【NIPS 2020】Self-paced Contrastive Learning with Hybrid Memory for Domain Adaptive Object Re-ID
方法概述
1,提出一种创新的带有混合内存的自我进度(self-paced)对比学习框架。 其中,混合内存 动态生成 源域类级、 目标域聚类级和 无聚类实体集 的监督信号。
2,self-paced 方法可以生成更加可信的聚类来 精炼混合内存和 学习目标。
文章目录
- 方法概述
- 内容概要
-
- 工作概述
- 成果概述
- 方法详解
-
- 方法框架
- 算法描述
- 具体实现
- 实验结果
- 总体评价
- 引用格式
- 参考文献
内容概要
| 论文名称 | 简称 | 会议/期刊 | 出版年份 | baseline | backbone | 数据集 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-paced Contrastive Learning with Hybrid Memory for Domain Adaptive Object Re-ID | SpCL | NIPS | 2020 | 【MMT】Ge, Y., Chen, D., Li, H.: Mutual mean-teaching: Pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. In: International Conference on Learning Representations. pp. 1–15 (2020) | ImageNet-pretrained [7] ResNet-50 [18] ,use DBSCAN [9] for clustering | Market-1501\MSMT17 |
在线链接:https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/file/821fa74b50ba3f7cba1e6c53e8fa6845-Paper.pdf
源码链接: https://github.com/yxgeee/SpCL.
工作概述
1。we propose a novel self-paced contrastive learning framework with hybrid memory. The hybrid memory dynamically gen- erates source-domain class-level, target-domain cluster-level and un-clustered instance-level supervisory signals for learning feature representations. Different from the conventional contrastive learning strategy, the proposed framework jointly distinguishes source-domain classes, and target-domain clusters and un-clustered instances.
- the proposed self-paced method gradually creates more reliable clusters to refine the hybrid memory and learning targets, and is shown to be the key to our outstanding performance.
成果概述
Our method outperforms state-of- the-arts on multiple domain adaptation tasks of object re-ID and even boosts the performance on the source domain without any extra annotations. Our general- ized version on unsupervised object re-ID surpasses state-of-the-art algorithms by considerable 16.7% and 7.9% on Market-1501 and MSMT17 benchmarks†
方法详解
方法框架
Figure 2: (a) The illustration of the proposed unified framework with a novel hybrid memory. (b) The proposed reliability criterion for measuring the cluster independence‡ and compactness
算法描述
具体实现
1,用于模型训练的数据分为三个部分。 源域带标注样本、目标域聚类伪标签样本,目标域无聚类实体样本(一个样本视为一个单独的类),整体的损失函数为 公式1。
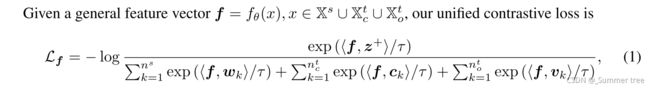
2,混合内存中存储了两个部分的数据。 一是源域类中心特征{w},二是目标域所有的样本特征{v}。
![]()
![]()
3,对{v}进行聚类,可以得到目标域聚类伪标签 和 无聚类实体样本。对聚类的伪标签样本 求聚类中心,得到{c}(公式2),用于公式1的计算。
![]()
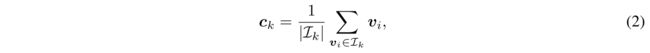
4,内存更新。w 和v 都是根据原有的版本和新计算的版本进行加权求和,分别如公式3和公式4所示。
![]()
![]()
5,Self-paced learning,决定如何划分目标域聚类伪标签样本和 无聚类实体样本。 设计了聚类独立性和紧凑性两个指标。独立性计算如公式5所示,紧凑性计算如公式6所示,最后通过两个指标来决定是否为聚类样本。
![]()
![]()
we preserve independent clusters with compact data points whose Rindep > α and Rcomp > β
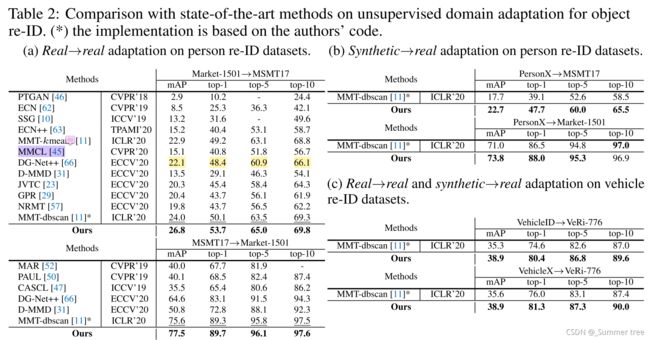
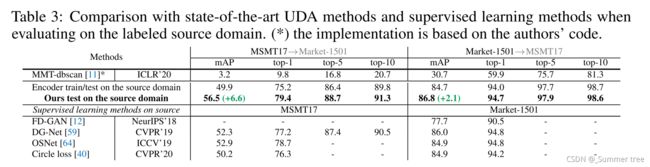
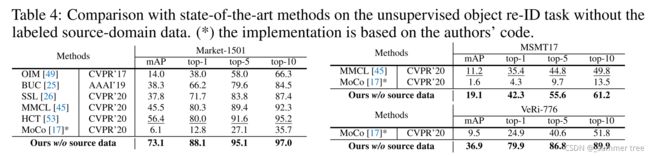
实验结果
总体评价
1, 将数据分为三个部分这一点还是很具有创新性的,如图1所示,确实有更好的利用有限数据。

2,利用混合内存进行存储其实和hpla很相似,都把上一阶段的计算结果进行了存储。不同的是,他只进行了加权求和,而hpla进行了知识融合。
3,独立性和紧凑性设计思路很常见,可优化。
引用格式
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/nips/Ge0C0L20,
author = {Yixiao Ge and
Feng Zhu and
Dapeng Chen and
Rui Zhao and
Hongsheng Li},
title = {Self-paced Contrastive Learning with Hybrid Memory for Domain Adaptive
Object Re-ID},
booktitle = {NeurIPS},
year = {2020}
}
小样本学习与智能前沿(下方↓公众号)后台回复“SpCL,即可获得论文电子资源。
![]()
参考文献
[1] Beeferman, D., Berger, A.: Agglomerative clustering of a search engine query log. In: Proceedings of the sixth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. pp. 407–416 (2000)
[2] Campello, R.J., Moulavi, D., Zimek, A., Sander, J.: Hierarchical density estimates for data clustering, visualization, and outlier detection. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data (TKDD) 10(1), 1–51 (2015)
