【Swin Transformer原理和源码解析】Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows
目录
- 前言
- 一、动机和改进点
- 二、整体架构:SwinTransformer
- 三、输入设置:PatchEmbed
- 四、4个重复的Stage:BasicLayer
-
- 4.1、SwinTransformerBlock
-
- 4.1.1、创建mask
- 4.1.2、shift特征
- 4.1.3、为shift后的特征划分窗口
- 4.1.4、W-MSA VS SW-MSA
- 4.2、PatchMerging
- 五、总结
- 六、一些问题
-
- 6.1.为什么要W-MSA和SW-MSA混合使用?
- Reference
前言
ViT让Transformer第一次在视觉任务中暂露头角,而Swin Transfomer直接让Transformer在视觉任务中大放光彩,直接打败了当时的所有的CNN网络,一出来就直接是当时的Sota。现在的很多厉害的Transfomer变体都是Swin改进的,而且Swin Transformer这个网络在很多比赛上都会用它,分类、分割、检测基本上用它都不会差,我打的一个分类比赛就是用的它: 【记第一次kaggle比赛】PetFinder.my - Pawpularity Contest 宠物预测。当时打的时候是掉包的,两句话就创建了Model了,知其然不知所以然,这怎么行,所以今天有必要学习一下。
论文地址: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030.pdf
源码地址: https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer
这里我用的是b站大佬 霹雳吧啦Wz 改编后(相对源码作了微小改动,增加了多尺度训练)的代码:
WZMIAOMIAO
注释版本代码也同样分享到了我的Github:https://github.com/HuKai97/Classification-Annotations
一、动机和改进点
VIT为了让图像可以像词向量那样输入Encoder中,而且计算量还不能太大,就直接将图像切分成一个个小的Patch,再把每个Patch当成一个词向量,把所有Patch拼接起来送入Encoder,这样当然可以降低参数量和计算量,但是当图像变大,Patch数目变多,复杂度太大。还有没有更好的输入方式了呢?
VIT主要是改变了一下图片的输入,让Transformer的Encoder可以适用于图像任务中,但是对于整个模型的架构(之前讲LN提前了),VIT是没有做什么改进的,用的还是原始的Transformer中的Encoder(整个Encoder内部各个encoder变换,但是特征的shape是不变的)。那么原始的Transformer的Encoder模块真的就适用于图像任务吗,还有没有更好的Encoder结构?
所以总结下,ViT有两个问题:
- 尺度问题,数据集物体大大小小,但是整个Encoder过程特征尺度是不变的,效果肯定不好;
- 划分patch,再把整张图片的所有patch都输入Encoder中,计算量太大;
所以,Swin Transformer针对这两点做出了改进:
- Encode呈现金字塔形状。每过一个Encode图片shape变小,感受野在不停的增大,解决了尺度问题。
- 注意力机制放在一个窗口内部。不再把整张图片的所有patch都输入Encoder,而是将各个Patch单独的输入Encoder,解决了计算量太大的问题。
二、整体架构:SwinTransformer
- Patch Embeded:对输入图片 [bs,3,H_,W_] 进行处理。第一步:先经过Patch Partition,将图像划分为一个个的patch,每个patch是4x4x3大小(4x4Conv实现)得到一个 [bs,48,H_/4, W_/4] 大小的特征图;第二步:经过一个Linear Embedding层,进行Linear线性变换,得到 [bs, H_/4 * W_/4, C=96];(但是实际代码是通过一个4x4Conv s=4实现的,其实本质还是在学习参数,一样的)
- 经过4个stage:每个stage是若干个Swin Transformer Block + Patch Merging。前者计算相关性,后者进行采样,实现多尺度;最终经过4个stage后,特征下采样为 [bs,H_/32 * W_/32,8C=768];
- 分类:经过一个avgpool+flatten+Linear进行分类预测,最终得到 [bs,num_classes];
源码:
class SwinTransformer(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer
A PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030
"""
def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=96, depths=(2, 2, 6, 2), num_heads=(3, 6, 12, 24),
window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True,
drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, patch_norm=True,
use_checkpoint=False, **kwargs):
"""
patch_size: 每个patch的大小 4x4
in_chans: 输入图像的通道数 3
num_classes: 分类类别数 默认1000
embed_dim: 通过Linear Embedding后映射得到的通道数 也就是图片中的C 默认96
depths: 每个stage中重复swin-transformer block的次数 默认(2, 2, 6, 2)
num_heads: 每个stage中swin-transformer block的muti-head的个数 默认(3, 6, 12, 24)
window_size: 滑动窗口的大小 默认7x7
mlp_ratio: MLP中第一个全连接层Linear会将channel翻多少倍 默认4倍
qkv_bias: 在muti-head self-attention中是否使用偏置 默认使用True
drop_rate:
attn_drop_rate: 在muti-head self-attention中使用的drop rate
drop_path_rate: 在每个swin-transformer block中使用的drop rate 从0慢慢增加到0.1
norm_layer: LN
patch_norm:
use_checkpoint: 使用可以节省内存 默认不使用
"""
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes # 5
self.num_layers = len(depths) # 4
self.embed_dim = embed_dim # C = 96
self.patch_norm = patch_norm # True
# stage4输出特征矩阵的channels
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_layers - 1)) # 768 = 8C
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio # 4.0
# split image into non-overlapping patches
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
