=x,y∑xpyqI(x,y)
其中 x , y x,y x,y分别表示像素点周围圆上所选取点的横坐标和纵坐标, I ( x , y ) I(x,y) I(x,y)表示灰度值大小, p , q p,q p,q表示指数,角度计算的方法如下
θ = atan 2 ( m 01 , m 10 ) \theta=\operatorname{atan} 2(\mathrm{m_{01}}, \mathrm{m_{10}}) θ=atan2(m01,m10)
5.2 特征描述
ORB法采用BRIEF描述子计算算法实现,BRIEF算法可分为两步
- 特征点大小的对比
以特征点为中心,取邻域窗口,在窗口上选择两个点p(x)和p(y),比较两个点像素值的大小
τ ( p ; x , y ) : = { 1 i f p ( x ) < p ( y ) 0 otherwise \tau(p ; x, y):=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} 1 & if\quad p(x)
- 重复第一步进行像素值大小的比较,形成二进制编码
OBR算法对BRIEF有两种改变,分别为 steer BRIEF 和 rBRIEF
-
steer BRIEF具备旋转不变形的特征,已知 $ /theta $,将该点周围的点旋转 $ /theta $ 度,得到新的点对
D θ = R θ D D_{\theta}=R_{\theta} D Dθ=RθDR R R 为旋转矩阵
旋转后,在新的位置上比较像素值的大小,得到描述子 -
rBRIEF算法通过改变描述子的计算方法,进一步减弱同一图像中特征点的描述子的相关性,对每个角点,考虑其 31 X 31 31X31 31X31 的邻域,使用领域中每个点周围的 5 X 5 5X5 5X5 的邻域的像素值平均值作为该点的像素值,进而比较点对的大小。上面计算可得到 ( 31 − 5 + 1 ) ∗ ( 31 − 5 + 1 ) = 729 (31-5+1)*(31-5+1)=729 (31−5+1)∗(31−5+1)=729 个子窗口,提取点对的方法有 729 X 728 = 265356 729X728=265356 729X728=265356 种,通过在这 265356 265356 265356 中方法中选取 256 256 256 种取法,形成描述子
5.3 特征匹配
本例使用 Brute-Force Matcher 进行特征匹配,也就是暴力匹配
结果
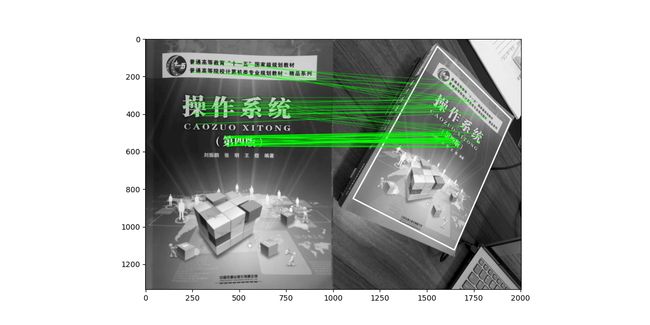
6. 映射
将参考图像表面的平面的点映射到用例图像的平面上,也就是单应性变换,单应性变换是将一个平面(齐次坐标)中的点映射到另一个平面的二维投影变换
[ x ′ y ′ z ′ ] = [ h 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 6 h 7 h 8 h 9 ] [ x y z ] \left[\begin{array}{l} x^{\prime} \\ y^{\prime} \\ z^{\prime} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{lll} h_{1} & h_{2} & h_{3} \\ h_{4} & h_{5} & h_{6} \\ h_{7} & h_{8} & h_{9} \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} x \\ y \\ z \end{array}\right] ⎣ ⎡x′y′z′⎦ ⎤=⎣ ⎡h1h4h7h2h5h8h3h6h9⎦ ⎤⎣ ⎡xyz⎦ ⎤
从两个图像中传递点集,它将找到该对象的透视变换,至少需要四个正确的点才能找到转换,但两幅图像之间的单应性变换包含不适合的点。会导致匹配时出现错误,影响结果,使用 RANSAC 迭代法验证拟合
结果
7. 3D 绘制
使用 yarolig的OBJFileLoader 加载 3D obj 模型 (代码见 objloader_simple.py)
8. 结果
ar_python_opencv.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from objloader_simple import *
referenceImage = cv2.imread('/home/pacaep/Tests/OpenCvArDemo/img/referenceImage.png',0)
plt.imshow(referenceImage, cmap = 'gray')
sourceImage = cv2.imread('/home/pacaep/Tests/OpenCvArDemo/img/sourceImage.png',0)
plt.imshow(sourceImage, cmap='gray')
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
referenceImagePts = orb.detect(referenceImage, None)
sourceImagePts = orb.detect(sourceImage, None)
referenceImagePts, referenceImageDsc = orb.compute(referenceImage, referenceImagePts)
sourceImagePts, sourceImageDsc = orb.compute(sourceImage, sourceImagePts)
referenceImageFeatures = cv2.drawKeypoints(referenceImage, referenceImagePts,
referenceImage, color = (0,255,0), flags = 0)
sourceImageFeatures = cv2.drawKeypoints(sourceImage, sourceImagePts,
sourceImage, color = (0,255,0), flags = 0)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(referenceImageFeatures, cmap = 'gray')
plt.title('Reference Image Features')
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(sourceImageFeatures,cmap='gray')
plt.title('Source Image Features')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
MIN_MATCHES = 30
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck = True)
referenceImagePts, referenceImageDsc = orb.detectAndCompute(referenceImage, None)
sourceImagePts, sourceImageDsc = orb.detectAndCompute(sourceImage, None)