[3] Chang, W.G., You, T., Seo, S., Kwak, S., Han, B.: Domain-specific batch normalization for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 7354–7362 (2019)
[4] Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. International Conference on Machine Learning (2020)
[5] Chen, Y., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Instance-guided context rendering for cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 232–242 (2019)
[6] Choi, J., Jeong, M., Kim, T., Kim, C.: Pseudo-labeling curriculum for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) (2019)
[7] Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 248–255 (2009)
[8] Deng, W., Zheng, L., Ye, Q., Kang, G., Yang, Y., Jiao, J.: Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 994–1003 (2018)
[9] Ester, M., Kriegel, H.P., Sander, J., Xu, X.: A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. p. 226–231. KDD’96, AAAI Press (1996)
[10] Fu, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, Y., Shi, H., Huang, T.S.: Self-similarity grouping: A simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 6112–6121 (2019)
[11] Ge, Y., Chen, D., Li, H.: Mutual mean-teaching: Pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. In: International Conference on Learning Representations. pp. 1–15 (2020)
[12]Ge, Y., Li, Z., Zhao, H., Yin, G., Yi, S., Wang, X., et al.: Fd-gan: Pose-guided feature distilling gan for robust person re-identification. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp. 1222–1233 (2018)
[13] Ge, Y., Wang, H., Zhu, F., Zhao, R., Li, H.: Self-supervising fine-grained region similarities for large-scale image localization. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2020)
[14] Ge, Y., Zhu, F., Zhao, R., Li, H.: Structured domain adaptation with online relation regularization for unsupervised person re-id (2020)
[15] Guo, S., Huang, W., Zhang, H., Zhuang, C., Dong, D., Scott, M.R., Huang, D.: Curriculumnet: Weakly supervised learning from large-scale web images. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). pp. 135–150 (2018)
[16] Guo, X., Liu, X., Zhu, E., Zhu, X., Li, M., Xu, X., Yin, J.: Adaptive self-paced deep clustering with data augmentation. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (2019)
[17] He, K., Fan, H., Wu, Y., Xie, S., Girshick, R.: Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 9729–9738 (2020)
[18] He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 770–778 (2016)
[19] Hjelm, R.D., Fedorov, A., Lavoie-Marchildon, S., Grewal, K., Bachman, P., Trischler, A., Bengio, Y.: Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations. pp. 1–15 (2019)
[20] Jiang, L., Zhou, Z., Leung, T., Li, L.J., Fei-Fei, L.: Mentornet: Learning data-driven curriculum for very deep neural networks on corrupted labels. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 2304–2313 (2018)
[21] Kumar, M.P., Packer, B., Koller, D.: Self-paced learning for latent variable models. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp. 1189–1197 (2010)
[22] LeCun, Y., Boser, B., Denker, J.S., Henderson, D., Howard, R.E., Hubbard, W., Jackel, L.D.: Backpropaga- tion applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural computation 1(4), 541–551 (1989)
[23] Li, J., Zhang, S.: Joint visual and temporal consistency for unsupervised domain adaptive person re- identification. pp. 1–14 (2020)
[24] Lin, L., Wang, K., Meng, D., Zuo, W., Zhang, L.: Active self-paced learning for cost-effective and progressive face identification. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 40(1), 7–19 (2017)