patch_size=patch_size, in_c=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate) # p=0
# stochastic depth
# [0.0, 0.00909090880304575, 0.0181818176060915, 0.027272727340459824, 0.036363635212183, 0.045454543083906174, 0.054545458406209946, 0.06363636255264282, 0.0727272778749466, 0.08181818574666977, 0.09090909361839294, 0.10000000149011612]
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule
# build layers/stages 4个
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
# 注意这里构建的stage和论文图中有些差异
# 这里的stage不包含该stage的patch_merging层,包含的是下个stage的
# stage1-3: Swin Transformer Block + Patch Merging
# Stage4: Swin Transformer Block
layers = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
self.layers.append(layers)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features) # LN(768)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity() # 分类头 768 -> 5
self.apply(self._init_weights) # 初始化
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
def forward(self, x):
"""
x: [bs, 3, H_, W_]
"""
# 1、Patch Partition + Linear Embedding
# [bs, 3, H_, W_] -> [bs, H_/4 * W_/4, C] -> [bs, H_/4 * W_/4, C] C=96
x, H, W = self.patch_embed(x) # H = H_/4 W = W_/4
x = self.pos_drop(x)
# 2、4 stage = 4 x (Swin Transformer Block x n + Patch Merging)
# x: [bs, H_/4 * W_/4, C] -> [bs, H_/8 * W_/8, 2C] -> [bs, H_/16 * W_/16, 4C] -> [bs, H_/32 * W_/32, 8C]
for layer in self.layers:
x, H, W = layer(x, H, W)
# 3、分类
x = self.norm(x) # LN(8C=768)
x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # [bs, H_/32 * W_/32, 8C] -> [bs, 8C, H_/32 * W_/32] -> [bs, 8C, 1]
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # [bs, 8C, 1] -> [bs, 8C]
x = self.head(x) # [bs, num_classes]
return x
三、输入设置:PatchEmbed
源码和论文有出入,这里直接使用一个4x4Conv s=4,实现下采样的过程。对输入图片 [bs,3,H_,W_]进行初步处理,得到一个[bs, H_/4 * W_/4, C=96]大小的特征图。源码如下:
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
"""
2D Image to Patch Embedding [bs, 3, H_, W_] -> [B, H_/4 * W_/4, C=96]
"""
def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_c=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
"""
patch_size: 每个patch的大小 4x4
in_c: 输入图像的channel 3
embed_dim: 96 = C
norm_layer: LN
"""
super().__init__()
patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size)
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.in_chans = in_c
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_c, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size) # 4x4Conv 下采样4倍 c:3->96
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
# x: [bs, 3, H_, W_]
_, _, H, W = x.shape
# padding
# 如果输入图片的H,W不是patch_size的整数倍,需要进行padding
pad_input = (H % self.patch_size[0] != 0) or (W % self.patch_size[1] != 0) # False
if pad_input:
# to pad the last 3 dimensions,
# (W_left, W_right, H_top,H_bottom, C_front, C_back)
x = F.pad(x, (0, self.patch_size[1] - W % self.patch_size[1],
0, self.patch_size[0] - H % self.patch_size[0],
0, 0))
# 1、Patch Partition
# 下采样patch_size倍 [bs, 3, H_, W_] -> [bs, C=96, H_/4, W_/4]
x = self.proj(x)
_, _, H, W = x.shape # H=H_/4 W=W_/4
# flatten: [B, C, H_/4, W_/4] -> [B, C, H_/4 * W_/4]
# transpose: [B, C, H_/4 * W_/4] -> [B, H_/4 * W_/4, C]
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x)
return x, H, W
四、4个重复的Stage:BasicLayer
每个stage都由若干个Swin Transformer Block 和 1个Patch Merging组成。
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
"""A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage."""
