利用GPU训练模型的两种方法及Google colab的使用
本文主要介绍了利用GPU训练模型的两种方法,以及如何利用Google collab来进行训练模型。
文章目录
一、利用GPU训练模型
1 方法一
2 方法二
二、Google colab的使用
一、利用GPU训练模型
1 方法一
需要3个变量
网络模型
损失函数
数据(输入,输出)
像数据集,优化器都没有cuda()这个方法, 所以无法调用
方法一是调用.cuda() 方法, 再进行返回
具体代码如下:
# 网络模型转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
test = test.cuda() # 利用GPU训练模型, 调用.cuda() 方法, 返回损失函数转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
loss_fc = loss_fc.cuda()# 训练数据转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
imgs = imgs.cuda()
targets = targets.cuda()# 测试数据转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
imgs = imgs.cuda()
targets = targets.cuda()
其中:
if torch.cuda.is_available(): 的作用就是,如果你的电脑有gpu则可以利用gpu来训练模型,没有gpu则跳过,在cpu上运行。
我们这里,如果不写:if torch.cuda.is_available():
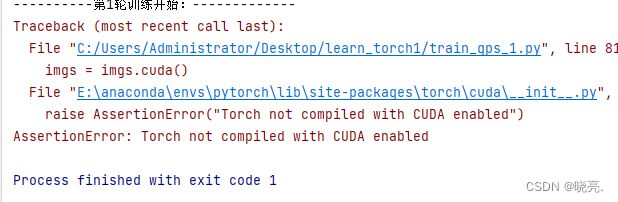
由于我的电脑没有gpu, 所以它会直接报错:
AssertionError: Torch not compiled with CUDA enabled
完整代码:
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import time
# from model import *
# 准备数据集
train_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset", train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
test_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset", train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 数据集的 length 长度
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
print("训练数据集的长度为:{}".format(train_data_size))
print("测试数据集的长度为:{}".format(test_data_size))
# 利用 DataLoader 来加载数据集
dataloder_train = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64, drop_last=False)
dataloder_test = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64, drop_last=False)
# 搭建神经网络
class Test(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Test, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=64),
nn.Linear(in_features=64, out_features=10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
# 创建网络模型
test = Test()
# 网络模型转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
test = test.cuda() # 利用GPU训练模型, 调用.cuda() 方法, 返回
# 损失函数
loss_fc = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 损失函数转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
loss_fc = loss_fc.cuda()
# 优化器
learning_rate = 1e-2 # 1e-2 = 1 * 10^(-2) = 1/100 = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(test.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 设置训练网络的一些参数
# 记录训练的次数
total_train_step = 0
# 记录测试的次数
total_test_step = 0
# 训练的轮数
epoch = 10
# 添加 tensorboard
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
# 获取开始的时间
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(epoch):
print("----------第{}轮训练开始:-------------".format(i+1))
# 训练步骤开始
test.train() #只对一些特殊的层起作用,代码中没有这些层也可以写上
for data in dataloder_train:
imgs, targets = data
# 训练数据转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
imgs = imgs.cuda()
targets = targets.cuda()
output_train = test(imgs)
loss = loss_fc(output_train, targets) # 获得损失值 loss
# 使用优化器优化模型
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 调用损失 loss,得到每一个参数的梯度
optimizer.step() #调用优化器 optimizer 对我们的参数进行优化
total_train_step = total_train_step + 1 #记录训练次数
if total_train_step % 100 == 0:
end_time = time.time() # 没运行100次结束的时间
print("{}秒".format(end_time - start_time)) # 模型运行需要多长时间
print("训练次数:{}, 损失值:{}".format(total_train_step, loss.item()))
# loss.item()与loss时有区别的,loss.item()返回的是数字
writer.add_scalar("train_loss", loss.item(), total_train_step) # 逢100的整数记录
# 测试步骤开始
test.eval() #只对一些特殊的层起作用,代码中没有这些层也可以写上
