数字滤波器的MATLAB与FPGA实现之读书笔记(一 混频器设计分析实例)
目录
第一章 设计语言及环境介绍
一、MATLAB 软件
1、MATLAB 常用信号产生函数演示示例
2、MATLAB 常用信号分析处理函数演示示例
3、快速傅里叶函数演示示例
4、混频器设计分析实例
第一章 设计语言及环境介绍
一、MATLAB 软件
1、MATLAB 常用信号产生函数演示示例
%E2_1_BasicWave.m文件源代码
%Matlab常用信号产生函数演示实例:编写一个M文件,依次产生均匀分布的随机序列、高斯白噪声随机序列、方波信号序列、三角波信号序列、正弦波信号序列,
%以及信噪比SNR为10dB的加性高斯白噪声正弦信号。
%产生方波、三角波及正弦波序列信号
%定义参数
Ps=10; %正弦信号功率为10dBW
Pn=1; %噪声信号功率为0dBW
f=100; %信号频率为100Hz
Fs=1000; %采样频率为1KHz
width=0.5; %函数SAWTOOTH()的尺度参数为0.5
duty=50; %函数SQUARE()的尺度参数为50
%产生信号
t=0:1/Fs:0.1;
c=2*pi*f*t;
sq=square(c,duty);%产生方波
tr=sawtooth(c,width);%产生三角波
si=sin(c);%产生正弦波
%产生随机序列信号
noi=rand(1,length(t));%产生均匀分布的随机序列
noise=randn(1,length(t));%产生高斯白噪声序列
%产生带有加性高斯白噪声的正弦信号序列
sin_noise=sqrt(2*Ps)*si+sqrt(Pn)*noise;
sin_noise=sin_noise/max(abs(sin_noise));%归一化处理
%画图
subplot(321); plot(t,noi); axis([0 0.1 -1.1 1.1]);
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8,'position',[0.08,-1.3,0]); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('均匀分布随机信号','fontsize',8);
subplot(322); plot(t,noise); axis([0 0.1 -max(abs(noise)) max(abs(noise))]);
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8,'position',[0.08,-3.2,0]); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('高斯白噪声信号','fontsize',8);
subplot(323); plot(t,sq); axis([0 0.1 -1.1 1.1]);
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8,'position',[0.08,-1.3,0]); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('方波信号','fontsize',8);
subplot(324); plot(t,tr); axis([0 0.1 -1.1 1.1]);
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8,'position',[0.08,-1.3,0]); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('三角波信号','fontsize',8);
subplot(325); plot(t,si); axis([0 0.1 -1.1 1.1]);
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8,'position',[0.08,-1.3,0]); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('正弦波信号','fontsize',8);
subplot(326); plot(t,sin_noise); axis([0 0.1 -1.1 1.1]);
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8,'position',[0.08,-1.3,0]); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('SNR=10dB的正弦波信号','fontsize',8);
2、MATLAB 常用信号分析处理函数演示示例
%E2_2_SignalProcess.m文件源代码
%Matlab常用信号分析处理函数演示实例:编写一个M文件,分别用filter及impz函数获取指定离散系统
%(b=[0.8 0.5 0.6],a=[1 0.2 0.4 -0.8])的单位抽样响应;用freqz函数获取系统的频率响应;分
