通信原理大作业--基于MATLAB的数字通信系统仿真设计
% 数字通信系统仿真,主要模块:信源、信源编码、信道编码,调制;信道;解调制、信道译码、信源译码、信宿;
% (1)信源:产生一个模拟信号或数字信号 --正弦信号
% (2)信源编码:任何一种压缩编码 --PCM-脉冲编码调制方式
% (3)信道编码:任何一种纠错码(奇偶校验,分组码,等); --线性分组码
% (4)调制: 任何一种调制(2ASK,2PSK,等); --2PSK-二进制相移键控法
% (5)信道:任何一种信道(理想,高斯,等); --高斯白噪声模拟信道噪声
% (6)解调制:解调(4); --相干解调法
% (7)信道译码:译(3); --错码率
% (8)信源译码:译(2)
% (9)信宿:得到一个一个模拟信号或数字信号,即:返原(1)
main-主函数
% (1)信源:产生一个模拟信号或数字信号
t=0:2*pi/399:2*pi; %1个周期-400个点
x=sin(2*t); %2个周期,一个200点
len=length(t); %400
% (2)信源编码:任何一种压缩编码
socode=Sourcecode(t,x); %len-400行-8列
% (3)信道编码:任何一种纠错码(奇偶校验,分组码,等); --线性分组码
chcode=Channelcode(t,socode); %len-400行-12列
% % (4)-(6)调制与解调
% %2PSK+高斯白噪声模拟信道噪声+相干解调法
code=Moanddemodulation1(t,chcode,len);
% (7)信道译码:译(3); --错码率
chdecode=Channeldecode(t,code,len);
% (8)信源译码:译(2)
desocoding=Sourcedecode(t,chdecode);
1.信源编码-量化编码-z=Sourcecode(t,x)
function z=Sourcecode(t,x) %信源编码
%2.量化
A=87.6;
y=quantificat(x,A);
%3.编码
z=a_pcm(y);
figure(1)
subplot(4,1,1);plot(t,x);
axis([0 2*pi -1.2 1.2]);
xlabel('时间');ylabel('幅度');title('原始信号');
subplot(4,1,2);plot(t,y)
axis([0 2*pi -1.2 1.2]);
xlabel('时间');ylabel('幅度');title('A律量化后的信号');
figure(2)
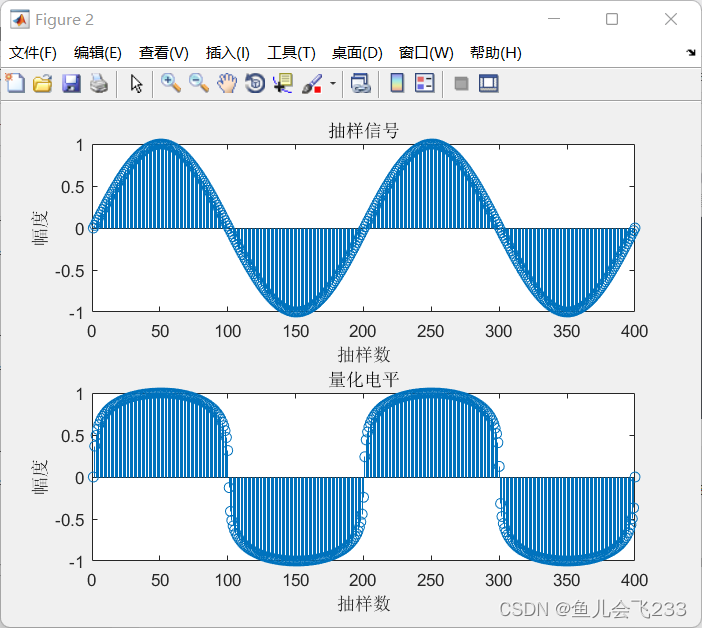
subplot(2,1,1);
stem(x);
xlabel('抽样数');ylabel('幅度');title('抽样信号');
subplot(2,1,2);
stem(y);
xlabel('抽样数');ylabel('幅度');title('量化电平');
end
1.1 量化-A率13折线-y=quantificat(x,A)
function y=quantificat(x,A) %量化
a=1/A; %0.0114
for i=1:length(x)
if x(i)>=0
if(x(i)<=a)
y(i)=(A*x(i))/(1+log(A));
else
y(i)=(1+log(A*x(i)))/(1+log(A));
end
else
if(x(i)>=-a)
y(i)=-(A*-x(i))/( 1+log(A));
else
y(i)=-(1+log(A*-x(i)))/(1+log(A));
end
end
end
end
1.2 编码-4位码字16份-z=a_pcm(y)
function z=a_pcm(y) %编码
paragraphcode(y); %极性-段落码
pieceofcode(y); %段内码
function paragraphcode(y)
for i=1:length(y)
I=y(i)*2048; %转换为量化单位
%>--1,<--0
if I>0
z(i,1)=1; %极性码-正-1
else
z(i,1)=0; %极性码-负-0
I=-I;
end
if I>128
z(i,2)=1;
if I>512
z(i,3)=1;
if I>1024
z(i,4)=1;
else
z(i,4)=0;
end
else
z(i,3)=0;
if I>256