[25] Lin, Y., Dong, X., Zheng, L., Yan, Y., Yang, Y.: A bottom-up clustering approach to unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. vol. 33, pp. 8738–8745 (2019)
[26] Lin, Y., Xie, L., Wu, Y., Yan, C., Tian, Q.: Unsupervised person re-identification via softened similarity learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 3390–3399 (2020)
[27] Liu, H., Tian, Y., Yang, Y., Pang, L., Huang, T.: Deep relative distance learning: Tell the difference between similar vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 2167–2175 (2016)
[28] Liu, X., Liu, W., Mei, T., Ma, H.: A deep learning-based approach to progressive vehicle re-identification for urban surveillance. In: European conference on computer vision. pp. 869–884. Springer (2016)
[29] Luo, C., Song, C., Zhang, Z.: Generalizing person re-identification by camera-aware invariance learning and cross-domain mixup. pp. 1–14 (2020)
[30] Luo, H., Gu, Y., Liao, X., Lai, S., Jiang, W.: Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re- identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. pp. 1–8 (2019)
[31] Mekhazni, D., Bhuiyan, A., Ekladious, G., Granger, E.: Unsupervised domain adaptation in the dissimilarity space for person re-identification. pp. 1–14 (2020)
[32] Naphade, M., Wang, S., Anastasiu, D., Tang, Z., Chang, M.C., Yang, X., Zheng, L., Sharma, A., Chellappa, R., Chakraborty, P.: The 4th ai city challenge (2020)
[33] Oord, A.v.d., Li, Y., Vinyals, O.: Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. In: Advances in neural information processing systems (2018)
[34] Pan, X., Luo, P., Shi, J., Tang, X.: Two at once: Enhancing learning and generalization capacities via ibn-net. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). pp. 464–479 (2018)
[35] Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., et al.: Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp. 8026–8037 (2019)
[36] Riccitiello, J.: John riccitiello sets out to identify the engine of growth for unity technologies (interview). VentureBeat. Interview with Dean Takahashi. Retrieved January 18, 3 (2015)
[37] Ristani, E., Solera, F., Zou, R., Cucchiara, R., Tomasi, C.: Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 17–35 (2016)
[38] Song, L., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Du, B., Zhang, Q., Huang, C., Wang, X.: Unsupervised domain adaptive re-identification: Theory and practice. Pattern Recognition 102, 107173 (2020)
[39] Sun, X., Zheng, L.: Dissecting person re-identification from the viewpoint of viewpoint. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 608–617 (2019)
[40] Sun, Y., Cheng, C., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Zheng, L., Wang, Z., Wei, Y.: Circle loss: A unified perspective of pair similarity optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 6398–6407 (2020)
[41] Tang, K., Ramanathan, V., Fei-Fei, L., Koller, D.: Shifting weights: Adapting object detectors from image to video. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. pp. 638–646 (2012)
[42] Tang, Z., Naphade, M., Birchfield, S., Tremblay, J., Hodge, W., Kumar, R., Wang, S., Yang, X.: Pamtri: Pose-aware multi-task learning for vehicle re-identification using highly randomized synthetic data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 211–220 (2019)
[43] Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: Weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp. 1195–1204 (2017)
[44] Tian, Y., Krishnan, D., Isola, P.: Contrastive multiview coding. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). pp. 1–14 (2020)
[45] Wang, D., Zhang, S.: Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 10981–10990 (2020)