%别用root及zplane函数获取系统的零极点图及增益。
L=128; %单位抽样序列的长度
Fs=1000; %采样频率为1KHz
b=[0.8 0.5 0.6]; %系统函数的分子系数向量
a=[1 0.2 0.4 -0.8]; %系统函数的分母系数向量
delta=[1 zeros(1,L-1)]; %生成长度为L的单位抽样序列
FilterOut=filter(b,a,delta); %filter函数获取单位抽样响应
ImpzOut=impz(b,a,L); %impz函数获取单位抽样响应
[h,f]=freqz(b,a,L,Fs); %freqz函数求频率响应
mag=20*log(abs(h))/log(10); %幅度转换成dB单位
ph=angle(h)*180/pi; %相位值单位转换
zr=roots(b) %求系统的零点,并显示在命令窗口
pk=roots(a) %求系统的极点,并显示在命令窗口
g=b(1)/a(1) %求系统的增益,并显示在命令窗口
%绘图
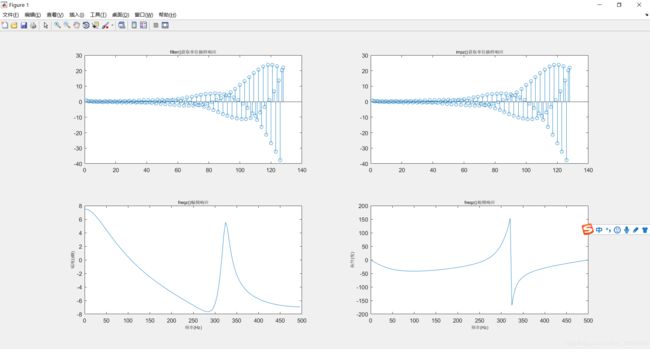
figure(1);
subplot(221);stem(FilterOut);
title('filter()获取单位抽样响应','fontsize',8);
subplot(222);stem(ImpzOut);
title('impz()获取单位抽样响应','fontsize',8);
subplot(223);plot(f,mag);
xlabel('频率(Hz)','fontsize',8);
ylabel('幅度(dB)','fontsize',8);
title('freqz()幅频响应','fontsize',8);
subplot(224);plot(f,ph);
xlabel('频率(Hz)','fontsize',8);
ylabel('相位(度)','fontsize',8);
title('freqz()相频响应','fontsize',8);
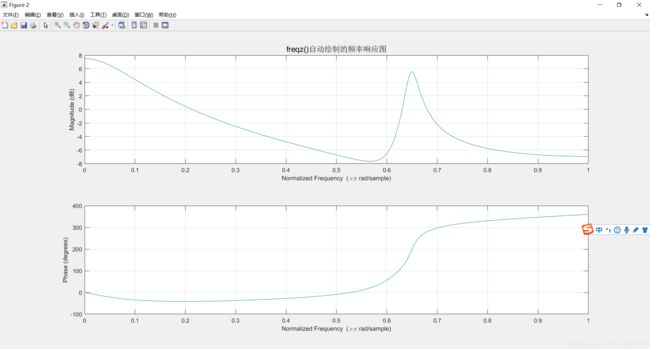
figure(2);
freqz(b,a); %用feqz函数绘制系统频率响应
title('freqz()自动绘制的频率响应图','fontsize',14);
figure(3);
zplane(b,a);%用zplane函数绘制系统零极点图
title('zplane()自动绘制的系统零极点图','fontsize',14);3、快速傅里叶函数演示示例
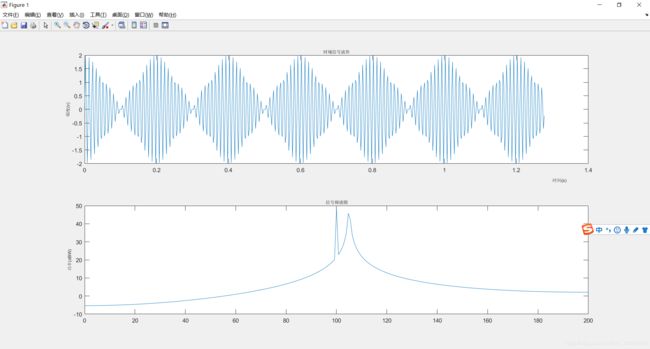
%E2_3_fft.m文件源代码
%快速傅立叶函数演示实例:编写一个M文件,产生频率为100Hz和105Hz正弦信号叠加后的信号,用fft函数
%对信号进行频率分析,要求在频率上能分辨出两种频率的正弦信号,分别绘出信号的时域及频域波形。
N=512; %数据长度
f1=100; %信号频率,单位为Hz
f2=105;
Fs=400; %采样频率,单位为Hz
t=0:1/Fs:1/Fs*(N-1); %产生时间序列
s=sin(2*pi*f1*t)+sin(2*pi*f2*t); %产生两个频率信号的叠加信号
f=fft(s,N); %计算傅立叶变换
f=20*log(abs(f))/log(10); %换算成dBW单位
ft=[0:(Fs/N):Fs/2]; %转换横坐标以Hz为单位
f=f(1:length(ft));
%绘图
subplot(211);plot(t,s);
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8,'position',[1.32,-2.5,0]); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('时域信号波形','fontsize',8);
subplot(212);plot(ft,f);
xlabel('频率(Hz)','fontsize',8,'position',[180,-34.38,0]); ylabel('功率(dBW)','fontsize',8);
title('信号频谱图','fontsize',8);4、混频器设计分析实例
在FPGA中实现一个简单的混频器电路,模拟仿真两个625 kHz正弦波信号相乘输出,其中625 kHz的本振信号由FPGA内部的数字控制振荡器(Numerically Controlled Oscillator, NCO)产生,625 kHz输入正弦波信号通过读取外部TXT文件(SinIn.txt)产生。文件 SinIn.txt由MATLAB仿真程序(E2_4_SimSigPrduce.m)产生,电路还需将混频后的信号滤除直流分量,并将滤除直流分量的1.25 MHz的正弦信号输出。
为便于在 FPGA 电路板上直观显示结果,将输入的625 kHz信号及输出的1.25 MHz信号均进仃625 000分频处理,开整形输出(过零检测),驱动电路板上的LED灯显示。设置信号采样频率为5 MHz,FPGA的系统时钟为5 MHz,输入数据为10 bit,混频输出数据为20 bit。FPGA目标芯片为Altera 的Cyclone IV系列芯片EP4CE15F17C8。