z(i,4)=1;
else
z(i,4)=0;
end
end
else
z(i,2)=0;
if I>32
z(i,3)=1;
if I>64
z(i,4)=1;
else
z(i,4)=0;
end
else
z(i,3)=0;
if I>16
z(i,4)=1;
else
z(i,4)=0;
end
end
end
end
end
function pieceofcode(y)
for i=1:length(y)
I=y(i)*2048; %转换为量化单位
if I<0
I=-I;
end
parcode=z(i,2)*4+z(i,3)*2+z(i,4)+1; %段落位置序号
stalevel=2^(parcode+2); %该段落起始电平
zhishu=parcode-2;
if parcode-2<0
zhishu=0;
end
deta=2^zhishu; %量化间隔
if I>stalevel+8*deta
z(i,5)=1;
if I>stalevel+12*deta
z(i,6)=1;
if I>stalevel+14*deta
z(i,7)=1;
if I>stalevel+15*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
else
z(i,7)=0;
if I>stalevel+13*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
end
else
z(i,6)=0;
if I>stalevel+10*deta
z(i,7)=1;
if I>stalevel+11*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
else
z(i,7)=0;
if I>stalevel+9*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
end
end
else
z(i,5)=0;
if I>stalevel+4*deta
z(i,6)=1;
if I>stalevel+6*deta
z(i,7)=1;
if I>stalevel+7*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
else
z(i,7)=0;
if I>stalevel+5*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
end
else
z(i,6)=0;
if I>stalevel+2*deta
z(i,7)=1;
if I>stalevel+3*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
else
z(i,7)=0;
if I>stalevel+1*deta
z(i,8)=1;
else
z(i,8)=0;
end
end
end
end
end
end
end
2.信道编码-线性分组码-chcode=Channelcode(t,socode)
function A=Channelcode(t,x) %信道编码
%400-len行-12列
A=[];
k=8;r=4;n=12; %分组码各部分长度
IR=eye(r);IK=eye(k);
P=[1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1
0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1];
Q=P';
H=[P,IR]; %监督矩阵
G=[IK ,Q];%生成矩阵
for i=1:length(t)
A(i,:)=x(i,:)*G; %
for j=9:12
if mod(A(i,j), 2) == 0
A(i,j)=0;
else
A(i,j)=1;
end
end
end
end
3.调制与解调-2PSK与相干解调法-code=Moanddemodulation1(t,chcode,len)
function z=Moanddemodulation1(t,x,len) %调制与解调
%%x--len-400行-12列
g=x(:)'; %4800列--按x第一列所有...最后一列所有
f=6;
cp=[];mod=[];bit=[];
%之前一个元素-->400个元素,通过信道后取400个元素中较多的作为解码