def __init__(self, dim, depth, num_heads, window_size,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False):
"""
dim: C = 96
depth: 重叠的Swin Transformer Block个数
num_heads: muti-head self-transformer的头数
window_size: 窗口大小7x7
mlp_ratio: MLP中第一个全连接层Linear会将channel翻多少倍 默认4倍
qkv_bias: 在muti-head self-attention中是否使用偏置 默认使用True
drop: patch_embed之后一般要接一个Dropout 但是默认是 0.0
attn_drop: 在muti-head self-attention中使用的drop rate 0.0
drop_path: list: depth 存放这个stage中depth个transformer block的drop rate
norm_layer: LN
downsample: Pathc Merging进行下采样
use_checkpoint: Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False
"""
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.depth = depth
self.window_size = window_size
self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint
self.shift_size = window_size // 2 # 3
# 调用depth个swin transformer block
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
SwinTransformerBlock(
dim=dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else self.shift_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer)
for i in range(depth)])
# patch merging layer
if downsample is not None:
self.downsample = downsample(dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer)
else:
self.downsample = None
def create_mask(self, x, H, W):
...
def forward(self, x, H, W):
# 1、depth个swin transformer block
# 因为每个stage中的特征图大小是不变的,所以每个block的mask大小是相同的 所以只需要创建一次即可
# [64,49,49] 64个网格 49x49每个网格中的每个位置(49个位置)对该网格中所有位置(49个位置)的注意力蒙版
attn_mask = self.create_mask(x, H, W) # [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
for blk in self.blocks:
blk.H, blk.W = H, W
if not torch.jit.is_scripting() and self.use_checkpoint:
x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x, attn_mask)
else:
# 默认执行 调用swin transformer block
x = blk(x, attn_mask)
# 2、下采样 Patch Merging
# 最后一个stage是None 不执行下采样
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x, H, W)
H, W = (H + 1) // 2, (W + 1) // 2 # 下采样 重新计算H W
return x, H, W
值得注意的是创建attention mask(create_mask)的步骤,这一步是下面SW-MSA和W-MSA的关键点,下面再详细讲解。
4.1、SwinTransformerBlock
4.1.1、创建mask
在SwinTransformerBlock中,主要是负责创建attention mask,只在shift windows muti-head attention中使用,主要是告诉我们当前位置和哪些其他位置是同属于一个windows的(因为之前有一步shift window的操作),同属于一个windows的位置的mask=0,不同属于一个位置的mask=-100。
这样到后面计算出attention之后,同一个windows位置的attention + mask再softmax值是不变的,但是不同windows位置的attention + mask(-100),再softmax值就趋近于0了。
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
"""A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage."""
