知识图谱嵌入:TransE算法原理及代码详解
目录
KGE
TransE
TransE代码详解
KGE
知识图谱中,离散符号化的知识不能够进行语义计算,为帮助计算机对知识进行计算,解决数据稀疏性,可以将知识图谱中的实体、关系映射到低维连续的向量空间中,这类方法称为知识图谱嵌入(Knowledge Graph Embedding, KGE)。
TransE
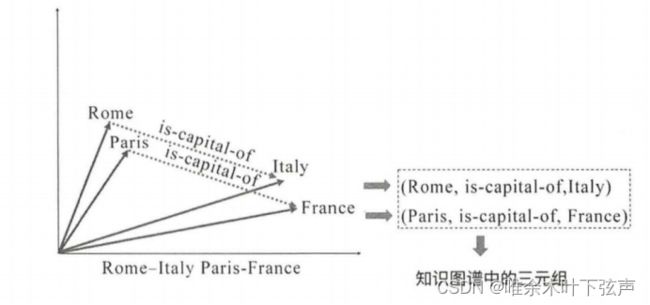
受到词向量中平移不变性的启发,TransE将关系的向量表示解释成头、尾实体向量之间的转移向量,算法简单而高效。并且在模型训练过程中,可以学习到一定的语义信息。其基本思想是,如果一个三元组(h, l, t)为真,那么向量空间中对应向量需要符合h + l ≈ t。例如:
vec(Rome) + vec(is-capital-of) ≈ vec(Italy)
vec(Paris) + vec(is-capital-of) ≈ vec(France)
据此可以对缺失的三元组(Beijing,is-capital-of,?)、(Beijing,?,China)、(?,is-capital-of,China)进行补全,即链接预测。
TransE是最早的翻译模型,后面还推出了TransD、TransR、TransH、TransA等等,换汤不换药,主要是对TransE进行改进和补充。
优点:
能够解决数据稀疏的难题,提升知识计算的效率。
能够自动捕捉推理特征,无须人工设计。
算法简单,学习的参数少,计算复杂度低。
缺点:
无法有效处理一对多、多对一、多对多、自反等复杂关系。
仅考虑一跳关系,忽略了长距离的隐关系。
嵌入模型不能快速收敛。
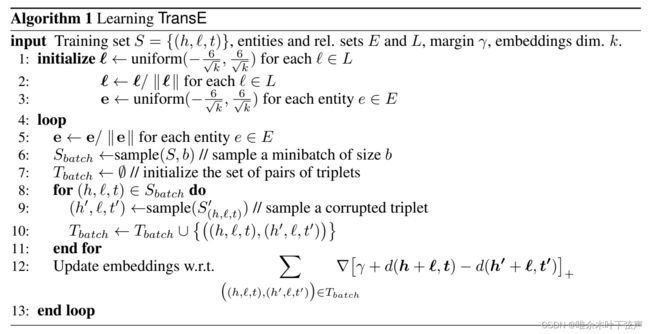
伪代码:
输入:训练集![]() ,实体集E,关系集L,margin值γ,嵌入向量维度k
,实体集E,关系集L,margin值γ,嵌入向量维度k
2: 对于每个关系向量![]() ← 除以自身的L2范数
← 除以自身的L2范数
4:循环:
5: 对于每个实体向量![]() ← 除以自身的L2范数
← 除以自身的L2范数
6: 从训练集S中取出数量为b的样本作为一个![]()
7: 初始化三元组集合![]() 为一个空列表
为一个空列表
8: 遍历:![]() ,执行
,执行
9: 替换正确三元组的头实体或者尾实体构造负样本![]() 或
或![]()
10: 将正样本三元组和负样本三元组都放在![]() 列表中
列表中
11: 遍历结束
12: 根据梯度下降更新实体、关系向量
13:循环结束
TransE代码详解
1、加载数据
传入训练集![]() ,实体集E,关系集L这三个数据文件的地址
,实体集E,关系集L这三个数据文件的地址
返回三个列表:实体,关系,三元组。(其中实体、关系都以id表示)
import codecs
import numpy as np
import copy
import time
import random
def dataloader(file1, file2, file3):
print("load file...")