for n=1:length(g);%调制过程 4800个元素
if g(n)==0;
cp1=ones(1,len); %400-len列个1
bit1=zeros(1,len);
else if g(n)==1;
cp1=-ones(1,len);%400-len列个-1
bit1=ones(1,len);
end
end
c=sin(f*2*t); %400-len个点
cp=[cp cp1]; %1920000列 x==0--100个1,x==1---100个-1
mod=[mod c]; %1920000列-一个周期sin数值
bit=[bit bit1];%1920000列 x==0--100个0,x==1---100个1
end
psk=cp.*mod; %1920000列
tz=awgn(psk,16);%信号 psk 中加入白噪声,信噪比为16
demod=2*mod.*tz;%psk 同步解调
%————带通-低通滤波器——%
Fp=600;%通带截止频率
Fs=1300;%阻带起始频率
Rp=3; %通带内波动(dB)即通带内所允许的最大衰减
Rs=20;%阻带内最小衰减(dB)
Fn=11025;%采样率
Ws=Fs/(Fn/2);%阻带起始角频率
Wp=Fp/(Fn/2); %通带截止角频率( rad/s)计算归一化角频率
[n,wn]=buttord(Wp, Ws,Rp,Rs);%计算阶数和截止频率
[b,a]=butter(n,wn);%计算H(z)
dmod1=filter(b,a,demod); %一维滤波器 1920000列19200*len
%——抽样判决———%
for m=1:len*length(g);
if dmod1(m)<0;
dmod(m)=1;
else if dmod1(m)>=0;
dmod(m)=0;
end
end
end
zer=0;one=0;
for i=0:length(g)-1
for j=1:len
if dmod(i*len+j)==0
zer=zer+1;
else if dmod(i*len+j)==1
one=one+1;
end
end
end
if zer>=one
z1(i+1)=0;
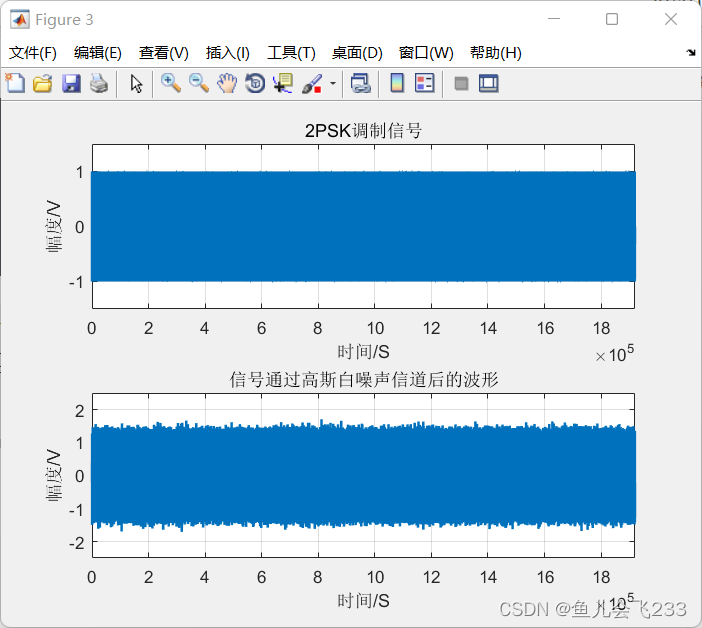
else if zerLinewidth',1.5);grid on;
title('2PSK调制信号');%标题显示
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
axis([0 len*length(g) -1.5 1.5]);
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(tz,'Linewidth',1.5);grid on
axis([0 len*length(g) -2.5 2.5]);
title('信号通过高斯白噪声信道后的波形');
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
figure(4)
subplot(2,1,1);
plot(psk,'Linewidth',1.5);grid on;
title('2PSK调制信号(局部)');%标题显示
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
axis([0 len/1600*length(g) -1.5 1.5]);
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(tz,'Linewidth',1.5);grid on
axis([0 len/1600*length(g) -1.5 1.5]);
title('信号通过高斯白噪声信道后的波形(局部)');
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
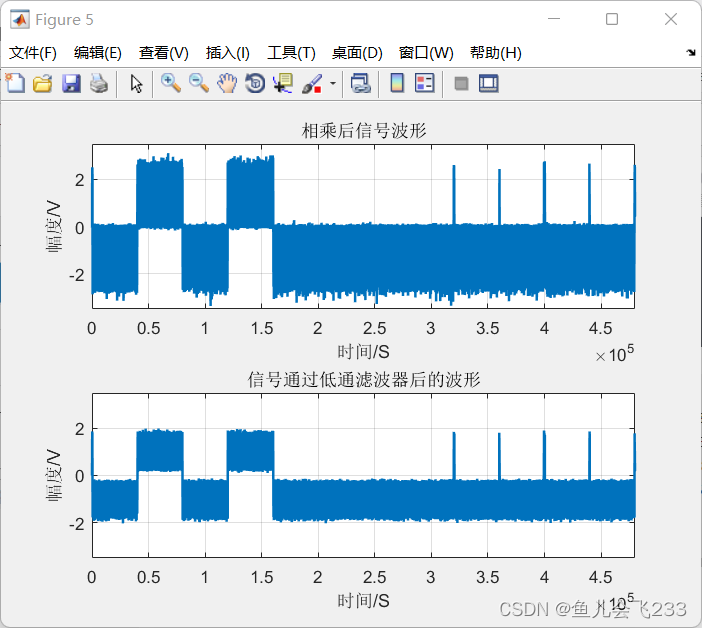
figure(5);
subplot(2,1,1);
plot(demod,'Linewidth',1.5);grid on
axis([0 100*length(g) -3.5 3.5]);title('相乘后信号波形');
