医学图像配准综述学习
医学图像配准综述学习
目前针对医学图像配准的综述较少,笔者只找到了两篇:
一篇发表在《Machine Vision and Applications》-- Deep Learning in Medical Image Registration: A Survey
另一篇发表在《Physics in Medicine and Biology》-- Deep Learning in Medical Image Registration: A Review
其他review papers on deep learning in mediacal image anlysis:
1、J. Ker, L. P. Wang, J. Rao, and T. Lim. Deep learning applications in medical image analysis. Ieee Access, 6:9375–9389, 2018. ISSN 2169-3536. doi: 10.1109/Access.2017.2788044.
2、G. Litjens, T. Kooi, B. E. Bejnordi, A. A. A. Setio, F. Ciompi, M. Ghafoorian, J. A. W. M. van der Laak, B. van Ginneken, and C. I. Sanchez. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Medical Image Analysis, 42:60–88, 2017. ISSN 1361-8415. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005.
3、Y. Liu, X. Chen, Z. F.Wang, Z. J.Wang, R. K.Ward, and X. S.Wang. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects. Information Fusion, 42:158–173, 2018. ISSN 1566-2535. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.10.007.
4、A. Maier, C. Syben, T. Lasser, and C. Riess. A gentle introduction to deep learning in medical image processing. Zeitschrift Fur Medizinische Physik, 29(2):86–101, 2019. ISSN 0939-3889. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2018.12.003.
5、P. Meyer, V. Noblet, C. Mazzara, and A. Lallement. Survey on deep learning for radiotherapy. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 98:126–146, 2018. ISSN 0010-4825. doi: 10.1016/j. compbiomed.2018.05.018.
6、B. Sahiner, A. Pezeshk, L. M. Hadjiiski, X. S. Wang, K. Drukker, K. H. Cha, R. M. Summers, and M. L. Giger. Deep learning in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Medical Physics, 46(1): e1–e36, 2019. ISSN 0094-2405. doi: 10.1002/mp.13264.
7、Dinggang Shen, Guorong Wu, and Heung-Il Suk. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annual review of biomedical engineering, 19:221–248, 2017. ISSN 1545-42741523-9829. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044442.
8、Z. W. Zhang and E. Sejdic. Radiological images and machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 108:354–370, 2019. ISSN 0010-4825. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.02.017.
PMB这篇相对新且全面,故下面只对该论文的内容做总结。
由于计算机视觉领域更新很快,故学习综述信息相对滞后,建议直接看最新会议CV常用期刊及网址.
综述学习
医学图像配准的分类:
1、根据输入图像角度:单模态、多模态、不同病人、相同病人(同一天、不同天)配准。
2、根据变形模型角度:刚性、仿射、可变形。
3、根据部位:脑、肺、肝脏等。
4、根据图像维度:2D-2D、2D-3D、3D-2D、3D-3D配准。
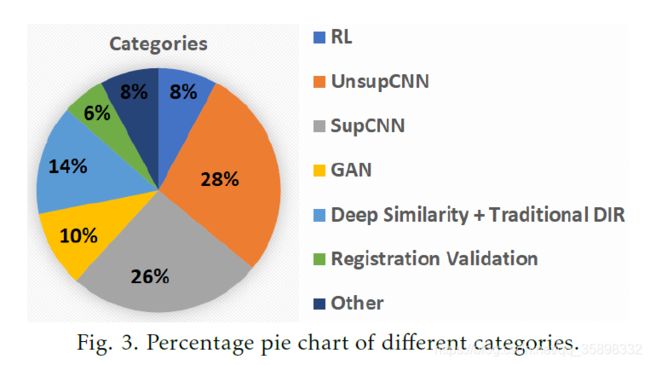
5、根据配准方法:RL-based、Deep-similarity-based、supervised、unsupervised、GAN、registration validation using DL、others.
DIR:Deformable image registration.
深度学习简介
1、CNN
2、U-net: U-net allows effective feature learning from a small number of training datasets
3、ResNet
4、DenseNet
5、RNN、LSTM
6、Reinforcement Learning (RL):a type of machine learning that focused on predicting the best actions to take given its current state in an environment. Q-learning、Bellman equation.