entity = []
relation = []
entities2id = {}
relations2id = {}
with open(file2, 'r') as f1, open(file3, 'r') as f2:
lines1 = f1.readlines()
lines2 = f2.readlines()
for line in lines1:
line = line.strip().split('\t')
if len(line) != 2:
continue
entities2id[line[0]] = line[1]
entity.append(line[1])
for line in lines2:
line = line.strip().split('\t')
if len(line) != 2:
continue
relations2id[line[0]] = line[1]
relation.append(line[1])
triple_list = []
with codecs.open(file1, 'r') as f:
content = f.readlines()
for line in content:
triple = line.strip().split("\t")
if len(triple) != 3:
continue
h_ = entities2id[triple[0]]
r_ = relations2id[triple[1]]
t_ = entities2id[triple[2]]
triple_list.append([h_, r_, t_])
print("Complete load. entity : %d , relation : %d , triple : %d" % (
len(entity), len(relation), len(triple_list)))
return entity, relation, triple_list
2、传参
传入实体id列表entity,关系id列表relation,三元组列表triple_list,向量维度embedding_dim=50,学习率lr=0.01,margin(正负样本三元组之间的间隔修正),norm范数,loss损失值。
class TransE:
def __init__(self, entity, relation, triple_list, embedding_dim=50, lr=0.01, margin=1.0, norm=1):
self.entities = entity
self.relations = relation
self.triples = triple_list
self.dimension = embedding_dim
self.learning_rate = lr
self.margin = margin
self.norm = norm
self.loss = 0.03、初始化
即伪代码中的步骤1-3。
将实体id列表、关系id列表转变为{实体id:实体向量}、{关系id:关系向量}这两个字典。
class TransE:
def data_initialise(self):
entityVectorList = {}
relationVectorList = {}
for entity in self.entities:
entity_vector = np.random.uniform(-6.0 / np.sqrt(self.dimension), 6.0 / np.sqrt(self.dimension),self.dimension)
entityVectorList[entity] = entity_vector
for relation in self.relations:
relation_vector = np.random.uniform(-6.0 / np.sqrt(self.dimension), 6.0 / np.sqrt(self.dimension),self.dimension)
relation_vector = self.normalization(relation_vector)
relationVectorList[relation] = relation_vector
self.entities = entityVectorList
self.relations = relationVectorList
def normalization(self, vector):
return vector / np.linalg.norm(vector)4、训练过程
即伪代码中的步骤4-13。
nbatches=100,即数据集分为100个batch依次训练,每个batch的样本数量即batch_size。epochs=1,即完整跑完100个batch的次数。
首先对实体向量进行归一化。
对于每一个batch,随机采样batch_size数量的三元组作为![]() ,即代码中的batch_samples。
,即代码中的batch_samples。
初始化三元组集合![]() 为一个空列表。
为一个空列表。
对于batch_samples中的每一个样本,随机替换头实体或者尾实体生成负样本三元组。
其中,while corrupted_sample[0] == sample[0]是一个过滤正样本三元组的过程,避免从实体集中采样的实体仍是原实体。不过,此处严格来说应使用while corrupted_sample in self.triples,防止采样的实体h2虽然不是原实体h1,但该三元组仍是正样本(即(h1,l,t)和(h2,l,t)都在三元组列表中,都成立)。但是这句代码需要遍历整个三元组列表,会使训练时间增加10倍,故将其简化。
将正样本和负样本三元组都放入![]() 列表中。
列表中。
调用update_triple_embedding函数,计算这一个batch的损失值,根据梯度下降法更新向量,然后再进行下一个batch的训练。
所有的100个batch训练完成后,将训练好的实体向量、关系向量输出到out_file_title目录下(为空,代表保存在当前目录)
class TransE:
def training_run(self, epochs=1, nbatches=100, out_file_title = ''):
batch_size = int(len(self.triples) / nbatches)
print("batch size: ", batch_size)
for epoch in range(epochs):
start = time.time()
self.loss = 0.0
# Normalise the embedding of the entities to 1
for entity in self.entities.keys():
self.entities[entity] = self.normalization(self.entities[entity]);
for batch in range(nbatches):
batch_samples = random.sample(self.triples, batch_size)
Tbatch = []
for sample in batch_samples:
corrupted_sample = copy.deepcopy(sample)
pr = np.random.random(1)[0]
if pr > 0.5:
# change the head entity
corrupted_sample[0] = random.sample(self.entities.keys(), 1)[0]
while corrupted_sample[0] == sample[0]:
corrupted_sample[0] = random.sample(self.entities.keys(), 1)[0]
else:
# change the tail entity
corrupted_sample[2] = random.sample(self.entities.keys(), 1)[0]
while corrupted_sample[2] == sample[2]:
corrupted_sample[2] = random.sample(self.entities.keys(), 1)[0]
if (sample, corrupted_sample) not in Tbatch:
Tbatch.append((sample, corrupted_sample))
self.update_triple_embedding(Tbatch)
end = time.time()
print("epoch: ", epoch, "cost time: %s" % (round((end - start), 3)))
print("running loss: ", self.loss)
with codecs.open(out_file_title +"TransE_entity_" + str(self.dimension) + "dim_batch" + str(batch_size), "w") as f1:
for e in self.entities.keys():
f1.write(e + "\t")
f1.write(str(list(self.entities[e])))
f1.write("\n")