...
def create_mask(self, x, H, W):
"""calculate attention mask for SW-MSA(shift window muti-head self-attention)
以第一个stage为例
x: [bs, 56x56, 96]
H: 56
W: 56
返回attn_mask: [64,49,49] 64个网格 49x49每个网格中的每个位置(49个位置)对该网格中所有位置(49个位置)的注意力蒙版
记录每个位置需要在哪些位置计算attention
"""
# 保证Hp和Wp是window_size的整数倍
Hp = int(np.ceil(H / self.window_size)) * self.window_size # 56
Wp = int(np.ceil(W / self.window_size)) * self.window_size # 56
# 拥有和feature map一样的通道排列顺序,方便后续window_partition
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, Hp, Wp, 1), device=x.device) # [1, 56, 56, 1]
# 对h和w先进行切片 划分为3个区域 0=(0,-7) (-7,-3) (-3,-1)
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
# 对3x3=9个区域进行划分 编号 0-8
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
# 将img_mask划分为一个个的窗口 64个7x7大小的窗口
# [1,56,56,1] -> [64,7,7,1] -> [64,7,7]
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # [nW, Mh, Mw, 1]
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size) # [nW, Mh*Mw]
# [nW, 1, Mh*Mw] - [nW, Mh*Mw, 1] -> [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]=[64,49,49]
# 数字相同的位置代表是同一个区域 我们就是要计算同一个区域的attention 相减之后为0的区域就是我们需要计算attention的地方
# 64个网格 49x49每个网格中的每个位置(49个位置)对该网格中所有位置(49个位置)的注意力蒙版
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
# 对于非零区域填上-100 这些区域是不需要计算attention的 所以在之后的softmax后就会为0
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
return attn_mask
这里涉及到划分窗口的操作:
def window_partition(x, window_size: int):
"""
将feature map按照window_size划分成一个个没有重叠的window
Args:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size (int): window size(M)
Returns:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = x.shape # 1 56 56 1
x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C) # [1,56,56,1] -> [1,8,7,8,7,1]
# permute: [B, H//Mh, Mh, W//Mw, Mw, C] -> [B, H//Mh, W//Mh, Mw, Mw, C]
# view: [B, H//Mh, W//Mw, Mh, Mw, C] -> [B*num_windows, Mh, Mw, C]
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C) # [1,8,7,8,7,1] -> [1,8,8,7,7,1] -> [64,7,7,1]
return windows
4.1.2、shift特征
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x, attn_mask):
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0: # SW-MSA
# 对x特征进行移动 0-shift_size列移动到最右侧 0-shift_size行移动到最下面
# -的就是从上往下 从左往右 +的就是从下往上 从右往左了
# 对应的attn_mask就是传入的attn_mask
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else: # W-MSA 不需要移动
shifted_x = x
attn_mask = None
最后计算完SW-MSA后需要将shift过的特征进行还原:
# 之前shift过windows 再还原 从下往上 从右往左 +
if self.shift_size > 0:
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = shifted_x
4.1.3、为shift后的特征划分窗口
# 为shifted_x划分窗口 与attn_mask划分的窗口对应 [bs,56,56,96] -> [512,7,7,96] 8x8xbs个7x7的窗口 x 96个通道
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # [nW*B, Mh, Mw, C]
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # [nW*B, Mh*Mw, C]=[512,49,96]
这里的划分窗口和上面mask的划分窗口一样,就不赘述。
4.1.4、W-MSA VS SW-MSA
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r"""W-MSA/SW-MSA
Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
"""
dim: C = 96
window_size: 窗口大小7x7
num_heads: muti-head self-transformer的头数
qkv_bias: 在muti-head self-attention中是否使用偏置 默认使用True
proj_drop: 在muti-head self-attention中使用的drop rate 0.0
"""
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # [7, 7]
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
# 初始化relative_position_bias_table
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # [2*7-1 * 2*7-1, num_heads]
# 1、生成绝对位置坐标索引
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0]) # tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1]) # tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
# coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w], indexing="ij"))
# [2, 7, 7] 7x7窗口的xy坐标
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w]))
# [2, 7, 7] -> [2, 49] 第一个是所有位置的行坐标 第二个是所有位置的列坐标
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1)
# 2、生成相对位置坐标索引
# [2, Mh*Mw, 1] - [2, 1, Mh*Mw] -> [2, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :]
# [2, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] -> [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw, 2]
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous()