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(dmod1,'Linewidth',1.5);grid on
axis([0 100*length(g) -3.5 3.5]);title('信号通过低通滤波器后的波形');
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
figure(6);
subplot(2,1,1);
plot(bit,'Linewidth',1.5);grid on;
title('二进制输入信号序列');%标题显示
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
axis([0 len*length(g) -0.2 1.2]);
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(dmod,'Linewidth',1.5);grid on
axis([0 len*length(g) -0.2 1.2]);title('2PSK解调波形');
xlabel('时间/S');ylabel('幅度/V');
end
4.信道译码-误码率-chdecode=Channeldecode(t,code,len)
function A=Channeldecode(t,x,len) %信道译码
error=0;
k=8;r=4;n=12; %分组码各部分长度
IR=eye(r);IK=eye(k);
P=[1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1
0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1];
Q=P';
H=[P,IR]; %监督矩阵
G=[IK ,Q];%生成矩阵
for i=1:length(t)
A(i,:)=x(i,1:8);
bh=H*x(i,:)';
for j=1:length(bh)
if mod(bh(j),2)==1
error=error+1;
break;
end
end
end
disp('错误数:')
error
disp('误码率')
error/len
end
5.信源译码-还原量化-desocoding=Sourcedecode(t,chdecode)
function ending=Sourcedecode(t,x) %信源译码
len=length(t);
for i=1:len
parcode=x(i,2)*4+x(i,3)*2+x(i,4)+1; %段落位置序号
stalevel=2^(parcode+2); %该段落起始电平
zhishu=parcode-2;
if parcode-2<0
zhishu=0;
end
deta=2^zhishu; %量化间隔
secode=x(i,5)*8+x(i,6)*4+x(i,7)*2+x(i,8); %段内位置序号
ID=stalevel+secode*deta+deta/2; %译码电平
z(i)=ID/2048; %实际电平
if x(i,1)==0
z(i)=-z(i);
end
end
%还原量化前电平
ending=quanreduction(z);
figure(1)
subplot(4,1,3);
plot(t,z);axis([0 2*pi -1.2 1.2]);
xlabel('时间');ylabel('幅度');title('译码电平');
subplot(4,1,4);
plot(t,ending);axis([0 2*pi -1.2 1.2]);
xlabel('时间');ylabel('幅度');title('信源译码');
end
5.1 还原量化前电平-ending=quanreduction(z)
```bash
function x=quanreduction(y) %还原量化前信号
A=87.6;
a=1/(1+log(A)); %
for i=1:length(y)
if y(i)>=0
if(y(i)<=a)
x(i)=y(i)*(1+log(A))/A;
else
x(i)=exp(y(i)*(1+log(A))-1)/A;
end
else
if(y(i)>=-a)
x(i)=-(-y(i)*(1+log(A)))/A;
else
x(i)=-exp(-y(i)*(1+log(A))-1)/A;
end
end
end
end
结果-图例: