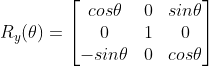机器人欧拉角转化为旋转矩阵
定义:欧拉角和旋转矩阵表示刚体在三维空间中的旋转,欧拉角(O,A,T)
形式:欧拉角形式可分为十二种,有XYZ,XZY,YZX,YXZ,ZXY,ZYX,XYX,XZX,YXY,YZY,ZXZ,ZYZ;其转换形式要根据机器人设定生成形式决定
公式:
如果旋转角度是绕X轴
如果旋转角度是绕Y轴
如果旋转角度是绕Z轴
下面以XYZ形式为例,R=Rz*RY*Rx,根据旋转轴确定旋转矩阵,最终的旋转矩阵是从结尾往前相乘。
代码(部分)
//机器人姿态欧拉角转化为旋转矩阵
void calibration::elur_translate_Rotation(Mat theta, Mat &R, string seq) {
theta /= (180 / CV_PI);
Mat R_X = (Mat_(3, 3) <<
1, 0, 0,
0, cos(theta.at(0, 0)), -sin(theta.at(0, 0)),
0, sin(theta.at(0, 0)), cos(theta.at(0, 0)));
Mat R_Y = (Mat_(3, 3) <<
cos(theta.at(0, 1)), 0, sin(theta.at(0, 1)),
0, 1, 0,
-sin(theta.at(0, 1)), 0, cos(theta.at(0, 1)));
Mat R_X2 = (Mat_(3, 3) <<
1,0,0,
0,cos(theta.at(0, 1)), -sin(theta.at(0, 1)),
0,sin(theta.at(0, 1)), cos(theta.at(0, 1)));
Mat R_Z = (Mat_(3, 3) <<
cos(theta.at(0, 2)), -sin(theta.at(0, 2)), 0,
sin(theta.at(0, 2)), cos(theta.at(0, 2)), 0,
0, 0, 1);
Mat R_Z1= (Mat_(3, 3) <<
cos(theta.at(0, 0)), -sin(theta.at(0, 0)),0,
sin(theta.at(0, 0)), cos(theta.at(0, 0)),0,
0,0,1);
if (seq == "zyx") R = R_X * R_Y * R_Z;
else if (seq == "yzx") R = R_X * R_Z * R_Y;
else if (seq == "zxy") R = R_Y * R_X * R_Z;
else if (seq == "yxz") R = R_Z * R_X * R_Y;
else if (seq == "xyz") R = R_Z * R_Y * R_X;
else if (seq == "xzy") R = R_Y * R_Z * R_X;
else if (seq == "zyz") R = R_Z1 * R_Y*R_Z;
else if (seq == "zxz") R = R_Z * R_X2*R_Z1;
else
{
cout << "Euler Angle Sequence string is wrong...";
}
}