total_test_loss = 0
# 正确率
total_accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad(): # 表示在 with 里的代码,它的梯度就没有了,保证不会进行调优
for data in dataloder_test:
imgs, targets = data
# 测试数据转移到 gpu 上
if torch.cuda.is_available():
imgs = imgs.cuda()
targets = targets.cuda()
output_test = test(imgs)
loss = loss_fc(output_test, targets)
total_test_loss = total_test_loss + loss
accuracy = (output_test.argmax(1) == targets).sum() # 计算预测与实际 一致的个数
total_accuracy = total_accuracy + accuracy # 总的正确的个数
print("整体测试集的损失值:{}".format(total_test_loss.item()))
print("整体测试的正确率为:{}".format(total_accuracy/test_data_size))
writer.add_scalar("test_loss", total_test_loss, total_test_step)
writer.add_scalar("test_accuracy", total_accuracy/test_data_size, total_test_step)
total_test_step = total_test_step + 1
# 保存每一轮训练的模型
torch.save(test, "test_{}.pth".format(i)) #方法以保存
# 下面是方法二保存模型,将参数保存成字典型
# torch.save(test.state_dict(), "test_{}".format(i))
print("模型已保存")
writer.close()因为我的电脑没有gpu,所以程序就是在cpu上运行的。
输出结果(部分):
Files already downloaded and verified
Files already downloaded and verified
训练数据集的长度为:50000
测试数据集的长度为:10000
----------第1轮训练开始:-------------
10.618798971176147秒
训练次数:100, 损失值:2.286679744720459
21.838643789291382秒
训练次数:200, 损失值:2.284773111343384
33.31450796127319秒
训练次数:300, 损失值:2.24947190284729
44.44334530830383秒
训练次数:400, 损失值:2.1513400077819824
55.304163217544556秒
训练次数:500, 损失值:2.0602264404296875
66.77502679824829秒
训练次数:600, 损失值:2.056307792663574
可以看见,运行的速度还是比较慢的。如果在gpu上运行,速度会快不少。
2 方法二
方法二也需要3个变量
网络模型
损失函数
数据(输入,输出)
调用.to(device) 调用.to到一个设备上去,设备叫device
device = torch.device("cpu") 代表这个device是cpu,
如果 device = torch.device("cuda") 这代表它在gpu上运行
device = torch.device("cpu") 中 “ ”里的变量,决定模型在gpu上运行还是在cpu上运行
也可以:
torch.device("cuda") 这样写 这个等于torch.device("cuda: 0")
torch.device("cuda: 0") 这是调用第一张显卡的意思
torch.device("cuda: 1") 这是调用第二张显卡的 意思
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import time
# 调用训练的设备
device = torch.device("cpu")
# device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" )
# 准备数据集
train_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset", train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
test_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset", train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 数据集的 length 长度
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
print("训练数据集的长度为:{}".format(train_data_size))
print("测试数据集的长度为:{}".format(test_data_size))
# 利用 DataLoader 来加载数据集
dataloder_train = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64, drop_last=False)
dataloder_test = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64, drop_last=False)
# 搭建神经网络
class Test(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Test, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=64),
nn.Linear(in_features=64, out_features=10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
# 创建网络模型
test = Test()
test = test.to(device) # 方法二
# test.to(device)
# 损失函数
loss_fc = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss_fc = loss_fc.to(device) # 方法二
# loss_fc.to(device)
# 优化器
learning_rate = 1e-2 # 1e-2 = 1 * 10^(-2) = 1/100 = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(test.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 设置训练网络的一些参数
# 记录训练的次数
total_train_step = 0
# 记录测试的次数
total_test_step = 0
# 训练的轮数
epoch = 10