matches = bf.match(referenceImageDsc, sourceImageDsc)
matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x: x.distance)
if len(matches) > MIN_MATCHES:
idxPairs = cv2.drawMatches(referenceImage, referenceImagePts,
sourceImage, sourceImagePts, matches[:MIN_MATCHES],0,flags =2)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(idxPairs, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Matching between features')
plt.show()
else:
print("Not enough matches have been found - %d/%d" %(len(matches), MIN_MATCHES))
matchesMask = None
if len(matches) > MIN_MATCHES:
sourcePoints = np.float32([referenceImagePts[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1,1,2)
destinationPoints = np.float32([sourceImagePts[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1,1,2)
homography, mask = cv2.findHomography(sourcePoints, destinationPoints, cv2.RANSAC, 5.0)
matchesMask = mask.ravel().tolist()
h, w = referenceImage.shape
corners = np.float32([[0, 0], [0, h - 1], [w - 1, h - 1], [w - 1, 0]]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
transformedCorners = cv2.perspectiveTransform(corners, homography)
sourceImageMarker = cv2.polylines(sourceImage, [np.int32(transformedCorners)], True,
255, 5, cv2.LINE_AA)
else:
print("Not enough matches are found - %d/%d" % (len(matches), MIN_MATCHES))
matchesMask = None
drawParameters = dict(matchColor=(0, 255, 0), singlePointColor=None,
matchesMask=matchesMask, flags=2)
result = cv2.drawMatches(referenceImage, referenceImagePts, sourceImageMarker,
sourceImagePts, matches, None, **drawParameters)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.imshow(result, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
camera_parameters = np.array([[1108.38916, 0, 513.796472],
[0, 1111.41724, 661.637500],
[0, 0, 1]])
obj = OBJ('/home/pacaep/Tests/OpenCvArDemo/models/fox.obj', swapyz = True)
def projection_matrix(camera_parameters, homography):
homography = homography * (-1)
rot_and_transl = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(camera_parameters), homography )
col_1 = rot_and_transl[:,0]
col_2 = rot_and_transl[:,1]
col_3 = rot_and_transl[:,2]
l = math.sqrt(np.linalg.norm(col_1, 2) * np.linalg.norm(col_2, 2))
rot_1 = col_1 / l
rot_2 = col_2 / l
translation = col_3 / l
c = rot_1 + rot_2
p = np.cross(rot_1, rot_2)
d = np.cross(c,p)
rot_1 = np.dot(c/np.linalg.norm(c,2) + d / np.linalg.norm(d,2), 1/math.sqrt(2))
rot_2 = np.dot(c/np.linalg.norm(c,2) - d / np.linalg.norm(d,2), 1/math.sqrt(2))
rot_3 = np.cross(rot_1, rot_2)
projection = np.stack((rot_1, rot_2, rot_3, translation)).T
return np.dot(camera_parameters, projection)
def render(img, obj, projection, model, color=False):
vertices = obj.vertices
scale_matrix = np.eye(3)*6
h,w = model.shape
for face in obj.faces:
face_vertices = face[0]
points = np.array([vertices[vertex -1] for vertex in face_vertices])
points = np.dot(points, scale_matrix)
points = np.array([[p[0] + w / 2, p[1] + h/2, p[2]] for p in points])
dst = cv2.perspectiveTransform(points.reshape(-1,1,3), projection)
imgpts = np.int32(dst)
cv2.fillConvexPoly(img, imgpts, (80, 217, 81))
return img
sourcePoints = np.float32([referenceImagePts[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1,1,2)