[46] Wei, L., Zhang, S., Gao, W., Tian, Q.: Person transfer gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 79–88 (2018)
[47] Wu, A., Zheng, W.S., Lai, J.H.: Unsupervised person re-identification by camera-aware similarity consis- tency learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 6922–6931 (2019)
[48] Wu, Z., Xiong, Y., Yu, S.X., Lin, D.: Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimina- tion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 3733–3742 (2018)
[49] Xiao, T., Li, S., Wang, B., Lin, L., Wang, X.: Joint detection and identification feature learning for person search. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 3415–3424 (2017)
[50] Yang, Q., Yu, H.X., Wu, A., Zheng, W.S.: Patch-based discriminative feature learning for unsupervised per- son re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 3633–3642 (2019)
[51] Yao, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, X., Naphade, M., Gedeon, T.: Simulating content consistent vehicle datasets with attribute descent. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.08855 (2019)
[52] Yu, H.X., Zheng, W.S., Wu, A., Guo, X., Gong, S., Lai, J.H.: Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 2148–2157 (2019)
[53] Zeng, K., Ning, M., Wang, Y., Guo, Y.: Hierarchical clustering with hard-batch triplet loss for person re- identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 13657–13665 (2020)
[54] Zhai, Y., Lu, S., Ye, Q., Shan, X., Chen, J., Ji, R., Tian, Y.: Ad-cluster: Augmented discriminative clustering for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 9021–9030 (2020)
[55] Zhang, X., Cao, J., Shen, C., You, M.: Self-training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 8222–8231 (2019)
[56] Zhang, Y., David, P., Gong, B.: Curriculum domain adaptation for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 2020–2030 (2017)
[57] Zhao, F., Liao, S., Xie, G.S., Zhao, J., Zhang, K., Shao, L.: Unsupervised domain adaptation with noise resistible mutual-training for person re-identification. pp. 1–14 (2020)
[58] Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp. 1116–1124 (2015)
[59] Zheng, Z., Yang, X., Yu, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Kautz, J.: Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
[60] Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Cao, D., Li, S.: Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 1318–1327 (2017)
[61] Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Kang, G., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Random erasing data augmentation. In: AAAI. pp. 13001–13008 (2020)
[62] Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Luo, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Invariance matters: Exemplar memory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 598–607 (2019)
[63] Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Luo, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Learning to adapt invariance in memory for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2020)
[64] Zhou, K., Yang, Y., Cavallaro, A., Xiang, T.: Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 3702–3712 (2019)
[65] Zhuang, C., Zhai, A.L., Yamins, D.: Local aggregation for unsupervised learning of visual embeddings. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 6002–6012 (2019)
[66] Zou, Y., Yang, X., Yu, Z., Kumar, B., Kautz, J.: Joint disentangling and adaptation for cross-domain person re-identification. pp. 1–14 (2020)
[67] Zou, Y., Yu, Z., Vijaya Kumar, B., Wang, J.: Unsupervised domain adaptation for semantic segmentation via class-balanced self-training. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). pp. 289–305 (2018)