# 添加 tensorboard
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
# 获取开始的时间
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(epoch):
print("----------第{}轮训练开始:-------------".format(i+1))
# 训练步骤开始
test.train() #只对一些特殊的层起作用,代码中没有这些层也可以写上
for data in dataloder_train:
imgs, targets = data
imgs = imgs.to(device) # 方法二
targets = targets.to(device)
output_train = test(imgs)
loss = loss_fc(output_train, targets) # 获得损失值 loss
# 使用优化器优化模型
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 调用损失 loss,得到每一个参数的梯度
optimizer.step() #调用优化器 optimizer 对我们的参数进行优化
total_train_step = total_train_step + 1 #记录训练次数
if total_train_step % 100 == 0:
end_time = time.time() # 没运行100次结束的时间
print("{}秒".format(end_time - start_time)) # 模型运行需要多长时间
print("训练次数:{}, 损失值:{}".format(total_train_step, loss.item()))
# loss.item()与loss时有区别的,loss.item()返回的是数字
writer.add_scalar("train_loss", loss.item(), total_train_step) # 逢100的整数记录
# 测试步骤开始
test.eval() #只对一些特殊的层起作用,代码中没有这些层也可以写上
total_test_loss = 0
# 正确率
total_accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad(): # 表示在 with 里的代码,它的梯度就没有了,保证不会进行调优
for data in dataloder_test:
imgs, targets = data
imgs = imgs.to(device) # 方法二
targets = targets.to(device)
output_test = test(imgs)
loss = loss_fc(output_test, targets)
total_test_loss = total_test_loss + loss
accuracy = (output_test.argmax(1) == targets).sum() # 计算预测与实际 一致的个数
total_accuracy = total_accuracy + accuracy # 总的正确的个数
print("整体测试集的损失值:{}".format(total_test_loss.item()))
print("整体测试的正确率为:{}".format(total_accuracy/test_data_size))
writer.add_scalar("test_loss", total_test_loss, total_test_step)
writer.add_scalar("test_accuracy", total_accuracy/test_data_size, total_test_step)
total_test_step = total_test_step + 1
# 保存每一轮训练的模型
torch.save(test, "test_{}.pth".format(i)) #方法以保存
# 下面是方法二保存模型,将参数保存成字典型
# torch.save(test.state_dict(), "test_{}".format(i))
print("模型已保存")
writer.close()
注意:
(1) 调用训练的设备
device = torch.device("cpu")
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" )
这两行代码都可以,但是用第二种的较多
if torch.cuda.is_available() ,返回为true, 则返回 device = torch.device("cuda") 在gpu上运行 ,
若返回为false, 则返回 device = torch.device("cpu") 在cpu上运行
(2) 网络模型和损失函数调用.to(device)有两种写法
test = test.to(device)
test.to(device)
loss_fc = loss_fc.to(device)
loss_fc.to(device)
这两种写法都是对的,但是test.to(device)和loss_fc.to(device)这样写比较常见,不需要返回值
与之对比,数据(输入,输出) 则必须这样写:
imgs = imgs.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
二、Google colab的使用
在cpu运行的速度还是比较慢的。在gpu上运行,速度会快不少。
但是如果我们电脑上没有gpu,那 怎么用gpu运行呢?
谷歌为我们提供了应该免费的gpu可以使用,
登录 https://colab.research.google.com 这个网站,就可以直接使用,
注意,需要科学上网和登录google账号
这个网站很像jupyter
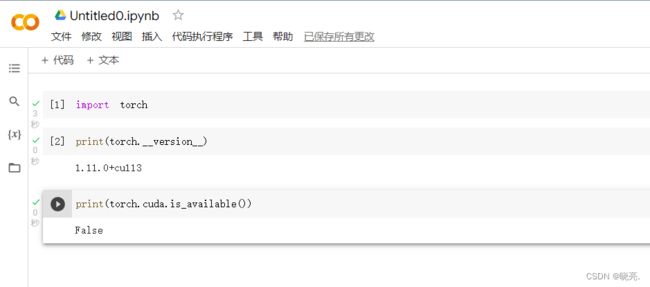
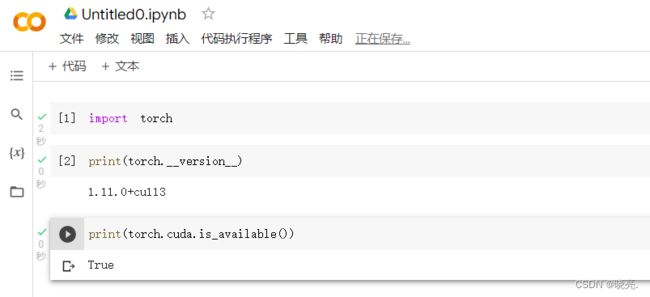
输入代码,可以查看是否正常gpu,
如果输入print(torch.cuda.is_available())
返回的是false
这时侯,只需要修改一下即可,
修改完成,输入上面的代码运行,
将上面的代码输入Google colab中,使用gpu运行,
结果如下:
训练数据集的长度为:50000
测试数据集的长度为:10000
----------第1轮训练开始:-------------
模型训练100次需要:4.819949626922607秒
训练次数:100, 损失值:2.296015501022339
模型训练100次需要:5.75621485710144秒
训练次数:200, 损失值:2.287379026412964
模型训练100次需要:6.697075128555298秒
训练次数:300, 损失值:2.2827587127685547
模型训练100次需要:7.62299370765686秒
训练次数:400, 损失值:2.236856460571289
模型训练100次需要:8.568002700805664秒
训练次数:500, 损失值:2.142932891845703
模型训练100次需要:9.562170505523682秒
训练次数:600, 损失值:2.0706043243408203
模型训练100次需要:10.492522954940796秒
训练次数:700, 损失值:2.0014054775238037
整体测试集的损失值:313.5710144042969
整体测试的正确率为:0.2870999872684479
模型已保存
可以看见运行的速度明显变快了。