opencv c++ 霍夫直线检测
目的:在进行图像边缘提取后,将数据从平面坐标转换到极坐标空间,即完成了直线的信息提取。
1、原理
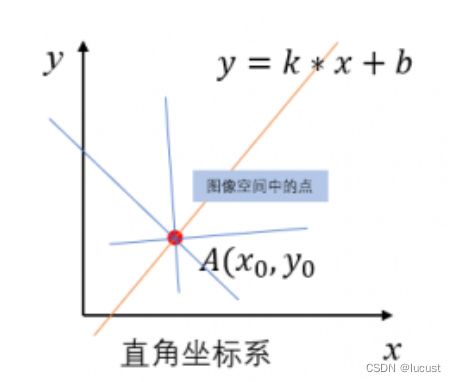
平面坐标系:通过之间的斜率k和截距b来确定一条直线。y = kx+b
极坐标系:通过半径r、角度θ来确定一条直线。r = xcosθ + y sinθ
注:在图像处理中,定义的平面坐标原点位于左上角,横轴为x,右方向为正方向,纵轴为y,下方向为正方向。
对于直线上任意一点![]() ,都有:
,都有:
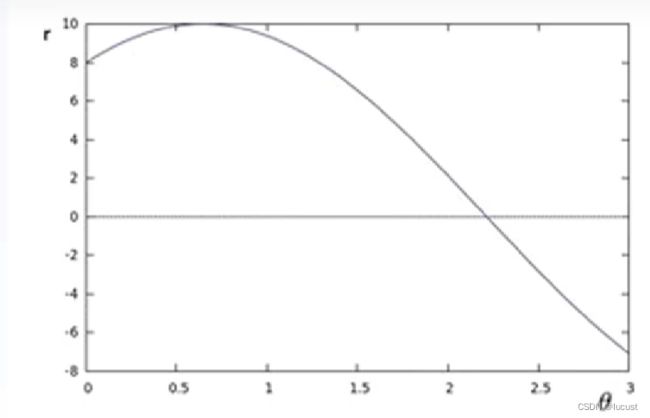
对于任意点![]() ,经过它的线有无数:
,经过它的线有无数:
将其通过公式![]() 转换为极坐标的形式,这些线就变成了θ-r坐标系上的一系列点:
转换为极坐标的形式,这些线就变成了θ-r坐标系上的一系列点:
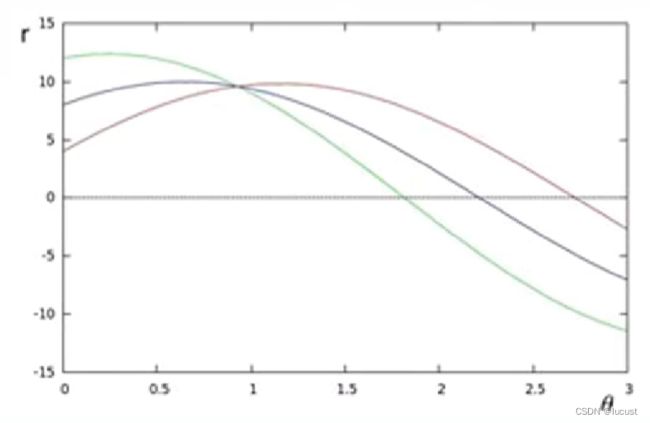
当引入其他点后,通过极坐标的曲线交点就能确定这些点所处的直线的r、θ信息。:
注:在实际算法中,会设定一个阈值T,当相交于同一点的点确定的曲线数量大于T时,才将这条被确定直线纳入统计,反之则排除它。
参考:(36条消息) 霍夫直线检测原理详解_秃头小苏的博客-CSDN博客_霍夫直线
2、API
OpenCV: Feature Detection
这两个计算直线的API的输出均为 vector
void cv::HoughLines ( InputArray image,
OutputArray lines,
double rho,
double theta,
int threshold,
double srn = 0,
double stn = 0,
double min_theta = 0,
double max_theta = CV_PI
)
void cv::HoughLinesP ( InputArray image,
OutputArray lines,
double rho,
double theta,
int threshold,
double minLineLength = 0,
double maxLineGap = 0
) image——二值化后的图像。
lines——输出的直线信息, vector/vector 。形式,分别储存距离、角度、累加值(用于判断该直线是否纳入统计)
rho——距离步长
theta ——角度步长
threshold ——累加值阈值,只统计交点累计格式大于该值的直线。
srn ——用于多阶霍夫变换, it is a divisor for the distance resolution rho . The coarse accumulator distance resolution is rho and the accurate accumulator resolution is rho/srn . If both srn=0 and stn=0 , the classical Hough transform is used. Otherwise, both these parameters should be positive.