# 3、将二元相对位置坐标索引转变成一元相对位置坐标索引
# 原始相对位置行/列标 = -6~6 + (window_size-1) -> 0~12
# 行标 + (2 * window_size - 1) -> 13~25
# 这时直接把行标 + 列标 直接把2D索引转换为1D索引 就不会出现(-1,0) (0,-1) 相加都是-1 无法区分的情况了
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # 行标 + (window_size-1)
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1 # 列标 + (window_size-1)
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1 # 行标 + (2 * window_size - 1)
# [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw, 2] -> [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] 行标 + 列标 直接转换为1元索引 与relative_position_bias_table一一对应
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1)
# 把relative_position_index放到缓存中 因为relative_position_index是固定值 不会变的 不需要修改
# 我们网络训练的其实是relative_position_bias_table中的参数 我们每次循环都从relative_position_bias_table中拿对应idx的值即可
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias) # 生成qkv 3倍dim = q+k+v
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop) # p=0.0
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim) # linear
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop) # linear dropout p=0
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02) # 初始化relative_position_bias_table参数
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1) # softmax层
def forward(self, x, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None):
"""
x: [bsx8x8, 49, 96] bsx 8x8个7x7大小的window size x96channel
mask: W-MSA和SW-MSA交替出现 None/[8x8,49,49] 记录8x8个7x7大小的window size 中 每个位置需要和哪些位置计算attention
=0的位置表示是需要计算attention的
Attention(Q,K,V) = SoftMax(Q*K的转置/scale + B)*V
"""
B_, N, C = x.shape # batch_size*num_windows=bsx8x8, Mh*Mw=7x7, total_embed_dim=96
# 生成qkv 和vit中的一样 和原始的transformer有区别 但是本质都是相同的 都是通过学习参数把输入的x映射到3个空间上
# qkv(): -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3 * total_embed_dim]
# reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# permute: -> [3, batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head] = [3,bsx8x8,3,7x7,32]
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
# 分别获得q k v
# [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head] = [bsx8x8,3,7x7,32]
q, k, v = qkv.unbind(0) # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
# 这里是先缩放再乘以k的转置 其实是一样的
# transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head, Mh*Mw]
# @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
# relative_position_bias_table.view: [Mh*Mw*Mh*Mw,nH] -> [Mh*Mw,Mh*Mw,nH]
# 生成相对位置偏置:生成相对位置index + 去relative_position_bias_table中去取相应的可学习的bias参数
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1)
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # [nH, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
# att + B
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
# softmax处理
if mask is not None:
# SW-MSA
# mask: [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]=[8x8,49,49] 记录8x8个7x7大小的window中每个位置需要和哪些位置计算attention
# =0的位置表示是需要计算attention的 不相同的区域位置是接近-100表示的
nW = mask.shape[0] # num_windows
# attn.view: [batch_size, num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
# mask.unsqueeze: [1, nW, 1, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
# 相同区域位置attn+0没有影响 不同区域位置attn+(-100) 再进行softmax 这个位置的attn就->0
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
# W-MSA
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# attn * v
# @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head]
# transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, total_embed_dim]
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
这个步骤和ViT中的其实差不多,只不过ViT是计算每个位置和所有位置的attention,而WindowAttention是按照窗口来计算每个位置和当前windows内所有位置的attention,计算量更小。
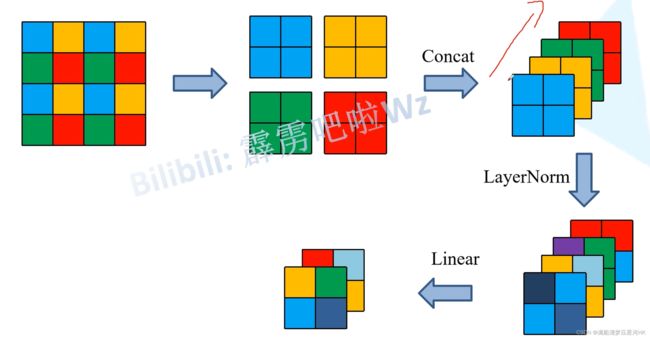
4.2、PatchMerging
这部分主要功能就是进行下采样,操作:每个一个元素取一个像素,有点类似YOLOv5中的Focus层。最后将4个特征拼接起来,再接一个Linear缩放通道。
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
r""" Patch Merging Layer. 下采样
输入[bs, H_/4 * W/4, C=96] -> 输出[bs, H_/8 * W/8, 2C]
"""
def __init__(self, dim, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim # 输入特征的channel = 96/192/384
self.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)
self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim) # LN
def forward(self, x, H, W):
"""
x: [bs, H_/4 * W/4, C=96]
"""
B, L, C = x.shape # B=8 C=96 L= H_/4*W/4
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
x = x.view(B, H, W, C) # [bs, H_/4 * W/4, C=96] -> [bs, H_/4, W_/4, C=96]