1、 MATLAB软件仿真
%E2_4_SimSigProduce.m程序清单
%设置系统参数
fi=625000; %输入信号的频率
fc=625000; %本振信号的频率
Fs=5000000; %采样频率
L=1024; %数据长度
N=10; %量化位数
%产生输入信号
t=0:1/Fs:(1/Fs)*(L-1); %产生采样频率的时间序列
theta=rand()*2*pi; %产生一个随机相位角度
si=sin(2*pi*fi*t+theta); %生成具有随机起始相位的正弦波输入信号
si=round(si*(2^(N-1)-1)); %10bit量化
%产生本振信号
sc=sin(2*pi*fc*t); %生成本振信号
sc=round(sc*(2^(N-1)-1)); %10bit量化
%仿真混频输出并画图
so=si.*sc; %混频器输出
sof=so-mean(so); %混频器滤除直流分量后输出
fso=abs(fft(so,L)); %求FFT变换的幅度值
%归一化处理
sc=sc/max(abs(sc));
si=si/max(abs(si));
so=so/max(abs(so));
sof=sof/max(abs(sof));
fso=fso/max(fso);
%转换成相对于原点对称的信号
fso=[fso(L/2+1:L),fso(1:L/2)];
%画图
m=[-L/2:1:(L/2-1)]*Fs/L*(10^(-6)); %生成频率坐标轴,单位为MHz
t=t*(10^6); %生成时间坐标轴,单位为?s
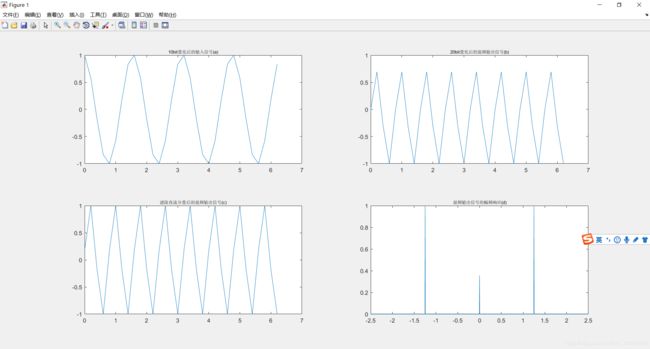
subplot(221);plot(t(1:32),si(1:32));
title('10bit量化后的输入信号(a)','fontsize',8);
subplot(222);plot(t(1:32),so(1:32));
title('20bit量化后的混频输出信号(b)','fontsize',8);
subplot(223);plot(t(1:32),sof(1:32));
title('滤除直流分量后的混频输出信号(c)','fontsize',8);
subplot(224);plot(m,fso);
title('混频输出信号的幅频响应(d)','fontsize',8);
%将生成的输入正弦信号数据,写入外部文本文件(SinIn.txt)中
f_s=si/max(abs(si));%归一化处理
Q_s=round(f_s*(2^(N-1)-1));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%新建文本文件前,必须建好文件存放的目录文件夹,否则出现提示信息:
%??? Error using ==> fprintf
%Invalid file identifier
fid=fopen('D:\Data\Matlab\My Programs\FPGA\SinIn.txt','w');
for k=1:length(Q_s)
B_s=dec2bin(Q_s(k)+(Q_s(k)<0)*2^N,N);
%k;
for j=1:N
if B_s(j)=='1'
tb=1;
else
tb=0;
end
fprintf(fid,'%d',tb);
end
fprintf(fid,'\r\n');
end
fprintf(fid,';');
fclose(fid);
2、 FPGA 设计与实现
1) FPGA 设计输入
创建NCO核:输出幅度位宽(Magnitude Precision)为10比特;时钟速率(Clock Rate)为50 MHz,输出信号频率(Desired Output Frequency)为625KHz;
编写顶层文件代码:Mixer.v
module Mixer (
rst,clk,din,
s_oc,dout,ldoc,ldmix);
input rst; //复位信号,高电平有效
input clk; //数据采样时钟/FPGA系统时钟,频率为5MHz
input [9:0] din; //输入的625KHz单频信号
output [9:0] s_oc; //本地OC输出的625KHz单频信号
output [19:0] dout; //输出混频滤波后的的1.25MHz单频信号
output ldoc; //对本地oc分频后的显示信号
output ldmix; //对混频输出信号分频后的显示信号
//实例化NCO IP核oc
wire reset_n,out_valid,clken;
wire [15:0] phi_inc_i;
wire [9:0] oc_sin;
assign reset_n = !rst; //oc的复位信号低电平有效
assign phi_inc_i = 16'd8192; //设置频率为625KHz
assign clken = 1'b1; //设置时钟允许信号始终有效
assign s_oc = oc_sin; //将oc的输出信号送至模块输出
oc U1(
.phi_inc_i(phi_inc_i),
.clk(clk),
.reset_n(reset_n),