with codecs.open(out_file_title +"TransE_relation_" + str(self.dimension) + "dim_batch" + str(batch_size), "w") as f2:
for r in self.relations.keys():
f2.write(r + "\t")
f2.write(str(list(self.relations[r])))
f2.write("\n")5、梯度下降
首先调用deepcopy函数深拷贝实体和关系向量,取出实体和关系id分别对应的向量,根据L1范数或L2范数计算得分函数。
L1范数计算得分:np.sum(np.fabs(h + r - t))
L2范数计算得分:np.sum(np.square(h + r - t))
再根据以下公式计算损失值loss:( ![]() 即margin值)
即margin值)
L2范数根据以下公式计算梯度:
L1范数的梯度向量中每个元素为-1或1。
最后根据梯度对实体、关系向量进行更新和归一化。
class TransE:
def update_triple_embedding(self, Tbatch):
copy_entity = copy.deepcopy(self.entities)
copy_relation = copy.deepcopy(self.relations)
for correct_sample, corrupted_sample in Tbatch:
correct_copy_head = copy_entity[correct_sample[0]]
correct_copy_tail = copy_entity[correct_sample[2]]
relation_copy = copy_relation[correct_sample[1]]
corrupted_copy_head = copy_entity[corrupted_sample[0]]
corrupted_copy_tail = copy_entity[corrupted_sample[2]]
correct_head = self.entities[correct_sample[0]]
correct_tail = self.entities[correct_sample[2]]
relation = self.relations[correct_sample[1]]
corrupted_head = self.entities[corrupted_sample[0]]
corrupted_tail = self.entities[corrupted_sample[2]]
# calculate the distance of the triples
if self.norm == 1:
correct_distance = norm_l1(correct_head, relation, correct_tail)
corrupted_distance = norm_l1(corrupted_head, relation, corrupted_tail)
else:
correct_distance = norm_l2(correct_head, relation, correct_tail)
corrupted_distance = norm_l2(corrupted_head, relation, corrupted_tail)
loss = self.margin + correct_distance - corrupted_distance
if loss > 0:
self.loss += loss
correct_gradient = 2 * (correct_head + relation - correct_tail)
corrupted_gradient = 2 * (corrupted_head + relation - corrupted_tail)
if self.norm == 1:
for i in range(len(correct_gradient)):
if correct_gradient[i] > 0:
correct_gradient[i] = 1
else:
correct_gradient[i] = -1
if corrupted_gradient[i] > 0:
corrupted_gradient[i] = 1
else:
corrupted_gradient[i] = -1
correct_copy_head -= self.learning_rate * correct_gradient
relation_copy -= self.learning_rate * correct_gradient
correct_copy_tail -= -1 * self.learning_rate * correct_gradient
relation_copy -= -1 * self.learning_rate * corrupted_gradient
if correct_sample[0] == corrupted_sample[0]:
# if corrupted_triples replaces the tail entity, the head entity's embedding need to be updated twice
correct_copy_head -= -1 * self.learning_rate * corrupted_gradient
corrupted_copy_tail -= self.learning_rate * corrupted_gradient
elif correct_sample[2] == corrupted_sample[2]:
# if corrupted_triples replaces the head entity, the tail entity's embedding need to be updated twice
corrupted_copy_head -= -1 * self.learning_rate * corrupted_gradient
correct_copy_tail -= self.learning_rate * corrupted_gradient
# normalising these new embedding vector, instead of normalising all the embedding together
copy_entity[correct_sample[0]] = self.normalization(correct_copy_head)
copy_entity[correct_sample[2]] = self.normalization(correct_copy_tail)
if correct_sample[0] == corrupted_sample[0]:
# if corrupted_triples replace the tail entity, update the tail entity's embedding
copy_entity[corrupted_sample[2]] = self.normalization(corrupted_copy_tail)
elif correct_sample[2] == corrupted_sample[2]:
# if corrupted_triples replace the head entity, update the head entity's embedding
copy_entity[corrupted_sample[0]] = self.normalization(corrupted_copy_head)
# the paper mention that the relation's embedding don't need to be normalised
copy_relation[correct_sample[1]] = relation_copy
# copy_relation[correct_sample[1]] = self.normalization(relation_copy)
self.entities = copy_entity
self.relations = copy_relation6、__main__
if __name__ == '__main__':
# file1 = "FB15k\\train.txt"
# file2 = "FB15k\\entity2id.txt"
# file3 = "FB15k\\relation2id.txt"
file1 = "WN18\\wordnet-mlj12-train.txt"
file2 = "WN18\\entity2id.txt"
file3 = "WN18\\relation2id.txt"
entity_set, relation_set, triple_list = dataloader(file1, file2, file3)
transE = TransE(entity_set, relation_set, triple_list, embedding_dim=50, lr=0.01, margin=1.0, norm=2)
transE.data_initialise()
transE.training_run(out_file_title="WN18_")参考:
代码来自于:论文笔记(一):TransE论文详解及代码复现 - 知乎,点击完整代码可下载代码。