# padding
# 如果输入feature map的H,W不是2的整数倍,需要进行padding
pad_input = (H % 2 == 1) or (W % 2 == 1) # False
if pad_input: # 跳过
# to pad the last 3 dimensions, starting from the last dimension and moving forward.
# (C_front, C_back, W_left, W_right, H_top, H_bottom)
# 注意这里的Tensor通道是[B, H, W, C],所以会和官方文档有些不同
x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, 0, W % 2, 0, H % 2))
# 每隔一个像素取一个元素 有点像yolov5的focus层 最后一个特征 -> 4个下采样的特征
# [bs, H_/4, W_/4, C=96] -> 4 x [bs, H_/8, W_/8, C=96]
x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :]
x1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :]
x2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :]
x3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :]
# 4 x [bs, H_/8, W_/8, 96] -> [bs, H_/8, W_/8, 96*4] -> [bs, H_/8 * W_/8, 4*C]
x = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1)
x = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C)
x = self.norm(x) # LN
# Linear 将通道从4C -> 2C [bs, H_/8 * W_/8, C*4] -> [bs, H_/8 * W_/8, 2*C]
x = self.reduction(x)
return x
五、总结
为了解决ViT存在的问题:
- 尺度问题:数据集物体大大小小,但是整个Encoder过程特征尺度是不变的,效果肯定不好;
- 计算量大:划分patch,再把整张图片的所有patch都输入Encoder中,计算量太大;
改进点:
- Encode呈现金字塔形状。每过一个Stage对特征进行一次下采样,感受野在不停的增大,解决了尺度问题。所以Swin-Transformer不进适合分类任务,在下游检测、分割任务可以充分利用这种多尺度信息,检测效果很好;
- 注意力机制放在一个窗口内部。不再把整张图片的所有patch都输入Encoder,而是将各个Patch单独的输入Encoder,解决了计算量太大的问题。
关于第二点改进点还有很多的细节:
- 提出Window Muti-head Self-Attention(W-MSA):把输入特征划分为一个个的windows窗口,只计算每个位置和当前windows窗口的所有位置的相关性Attention,其他窗口的不关心,这样就大大减少了计算量了;
- W-MSA有一个问题,不同窗口完全不相关了,那不同窗口的位置之间不就没法交互了,所以作者又提出了Shift-Window Muti-head Self-Attention(SW-MSA)。
- 特征图Shift操作其实很简单,就是特征某些行列平移,但是Shift了之后就会产生更多的窗口,计算量还是增加了,作者为了解决这个问题,引入了Mask,仍然是使用原先的窗口划分方式,但是用mask记录每个位置属于哪个窗口,相同窗口的位置mask=0,不同窗口的位置mask=-100,那么最后再用计算好的attention + mask,再softmax。于是,相同窗口的attention不变,不同窗口的attention=0,完美解决所有问题;
- 作者还在WindowAttention中引入了relative_position_bias,使用Attention(Q,K,V) = SoftMax(Q*K的转置/scale + B)*V计算公式;
六、一些问题
6.1.为什么要W-MSA和SW-MSA混合使用?
我的理解:单独的W-MSA和单独的SW-MSA其实都是固定的位置窗口(SW-MSA是对固定的区域进行shift,但是如果单独只使用SW-MSA,那么不还是固定的窗口),这样使用还是会有不同窗口无法信息交互的问题,但是混合起来使用,才能真正的起到交互作用。
Reference
b站: Swin Transformer论文精读【论文精读】
b站: 12.1 Swin-Transformer网络结构详解
b站: 12.2 使用Pytorch搭建Swin-Transformer网络