.clken(clken),
.fsin_o(oc_sin),
.out_valid(out_valid));
//乘法运算实现混频输出
reg signed [19:0] mult;
wire signed [9:0] s_din;
wire signed [9:0] s_oc_sin;
assign s_din = din; //将乘数转换成有符号数运算
assign s_oc_sin = oc_sin; //将乘数转换成有符号数运算
always @(posedge clk or posedge rst)
if (rst)
mult <= 20'd0;
else
mult <= s_din * s_oc_sin;
//求均值:类似于求直流分量
reg signed [19:0] m1,m2,m3,m4,m5,m6,m7;
always @(posedge clk or posedge rst)
if (rst)
begin
m1 <= 20'd0;
m2 <= 20'd0;
m3 <= 20'd0;
m4 <= 20'd0;
m5 <= 20'd0;
m6 <= 20'd0;
m7 <= 20'd0;
end
else
begin
m1 <= mult;
m2 <= m1;
m3 <= m2;
m4 <= m3;
m5 <= m4;
m6 <= m5;
m7 <= m6;
end
wire signed [22:0] madd;
wire signed [19:0] mean,mt;
assign madd = mult+m1+m2+m3+m4+m5+m6+m7;
assign mean = madd[22:3];//舍弃2-0位,相当于除了8;
//滤出直流分量(均值)
assign mt = mult -mean;
assign dout = mt;
//625K分频输出,驱动LED灯显示ldoc
integer i_oc;
reg doc;
always @(posedge oc_sin[9] or posedge rst)
if (rst)
begin
i_oc <= 0;
doc <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
if (i_oc == 312500)
begin
doc <= !doc;
i_oc <= 0;
end
else
i_oc <= i_oc +1;
end
assign ldoc = doc;
//625K分频输出,驱动LED灯显示ldmix
integer i_dmix;
reg dmix;
always @(posedge mt[19] or posedge rst)
if (rst)
begin
i_dmix <= 0;
dmix <= 1'b0;
end
else
if (i_dmix == 312500)
begin
dmix <= !dmix;
i_dmix <= 0;
end
else
i_dmix <= i_dmix +1;
assign ldmix = dmix;
endmodule
③编写用户约束文件,用于引脚分配
#------------------GLOBAL--------------------#
set_global_assignment -name RESERVE_ALL_UNUSED_PINS "AS INPUT TRI-STATED"
set_global_assignment -name ENABLE_INIT_DONE_OUTPUT OFF
#复位引脚
set_location_assignment PIN_M1 -to rst
#时钟引脚
set_location_assignment PIN_R9 -to clk
#LED对应的引脚
set_location_assignment PIN_J1 -to ldoc
set_location_assignment PIN_J2 -to ldmix
#输入信号对应的引脚
set_location_assignment PIN_R8 -to din[0]
set_location_assignment PIN_E1 -to din[1]
set_location_assignment PIN_T8 -to din[2]
set_location_assignment PIN_M2 -to din[3]
set_location_assignment PIN_T9 -to din[4]
set_location_assignment PIN_A8 -to din[5]
set_location_assignment PIN_G5 -to din[6]
set_location_assignment PIN_G11 -to din[7]
set_location_assignment PIN_C14 -to din[8]
set_location_assignment PIN_E7 -to din[9]④ 时钟信号进行时序约束
2) 综合实现及仿真
完成综合实现后,工作过程区显示整个设计所占用的器件资源情况:
① 编写设计测试激励文件
在激励文件中将部分仿真结果数据写入外部的文本文件中,以方便使用MATLAB软件读取数据,并进一步分析仿真结果。