stn ——用于多阶霍夫变换, it is a divisor for the distance resolution theta.
min_theta ——最小角度阈值
max_theta ——最大角度阈值。Must fall between min_theta and CV_PI.minLineLength Minimum line length. Line segments shorter than that are rejected.
maxLineGap ——当直线有间断时,认为互相间断的两条直线为同一直线的允许最大像素间隔数。
HoughLines 与 HoughLinesP 区别:
HoughLines 输出 vector
void QuickDemo::hough_line_detect(Mat& image)
{
GaussianBlur(image, image, Size(3, 3), 0);
Mat gray;
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat binary;
threshold(gray, binary, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU);
namedWindow("THRESH_OTSU", WINDOW_FREERATIO);
imshow("THRESH_OTSU", binary);
vector> contours;
vector hierachy;
findContours(binary, contours, hierachy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point());
//霍夫直线检测
vector lines;
HoughLines(binary, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180.0, 300, 0, 0);
//绘制检测出的直线
Point ptz1, ptz2;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); ++i) {
float rth = lines[i][0];//距离
float theta = lines[i][1];//角度
float accu = lines[i][2];//累加值
//cout << "rth:" << rth << ",theta:" << theta << ",accu:" << accu << endl;
double a = cos(theta);
double b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a * rth, y0 = b * rth;
ptz1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000 * (-b));
ptz1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000 * (a));
ptz2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000 * (-b));
ptz2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000 * (a));
//line(image, ptz1, ptz2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8);
//根据角度给线不同的颜色
int angle = round((theta / CV_PI) * 180);
if (rth > 0) {
line(image, ptz1, ptz2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8);
if(angle == 90)
line(image, ptz1, ptz2, Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2, 8);
if(angle < 1)
line(image, ptz1, ptz2, Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2, 8);
}
else
line(image, ptz1, ptz2, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8);
}
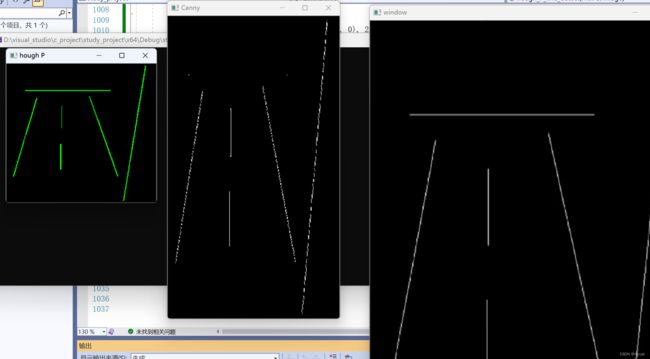
namedWindow("hough line", WINDOW_FREERATIO);
imshow("hough line", image);
} void QuickDemo::hough_P_line_detect(Mat& image)
{
Mat gray, binary;
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Canny(gray, binary, 80, 160, 3, false);
namedWindow("Canny", WINDOW_FREERATIO);
imshow("Canny", binary);
vector lines;
HoughLinesP(binary, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180.0, 80, 30, 10);
Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());
for (int i = 0; i < lines.size(); ++i) {
line(result, Point(lines[i][0], lines[i][1]), Point(lines[i][2], lines[i][3]), Scalar(0, 255, 0),2, 8);
}
namedWindow("hough P", WINDOW_FREERATIO);
imshow("hough P", result);
}