7、GAN
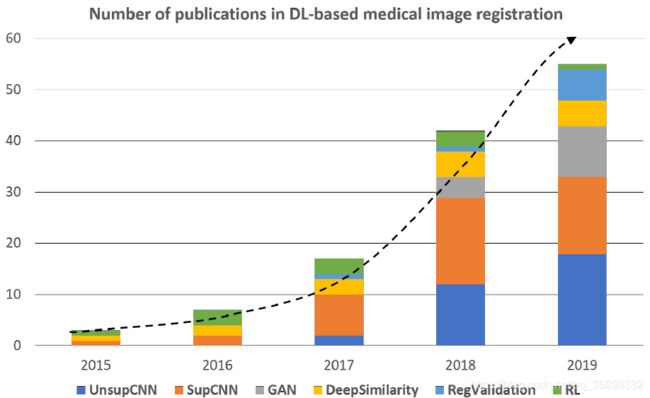
文章数量
深度学习在医学图像配准

DVF: Deformable vector field; SAM: Statistical appearance parameters; ADV: Adversarial; GT: Ground truth; DIR: Deformable image registration; TRE: Target registration error; RL: Reinforcement learning.
DL-based similarity measures
传统:intensity-based (SSD、MSD、(N)CC、(N)M, 一般传统相似度只适合单模态图像配准,MI可以用于多模态配准,一些MI的变种例如MIND效果可能更好一些。
DL-based similarity measures: 无固定形式,具体含义笔者还未深入理解,后续补充。一些DL-baed similarity metrics是非凸的,一些策略被提出来缓解非凸(比如优化一个凸的上确界)。
RL in medical image registration
结合RL和CNN将图像配准问题分解为一连串的分类任务。即寻找一系列动作,例如旋转、平移等来迭代的提高图像配准水平。
大多数RL-based methods进行的刚性配准。RL-based method 可以提高多模态配准的鲁棒性。
Supervised & Unsupervised
前面的方法都是迭代的,无监督和有监督的DL-based method是one-shot的,故可以减少配准时间。根据图3所示,目前有监督和无监督的方法比重加起来占到一半以上,且不断增加,以后研究的热点可能也是这两种。
Supervised: 需要Ground truth。一般可分为以下三类:
(1)Random transformation: 根据对齐好的image pair,任意给定已知的旋转,平移等变形。缺点是可能给定的变形不符合实际生物力学等情况。
(2)Traditional registration-generated transformations:用传统方法生成DVF作为GT。
(3)Model-based transformation generation:对于少量已知 GT DVF的image pair, 假定DVF参数的分布是高斯,再生成大量的合成的image pair。
FlowNet的GT生成用了上述三种方法。
Unsupervised: 例如VoxelMorph,更多用在单模态配准。
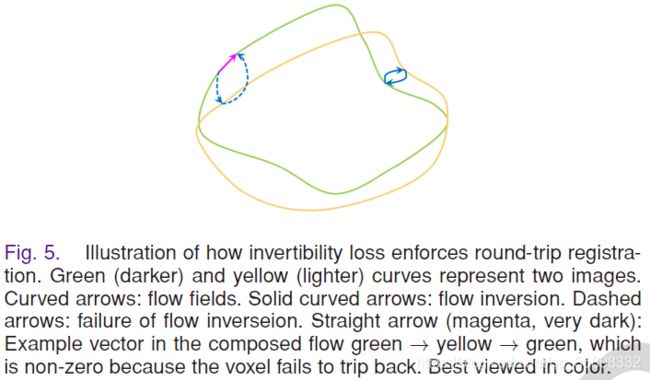
关于DVF Inverse Consistency的理解:笔者的理解是,对于registration应该是round-trip。对于一对未配准的图像I1、I2: I1->I2的DVF是f12,I2->I1的DVF是f21,那么f12·f21 = f21·f12=0,否则就是fails to trip back。
GAN in medical image registration
GAN网络在医学图像配准中主要有两个作用:
(1)对于多模态配准,可以先将多模态数据转为单模态数据,即做一个image translation,作为一种预处理,然后后面的流程与单模态配准类似。
(2)提供ADV loss。
疑问
文中多次提到图像配准是一个病态问题,笔者目前还未理解。