生成模块测试文件(Mixer.vt)
// Copyright (C) 1991-2012 Altera Corporation
// Your use of Altera Corporation's design tools, logic functions
// and other software and tools, and its AMPP partner logic
// functions, and any output files from any of the foregoing
// (including device programming or simulation files), and any
// associated documentation or information are expressly subject
// to the terms and conditions of the Altera Program License
// Subscription Agreement, Altera MegaCore Function License
// Agreement, or other applicable license agreement, including,
// without limitation, that your use is for the sole purpose of
// programming logic devices manufactured by Altera and sold by
// Altera or its authorized distributors. Please refer to the
// applicable agreement for further details.
// *****************************************************************************
// This file contains a Verilog test bench template that is freely editable to
// suit user's needs .Comments are provided in each section to help the user
// fill out necessary details.
// *****************************************************************************
// Generated on "05/17/2014 12:25:12"
// Verilog Test Bench template for design : Mixer
//
// Simulation tool : ModelSim-Altera (Verilog)
//
`timescale 1 ns/ 1 ns //设置仿真时间单位:ns
module Mixer_vlg_tst();
// constants
// general purpose registers
//reg eachvec;
// test vector input registers
reg clk;
reg [9:0] din;
reg rst;
// wires
wire [19:0] dout;
wire ldmix;
wire ldoc;
wire [9:0] s_oc;
// assign statements (if any)
Mixer i1 (
// port map - connection between master ports and signals/registers
.clk(clk),
.din(din),
.dout(dout),
.ldmix(ldmix),
.ldoc(ldoc),
.rst(rst),
.s_oc(s_oc)
);
parameter clk_period=200; //设置时钟信号周期(频率):5MHz
parameter clk_half_period=clk_period/2;
parameter data_num=800; //仿真数据长度
parameter time_sim=data_num*clk_period; //仿真时间
initial
begin
//设置时钟信号初值
clk=1;
//设置复位信号
rst=1;
#50 rst=0;
//设置仿真时间
#time_sim $finish;
//设置输入信号初值
din=10'd10;
end
//产生时钟信号
always
#clk_half_period clk=~clk;
//从外部TX文件(SinIn.txt)读入数据作为测试激励
integer Pattern;
reg [9:0] stimulus[1:data_num];
initial
begin
//文件必须放置在"工程目录\simulation\modelsim"路径下
$readmemb("SinIn.txt",stimulus);
Pattern=0;