destinationPoints = np.float32([sourceImagePts[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1,1,2)
homography, _ = cv2.findHomography(sourcePoints,destinationPoints, cv2.RANSAC, 5.0)
matchesMask = mask.ravel().tolist()
h, w = referenceImage.shape
corners = np.float32([[0,0],[0,h-1],[w-1,h-1],[w-1,0]]).reshape(-1,1,2)
transformedCorners = cv2.perspectiveTransform(corners, homography)
frame = cv2.polylines(sourceImage, [np.int32(transformedCorners)], True, 255,3,cv2.LINE_AA)
projection = projection_matrix(camera_parameters, homography)
frame = render(frame, obj, projection, referenceImage, True)
plt.figure(figsize=(6,12))
plt.imshow(frame, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
camera_calibration.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
import glob
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 30, 0.001)
objp = np.zeros((9 * 13, 3), np.float32)
objp[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:13, 0:9].T.reshape(-1, 2)
obj_points = []
img_points = []
images = glob.glob("/home/pacaep/Tests/OpenCvArDemo/calibration_img/*.png")
i=0;
for fname in images:
img = cv2.imread(fname)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
size = gray.shape[::-1]
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (13, 9), None)
if ret:
obj_points.append(objp)
corners2 = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (5, 5), (-1, -1), criteria)
if [corners2]:
img_points.append(corners2)
else:
img_points.append(corners)
cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (13, 9), corners, ret)
i+=1;
cv2.imwrite('conimg'+str(i)+'.png', img)
cv2.waitKey(1500)
print(len(img_points))
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(obj_points, img_points, size, None, None)
print("ret:", ret)
print("mtx:\n", mtx)
print("dist:\n", dist)
print("rvecs:\n", rvecs)
print("tvecs:\n", tvecs )
print("-----------------------------------------------------")
img = cv2.imread(images[2])
h, w = img.shape[:2]
newcameramtx, roi = cv2.getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(mtx,dist,(w,h),1,(w,h))
print (newcameramtx)
print("------------------use undistort-------------------")
dst = cv2.undistort(img,mtx,dist,None,newcameramtx)
x,y,w,h = roi
dst1 = dst[y:y+h,x:x+w]
cv2.imwrite('calibresult.png', dst1)
print ("dst:", dst1.shape)
objloader_simple.py
class OBJ:
def __init__(self, filename, swapyz=False):
self.vertices = []
self.normals = []
self.texcoords = []
self.faces = []
material = None
for line in open(filename, "r"):
if line.startswith('#'): continue
values = line.split()
if not values: continue
if values[0] == 'v':
v = list(map(float, values[1:4]))
if swapyz:
v = v[0], v[2], v[1]
self.vertices.append(v)
elif values[0] == 'vn':
v = list(map(float, values[1:4]))
if swapyz:
v = v[0], v[2], v[1]
self.normals.append(v)
elif values[0] == 'vt':
self.texcoords.append(map(float, values[1:3]))
elif values[0] == 'f':
face = []
texcoords = []
norms = []
for v in values[1:]:
w = v.split('/')
face.append(int(w[0]))
if len(w) >= 2 and len(w[1]) > 0:
texcoords.append(int(w[1]))
else:
texcoords.append(0)
if len(w) >= 3 and len(w[2]) > 0:
norms.append(int(w[2]))
else:
norms.append(0)
self.faces.append((face, norms, texcoords))