repeat(data_num)
begin
Pattern=Pattern+1;
din=stimulus[Pattern];
#clk_period;
end
end
//将仿真数据dout写入外部TXT文件中(out.txt)
integer file_out;
initial
begin
//文件放置在"工程目录\simulation\modelsim"路径下
file_out = $fopen("out.txt");
if(!file_out)
begin
$display("could not open file!");
$finish;
end
end
wire rst_write;
wire signed [19:0] dout_s;
assign dout_s = dout; //将dout转换成有符号数据
assign rst_write = clk & (!rst);//产生写入时钟信号,复位状态时不写入数据
always @(posedge rst_write )
$fdisplay(file_out,"%d",dout_s);
//将仿真数据s_oc写入外部TXT文件中(oc.txt)
integer file_oc;
initial
begin
//文件放置在"工程目录\simulation\modelsim"路径下
file_oc = $fopen("oc.txt");
if(!file_oc)
begin
$display("could not open file!");
$finish;
end
end
wire signed [9:0] oc_s;
assign oc_s = s_oc;//将oc_s转换成有符号数据
always @(posedge rst_write)
$fdisplay(file_oc,"%d",oc_s);
endmodule
行为仿真用于检查程序的语法功能,时序仿真可真实地反映程序运行情况;两种仿真过程中的使用及操作方法本身没有区别,下面以行为仿真为例讲解仿真过程及ModelSim的使用方法。
用ModelSim 进行仿真时,由于测试激励文件中编写了将仿真测试数据dout、s_oc 写入外部文本文件的代码,程序将自动在指定的文本文件中按设计要求写入仿真结果数据。从ModelSim 的波形界面中虽然能查看信号仿真波形,但要想对数据进行进一步详细分析,如查看信号的频谱等,就显得无能为力了。这一部分工作正好用MATLAB 软件来完成。
3、MATLAB 对仿真数据进行分析
%E2_4_FpgaSim.m
%设置系统参数
% fi=625000; %输入信号的频率
% fc=625000; %本振信号的频率
Fs=5000000; %采样频率
L=256; %数据长度
%从文本文件中读取数据
fid=fopen('D:\Data\FPGA\Mixer\simulation\modelsim\out.txt');
[FpgaOut,count]=fscanf(fid,'%d',inf);
fclose(fid);
fid=fopen('D:\Data\FPGA\Mixer\simulation\modelsim\oc.txt');
[FpgaOc,count]=fscanf(fid,'%d',inf);
fclose(fid);
%count
%取出一段数据进行计算
FpgaOut=FpgaOut(1:L)';%读出的数据为列向量,转换成行向量
FpgaOc=FpgaOc(1:L)';
Fout=abs(fft(FpgaOut,L)); %求FFT变换的幅度值
%归一化处理
FpgaOut=FpgaOut/max(abs(FpgaOut));
FpgaOc=FpgaOc/max(abs(FpgaOc));
Fout=Fout/max(Fout);
Fout=[Fout(L/2+1:L),Fout(1:L/2)]; %转换成相对于原点对称的信号
%生成时间及频率坐标轴
t=[0:L-1]; %生成时间坐标轴,单位为us
t=t*(1/Fs)*(10^6);
m=[-L/2:1:(L/2-1)]*Fs/L*(10^(-6));%生成频率坐标轴,单位为MHz
%画图
subplot(311);plot(t(1:32),FpgaOc(21:52));
xlabel('时间(us)','fontsize',8,'position',[6.5,-1.2,0]); ylabel('幅度','fontsize',8);
title('DDS产生的本振信号(a)','fontsize',8);
subplot(312);plot(t(1:32),FpgaOut(21:52));
xlabel('时间(us)','fontsize',8,'position',[6.5,-1.2,0]); ylabel('幅度','fontsize',8);
title('FPGA混频输出信号(b)','fontsize',8);
subplot(313);plot(m,Fout);
xlabel('频率(MHz)','fontsize',8,'position',[2.3,-0.3,0]); ylabel('幅度','fontsize',8);
title('FPGA混频输出信号的幅频响应(c)','fontsize',8);